filmov
tv
Nucleic acid digestion - brush border enzymes, end products & transport mechanism

Показать описание
Follow us:
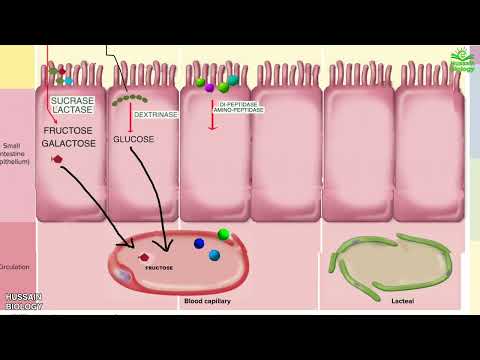
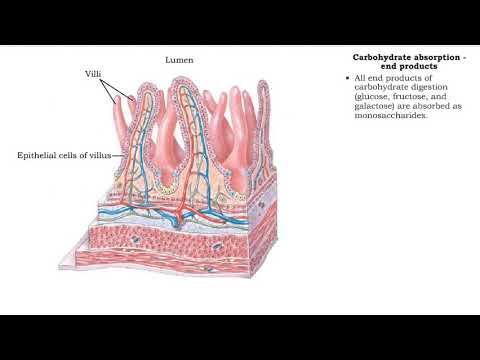
• Further digestion occurs at the microvilli (brush border) of the epithelial cells of the villi in the small intestine.
• Two brush border enzymes complete nucleic acid digestion:
• Phosphatases, which catalyze the cleavage of a phosphate to form a nucleoside (nitrogenous base and pentose sugar).
• Nucleosidases, which catalyze the breaking of the covalent bond that holds the nitrogenous base to the pentose sugar.
• The final end products of nucleic acid digestion are:
• nitrogenous oases.
• Pentose sugars.
• Phosphate ions.
• Absorption of nucleic acid mainly occurs in the duodenum and jejunum of the small intestine.
• At the intestinal villus, all nucleic acids are absorbed as:
• Nitrogenous bases.
• Pentose sugars.
• Phosphate ions.
• Membrane transport proteins carry the products of nucleotide digestion into epithelial cells from the lumen.
• Some involve active transport; some involve secondary active transport.
• Through diffusion, the products of nucleotide digestion are transported from the intestinal epithelial cells:
• Across the basolateral membrane.
• Into the interstitial fluid.
• And, finally, into the blood.
• The nucleotide digestion products are transported by blood circulation to the liver and other tissues where they undergo further degradation.
 0:02:10
0:02:10
 0:01:27
0:01:27
 0:03:44
0:03:44
 0:03:58
0:03:58
 0:10:37
0:10:37
 0:08:43
0:08:43
 0:00:40
0:00:40
 0:25:08
0:25:08
 0:06:53
0:06:53
 0:08:48
0:08:48
 0:01:41
0:01:41
 0:04:35
0:04:35
 0:38:06
0:38:06
 0:08:51
0:08:51
 0:09:42
0:09:42
 0:02:01
0:02:01
 0:12:34
0:12:34
 0:02:33
0:02:33
 0:18:15
0:18:15
 0:20:58
0:20:58
 0:45:02
0:45:02
 0:06:45
0:06:45
 0:12:43
0:12:43
 0:01:01
0:01:01