filmov
tv
What is LinkedHashMap in Java? - Explained | Java collections #10 | java9s

Показать описание
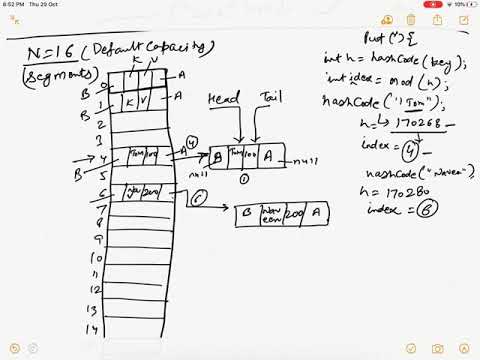
LinkedHashMap is a data structure Which maintains the insertion order for its entries. That means it arranges its entries exactly in the same order as they have been added. LinkedHashMap can be used in the scenarios where the First in first out kind of data model is needed.
LinkedHashMap can also maintain the access order for its entries where it moves all recently accessed entries to the bottom of the collection.
This kind of feature is useful in making LRU (Least Recently Used) caching mechanisms.
Complete Generics Tutorials playlist
Complete Java Beginners Tutorials:
Multithreading in Java tutorial:
Spring 3 MVC Framework tutorials:
Spring Framework Tutorials:
Design Patterns in Java:
Java Collections Tutorials:
LinkedHashMap can also maintain the access order for its entries where it moves all recently accessed entries to the bottom of the collection.
This kind of feature is useful in making LRU (Least Recently Used) caching mechanisms.
Complete Generics Tutorials playlist
Complete Java Beginners Tutorials:
Multithreading in Java tutorial:
Spring 3 MVC Framework tutorials:
Spring Framework Tutorials:
Design Patterns in Java:
Java Collections Tutorials:
Hashmap Vs LinkedHashMap Vs TreeMap #javadeveloper #java #coding
Java LinkedHashMap
Map and HashMap in Java - Full Tutorial
LinkedHashMap and LinkedHashSet in Java | Internal Working
What is LinkedHashMap in Java? - Explained | Java collections #10 | java9s
#14 - linkedhashmap vs hashmap in Java || How LinkedHashMap works internally - Naveen AutomationLabs
WHAT IS LINKED HASHMAP IN JAVA ? COLLECTION FRAMEWORK in java | Java tutorial for beginners !
What is LinkedHashMap in Java? (Java Collections)
LinkedHashMap In Java | Collection Framework | HashMap Vs LinkedHashMap
Difference between HashMap, LinkedHashMap and TreeMap | Core Java Interview Questions | Naresh IT
Java Collections and Generics 19 | LinkedHashMap in Java
LinkedHashMap In Java | LinkedHashMap Methods | put | get | remove | Size
What is a LinkedHashMap? | LinkedHashMap Introduction | Java Collection Framework
HashMap, LinkedHashMap and TreeMap in Java
Java Interview Questions - HashMap VS LinkedHashMap Vs TreeMap
LinkedHashMap Explained in Simple Terms | LRU Cache Made EASY | Coding Interview SECRET
Java Tutorial #57 - Java Linked HashMap Class with Examples (Map Data Structure)
Java LinkedHashMap Internals
What is LinkedHashMap in Java #shorts
Difference between HashMap, LinkedHashMap and TreeMap | Java Tutorial for beginners | Core Java
LinkedHashMap Java Program (Java Collections)
Java Interview Question series ( HashMap vs LinkedHashMap )
LinkedHashMap in Java | Java Collections | Collection Framework | Java Tutorial For Beginners
Java HashMap vs. LinkedHashMap ✍️
Комментарии
 0:00:58
0:00:58
 0:05:24
0:05:24
 0:10:10
0:10:10
 0:16:58
0:16:58
 0:07:32
0:07:32
 0:23:05
0:23:05
 0:05:51
0:05:51
 0:01:43
0:01:43
 0:07:05
0:07:05
 0:03:40
0:03:40
 0:02:21
0:02:21
 0:07:09
0:07:09
 0:03:12
0:03:12
 0:15:51
0:15:51
 0:02:10
0:02:10
 0:14:40
0:14:40
 0:10:39
0:10:39
 0:23:09
0:23:09
 0:00:39
0:00:39
 0:08:52
0:08:52
 0:01:08
0:01:08
 0:00:49
0:00:49
 0:05:33
0:05:33
 0:00:29
0:00:29