filmov
tv
Understanding Refrigeration Metering Devices: TEV, TXV, and How They Work

Показать описание
Refrigeration metering devices play a crucial role in the efficiency and functionality of refrigeration and air conditioning systems. Two commonly used metering devices are the Thermal Expansion Valve (TEV) and the Thermostatic Expansion Valve (TXV). In this video, we will explore these devices, how they work, and their importance in maintaining optimal system performance.
Get your free service and troubleshooting guide -
#Refrigeration
#Metering devices
#Thermal Expansion Valve
#TEV
#Thermostatic Expansion Valve
#TXV
#Refrigeration systems
#Cooling cycle
#Evaporator
#Condenser
Compressor
#Refrigerant
#Expansion process
#Superheat
#Subcooling
#Refrigeration efficiency
#Refrigeration maintenance
#HVAC systems
#Refrigerant flow control
#Evaporator coil
#Condensing coil
#Temperature control
#Pressure regulation
#Energy efficiency
#System performance
#Understanding Refrigeration Metering Devices:
Refrigeration Basics:
Refrigeration systems are designed to transfer heat from a low-temperature area (the evaporator) to a high-temperature area (the condenser) by utilizing a refrigerant. This process is critical for cooling and air conditioning in various applications, from homes to industrial settings.
The Role of Metering Devices:
Metering devices are components that control the flow of refrigerant through the system. They ensure that the refrigerant enters the evaporator coil at the right rate and temperature, enabling efficient heat absorption. TEVs and TXVs are two types of metering devices that excel at this task.
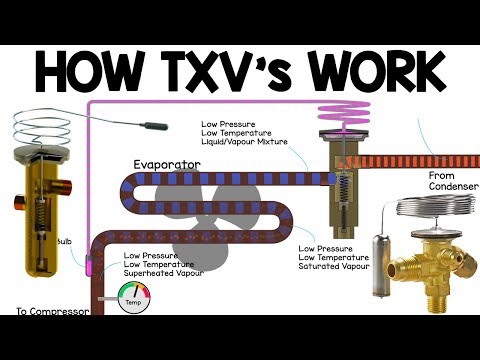
Thermal Expansion Valve (TEV):
The TEV is a mechanical valve that regulates the flow of refrigerant into the evaporator coil based on temperature and pressure conditions. It consists of several key components, including a sensing bulb, diaphragm, and valve orifice.
How TEV Works:
The sensing bulb is attached to the suction line near the evaporator coil and senses the refrigerant's temperature.
When the temperature rises, the refrigerant in the bulb expands, causing the diaphragm to open the valve orifice.
This allows more refrigerant to flow into the evaporator, maintaining the desired superheat level (the temperature difference between the refrigerant and the coil).
TEVs are highly responsive and adaptable, making them suitable for various applications.
Thermostatic Expansion Valve (TXV):
The TXV is another widely used metering device in refrigeration systems. It also responds to temperature and pressure conditions but operates on a different principle.
How TXV Works:
A TXV consists of a sensing bulb, a diaphragm, and a needle valve.
Similar to the TEV, the sensing bulb detects the evaporator's temperature.
However, the TXV's diaphragm is designed to modulate the needle valve, adjusting the flow of refrigerant more precisely.
This fine control ensures that the refrigerant flow matches the cooling load, enhancing system efficiency.
Importance in Refrigeration:
Both TEVs and TXVs play a vital role in maintaining optimal refrigeration system performance. They help achieve:
Efficient heat transfer in the evaporator coil.
Precise temperature control.
Energy savings through reduced compressor workload.
Prevention of refrigerant floodback and system damage.
Refrigeration metering devices like TEVs and TXVs are essential components that enable precise control of refrigerant flow, ensuring efficient cooling and temperature regulation in HVAC systems and refrigeration applications. Understanding how these devices work is crucial for maintaining system efficiency and performance while conserving energy and reducing operational costs.
