filmov
tv
Personal Computer Architecture
Показать описание
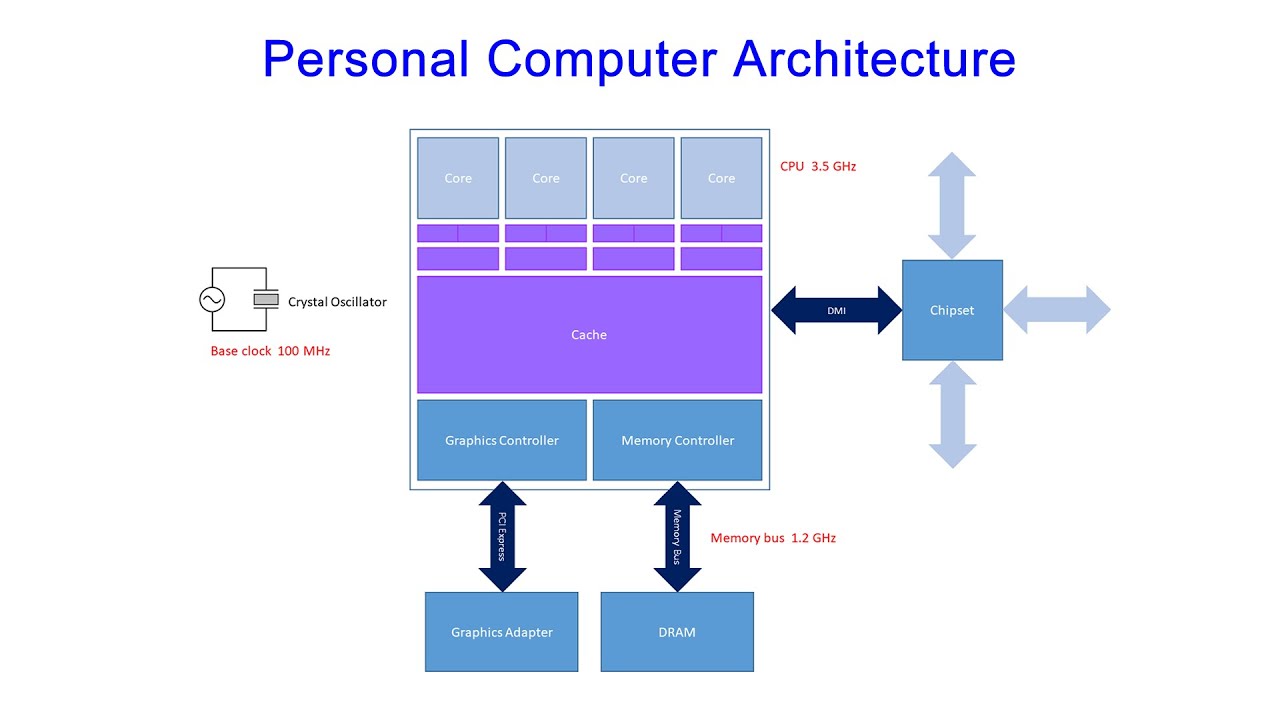
This computer science video includes useful information if you are thinking of buying, building, upgrading or overclocking your own personal computer. It also serves as a basis for further study of individual components such as DRAM or GPUs. The video introduces the architecture of a modern personal computer. The main components on a PC motherboard are identified including the central processing unit, the graphics adaptor, the Dynamic Random Access Memory (DRAM) and the so called chip set. The various busses connecting these components are also mentioned including the memory bus, PCI Express, and Direct Media Interface. The structure of a typical multi-core CPU is described including the built in memory controller, built in graphics controller and the CPU cache. The structure and operation of the CPU cache is illustrated; specifically the way in which the cache is organised in levels and the way that data and instructions move around in 64 byte blocks known as cache lines. The utility CPU-Z is then used to examine some of the components of real PC.
Комментарии
 0:18:06
0:18:06
 0:17:13
0:17:13
 0:02:17
0:02:17
 0:05:05
0:05:05
 1:26:19
1:26:19
 0:06:51
0:06:51
 0:07:48
0:07:48
 0:18:11
0:18:11
 0:07:51
0:07:51
 0:10:15
0:10:15
 0:10:02
0:10:02
 0:42:32
0:42:32
 0:42:30
0:42:30
 0:09:14
0:09:14
 0:01:07
0:01:07
 0:10:31
0:10:31
 0:11:01
0:11:01
 0:02:26
0:02:26
 0:07:51
0:07:51
 1:21:07
1:21:07
 0:08:34
0:08:34
 0:05:31
0:05:31
 0:27:13
0:27:13
 0:04:39
0:04:39