filmov
tv
How Pumped Storage Power Plants Work (Hydropower)

Показать описание
Want to continue learning about engineering with videos like this one? Then visit:
Want to teach/instruct with the 3D models shown in this video? Then visit:
###################################################
This video explains how pumped storage hydroelectric power stations work, what their main components are and their operating characteristics.
Like this video? Then check out our other videos!
📚Want to learn more about engineering?
Then join saVRee to access over 45 hours of engineering video courses! New courses every month!
Hope to see you on a course soon! 👋
🏫Want to use the 3D model in this video to present, instruct, or teach? Simply join saVRee! We have over 400 engineering models that will make your life a lot easier!
▶️Introduction
This type of power plant converts potential energy to electrical energy, or, electrical energy to potential energy. They achieve this by allowing water to flow from a high elevation to a lower elevation, or, by pumping water from a low elevation to a higher elevation. When water flows to a lower elevation, the power plant generates electricity. When water is pumped to a higher elevation, the power plant creates a store of potential energy. Pumped storage plants use Francis turbines because they can act as both a hydraulic pump and hydraulic turbine.
Pumped storage power plants are used to balance the frequency, voltage and power demands within the electrical grid. Pump storage plants are often utilised to add additional megawatt capacity to the grid during period of high power demand, for this reason, pumped storage plants are referred to as ‘peaking’ plants.
Because pumped storage plants can provide electrical grid operators with power ‘on-demand’, they have a high level of dispatchability (the ability to provide power to the grid as needed).
Components
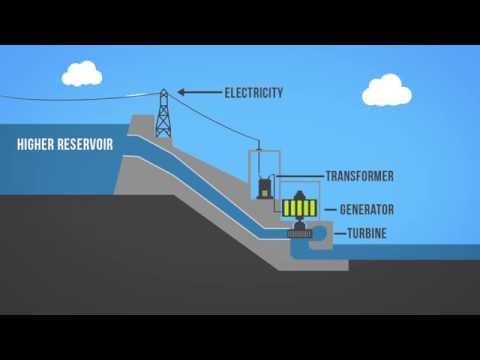
Irrespective geographical location, all pumped storage plants require an upper and lower reservoir. The difference in elevation between the upper and lower reservoirs is referred to as the ‘head’ (head of pressure) and it must be significant in order for the plant to operate efficiently.
A penstock connects the upper reservoir to a Francis turbine located in the power house. A draft tube and tail race connects the Francis turbine to the lower reservoir.
Operation - Generating Power (Electricity)
Water flows from the upper reservoir, through the penstock, and to the Francis turbine. As the water passes over the Francis runner blades, a pressure differential is created that causes torque (rotary force) to be applied to the runner. The runner begins to rotate.
The turbine runner is connected on a common shaft to an electrical generator. As the runner rotates, so too does the generator rotor. As the rotor rotates through the electromagnetic field within the generator, it induces current in the stator windings and electrical current begins to flow. The electrical current is usually then dispatched to end consumers via a switchyard and electrical transformer.
Water discharged from the turbine runner enters into a draft tube where some of the kinetic energy is recovered and converted to potential energy; the water then enters the tail race and is discharged to the lower reservoir.
In this example, the potential energy of water was converted by the turbine runner into mechanical energy. The mechanical energy was transferred on a common shaft to a generator, which converted the mechanical energy to electrical energy. The entire process can be continuous until the upper reservoir is emptied.
Operation – Storing Potential Energy
Water is pumped from the lower reservoir to the upper reservoir by the Francis turbine runner. The flow path is the same as when generating electricity, except the flow direction is reversed.
#saVRee #PowerEngineering #IndustrialEngineering
Want to teach/instruct with the 3D models shown in this video? Then visit:
###################################################
This video explains how pumped storage hydroelectric power stations work, what their main components are and their operating characteristics.
Like this video? Then check out our other videos!
📚Want to learn more about engineering?
Then join saVRee to access over 45 hours of engineering video courses! New courses every month!
Hope to see you on a course soon! 👋
🏫Want to use the 3D model in this video to present, instruct, or teach? Simply join saVRee! We have over 400 engineering models that will make your life a lot easier!
▶️Introduction
This type of power plant converts potential energy to electrical energy, or, electrical energy to potential energy. They achieve this by allowing water to flow from a high elevation to a lower elevation, or, by pumping water from a low elevation to a higher elevation. When water flows to a lower elevation, the power plant generates electricity. When water is pumped to a higher elevation, the power plant creates a store of potential energy. Pumped storage plants use Francis turbines because they can act as both a hydraulic pump and hydraulic turbine.
Pumped storage power plants are used to balance the frequency, voltage and power demands within the electrical grid. Pump storage plants are often utilised to add additional megawatt capacity to the grid during period of high power demand, for this reason, pumped storage plants are referred to as ‘peaking’ plants.
Because pumped storage plants can provide electrical grid operators with power ‘on-demand’, they have a high level of dispatchability (the ability to provide power to the grid as needed).
Components
Irrespective geographical location, all pumped storage plants require an upper and lower reservoir. The difference in elevation between the upper and lower reservoirs is referred to as the ‘head’ (head of pressure) and it must be significant in order for the plant to operate efficiently.
A penstock connects the upper reservoir to a Francis turbine located in the power house. A draft tube and tail race connects the Francis turbine to the lower reservoir.
Operation - Generating Power (Electricity)
Water flows from the upper reservoir, through the penstock, and to the Francis turbine. As the water passes over the Francis runner blades, a pressure differential is created that causes torque (rotary force) to be applied to the runner. The runner begins to rotate.
The turbine runner is connected on a common shaft to an electrical generator. As the runner rotates, so too does the generator rotor. As the rotor rotates through the electromagnetic field within the generator, it induces current in the stator windings and electrical current begins to flow. The electrical current is usually then dispatched to end consumers via a switchyard and electrical transformer.
Water discharged from the turbine runner enters into a draft tube where some of the kinetic energy is recovered and converted to potential energy; the water then enters the tail race and is discharged to the lower reservoir.
In this example, the potential energy of water was converted by the turbine runner into mechanical energy. The mechanical energy was transferred on a common shaft to a generator, which converted the mechanical energy to electrical energy. The entire process can be continuous until the upper reservoir is emptied.
Operation – Storing Potential Energy
Water is pumped from the lower reservoir to the upper reservoir by the Francis turbine runner. The flow path is the same as when generating electricity, except the flow direction is reversed.
#saVRee #PowerEngineering #IndustrialEngineering
Комментарии
 0:05:02
0:05:02
 0:02:23
0:02:23
 0:02:30
0:02:30
 0:00:16
0:00:16
 0:01:11
0:01:11
 0:00:30
0:00:30
 0:02:15
0:02:15
 0:09:13
0:09:13
 0:12:15
0:12:15
 0:16:53
0:16:53
 0:01:35
0:01:35
 0:01:21
0:01:21
 0:02:35
0:02:35
 0:01:43
0:01:43
 0:12:44
0:12:44
 0:01:57
0:01:57
 0:03:01
0:03:01
 0:00:47
0:00:47
 0:00:18
0:00:18
 0:05:01
0:05:01
 0:00:56
0:00:56
 0:03:13
0:03:13
 0:03:19
0:03:19
 0:08:04
0:08:04