By implementing the right metering device and conducting regular maintenance, individuals and businesses can enjoy reliable and energy-efficient refrigeration and air conditioning systems
Get your free service and troubleshooting guide -
#Refrigeration
#Metering devices
#Thermal Expansion Valve
#TEV
#Thermostatic Expansion Valve
#TXV
#Refrigeration systems
#Cooling cycle
#Evaporator
#Condenser
Compressor
#Refrigerant
#Expansion process
#Superheat
#Subcooling
#Refrigeration efficiency
#Refrigeration maintenance
#HVAC systems
#Refrigerant flow control
#Evaporator coil
#Condensing coil
#Temperature control
#Pressure regulation
#Energy efficiency
#System performance
#Understanding Refrigeration Metering Devices:
Refrigeration Basics:
Refrigeration systems are designed to transfer heat from a low-temperature area (the evaporator) to a high-temperature area (the condenser) by utilizing a refrigerant. This process is critical for cooling and air conditioning in various applications, from homes to industrial settings.
The Role of Metering Devices:
Metering devices are components that control the flow of refrigerant through the system. They ensure that the refrigerant enters the evaporator coil at the right rate and temperature, enabling efficient heat absorption. TEVs and TXVs are two types of metering devices that excel at this task.
Thermal Expansion Valve (TEV):
The TEV is a mechanical valve that regulates the flow of refrigerant into the evaporator coil based on temperature and pressure conditions. It consists of several key components, including a sensing bulb, diaphragm, and valve orifice.
How TEV Works:
The sensing bulb is attached to the suction line near the evaporator coil and senses the refrigerant's temperature.
When the temperature rises, the refrigerant in the bulb expands, causing the diaphragm to open the valve orifice.
This allows more refrigerant to flow into the evaporator, maintaining the desired superheat level (the temperature difference between the refrigerant and the coil).
TEVs are highly responsive and adaptable, making them suitable for various applications.
Thermostatic Expansion Valve (TXV):
The TXV is another widely used metering device in refrigeration systems. It also responds to temperature and pressure conditions but operates on a different principle.
How TXV Works:
A TXV consists of a sensing bulb, a diaphragm, and a needle valve.
Similar to the TEV, the sensing bulb detects the evaporator's temperature.
However, the TXV's diaphragm is designed to modulate the needle valve, adjusting the flow of refrigerant more precisely.
This fine control ensures that the refrigerant flow matches the cooling load, enhancing system efficiency.
Importance in Refrigeration:
Both TEVs and TXVs play a vital role in maintaining optimal refrigeration system performance. They help achieve:
Efficient heat transfer in the evaporator coil.
Precise temperature control.
Energy savings through reduced compressor workload.
Prevention of refrigerant floodback and system damage.
Refrigeration metering devices like TEVs and TXVs are essential components that enable precise control of refrigerant flow, ensuring efficient cooling and temperature regulation in HVAC systems and refrigeration applications. Understanding how these devices work is crucial for maintaining system efficiency and performance while conserving energy and reducing operational costs.
By implementing the right metering device and conducting regular maintenance, individuals and businesses can enjoy reliable and energy-efficient refrigeration and air conditioning systems
Комментарии
 0:01:37
0:01:37
 0:19:10
0:19:10
 0:08:28
0:08:28
 0:57:04
0:57:04
 0:06:38
0:06:38
 0:09:06
0:09:06
 0:03:04
0:03:04
 0:07:51
0:07:51
 0:09:05
0:09:05
 0:16:40
0:16:40
 0:00:39
0:00:39
 0:19:15
0:19:15
 0:06:45
0:06:45
 0:02:54
0:02:54
 0:00:29
0:00:29
 0:05:43
0:05:43
 0:06:59
0:06:59
 0:16:34
0:16:34
 0:17:07
0:17:07
 0:40:48
0:40:48
 0:05:24
0:05:24
 0:04:11
0:04:11
 0:00:40
0:00:40
 0:08:31
0:08:31