filmov
tv
Lexical relations in semantics | sense relations | Semantic relations | Semantics

Показать описание
𝐋𝐄𝐗𝐈𝐂𝐀𝐋 𝐑𝐄𝐋𝐀𝐓𝐈𝐎𝐍𝐒 | 𝐒𝐄𝐍𝐒𝐄 𝐑𝐄𝐋𝐀𝐓𝐈𝐎𝐍𝐒 | 𝐒𝐄𝐌𝐀𝐍𝐓𝐈𝐂 𝐑𝐄𝐋𝐀𝐓𝐈𝐎𝐍𝐒
𝐋𝐄𝐗𝐈𝐂𝐀𝐋 𝐑𝐄𝐋𝐀𝐓𝐈𝐎𝐍𝐒/𝐒𝐄𝐍𝐒𝐄 𝐑𝐄𝐋𝐀𝐓𝐈𝐎𝐍𝐒/𝐒𝐄𝐌𝐀𝐍𝐓𝐈𝐂 𝐑𝐄𝐋𝐀𝐓𝐈𝐎𝐍𝐒
The branch of semantics that deals with the word meaning is called lexical semantics. It is the study of systematic, meaning related structures of words. Lexical field or semantic field is the organization of related words and expressions in to a system, which shows their relationship with one another, e.g. set (angry, sad, happy, depressed, and afraid etc.). This set of words is a lexical field. All its words refer to emotional states. The relation of a word with another word is a lexical relation or sense relation or semantic relation. The principal relationships are Synonymy, Antonymy, Hyponymy, Meronymy, Polysemy, Homonymy etc.
𝐒𝐲𝐧𝐨𝐧𝐲𝐦𝐲
Synonyms are different words with almost identical or similar meanings. Words that are synonyms are said to be synonymous, and the state of being a synonym is called synonymy. The words car and automobile are synonyms. Similarly, if we talk about ‘a long time’ or ‘an extended time’, long and extended become synonyms. Note that synonyms are defined with respect to certain senses of words; for instance, ‘he expired’ means the same as ‘he died’, yet 'my passport has expired' cannot be replaced by 'my passport has died'.
𝐀𝐧𝐭𝐨𝐧𝐲𝐦𝐲
Antonym is a word having a meaning opposite to that of another word. Antonymy is the sense relation that exists between words which are opposite in meaning; for example, male : female, long : short, up : down, precede : follow etc.
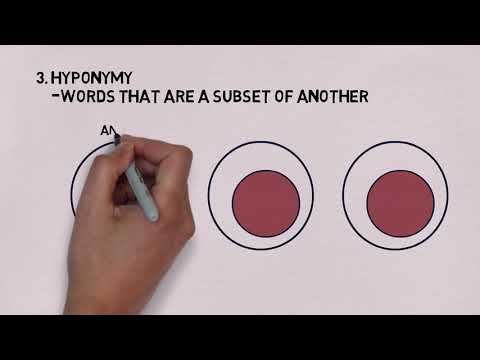
𝐇𝐲𝐩𝐨𝐧𝐲𝐦𝐲
In linguistics, a specific term used to designate a member of a class.
For instance, oak is a hyponym of tree, and dog is a hyponym of animal. Then scarlet, vermilion, carmine, and crimson are all hyponyms of red (their hypernym), which is, in turn, a hyponym of colour. The opposite of a hyponym is a hypernym.
𝐌𝐞𝐫𝐨𝐧𝐲𝐦𝐲
The semantic relation that holds between a part and the whole. Cover, page, for example, are meronyms of book. Meronymy is somewhat similar to hyponymy which is the semantic relation of being subordinate or belonging to a lower rank or class.
𝐏𝐨𝐥𝐲𝐬𝐞𝐦𝐲
It is the association of one word with two or more distinct meanings. A polyseme is a word or phrase with multiple meanings. Some examples Wood (a piece of a tree + a geographical area with many trees) Crane (a bird + a type of construction equipment)
Present (right now + the current moment + a gift + to show or display + to be physically somewhere) The opposite of polysemy is monosemy.
𝐇𝐨𝐦𝐨𝐧𝐲𝐦𝐲
It is the state or quality of a given word’s having the same spelling and the same sound or pronunciation as another word, but with a different meaning, as ‘race’ (tribe) and ‘race’ (running contest).
In other words in linguistics, a homonym is, in the strict sense, one of a group of words that share the same spelling and the same pronunciation but have different meanings. Examples of homonyms are the pair ‘stalk’ (part of a plant) and ‘stalk’ (follow/harass a person) and the pair ‘left’ (past tense of leave) and ‘left’ (opposite of right), the verb ‘bear’ (to carry or endure) and the noun ‘bear’ (the name of an animal).
Homophony: a phenomenon of two or more words having the same pronunciation but different meaning or spelling. e.g. sea : see, knew : new, some : sum, sun : son etc.
𝐌𝐞𝐭𝐨𝐧𝐲𝐦𝐲
Metonymy means calling something, not by its true name, but by something associated with it. The use of word crown for the king is an example of metonymy. Grey hair should be respected. (Old Man) These days I am reading Ghalib. (The Poetry of Ghalib)
𝐂𝐨𝐥𝐥𝐨𝐜𝐚𝐭𝐢𝐨𝐧
Collocation refers to the tendency for certain words to occur together. A word like ‘clear’, for example, can be found with a number of nouns, clear sky, clear conscience, clear idea, clear road. In each term clear has a slightly different meaning because of the word it is qualifying. It is an arrangement or juxtaposition of words or other elements, especially those that commonly co-occur, as dead serious, iron will, green with jealously etc.
𝐋𝐄𝐗𝐈𝐂𝐀𝐋 𝐑𝐄𝐋𝐀𝐓𝐈𝐎𝐍𝐒/𝐒𝐄𝐍𝐒𝐄 𝐑𝐄𝐋𝐀𝐓𝐈𝐎𝐍𝐒/𝐒𝐄𝐌𝐀𝐍𝐓𝐈𝐂 𝐑𝐄𝐋𝐀𝐓𝐈𝐎𝐍𝐒
The branch of semantics that deals with the word meaning is called lexical semantics. It is the study of systematic, meaning related structures of words. Lexical field or semantic field is the organization of related words and expressions in to a system, which shows their relationship with one another, e.g. set (angry, sad, happy, depressed, and afraid etc.). This set of words is a lexical field. All its words refer to emotional states. The relation of a word with another word is a lexical relation or sense relation or semantic relation. The principal relationships are Synonymy, Antonymy, Hyponymy, Meronymy, Polysemy, Homonymy etc.
𝐒𝐲𝐧𝐨𝐧𝐲𝐦𝐲
Synonyms are different words with almost identical or similar meanings. Words that are synonyms are said to be synonymous, and the state of being a synonym is called synonymy. The words car and automobile are synonyms. Similarly, if we talk about ‘a long time’ or ‘an extended time’, long and extended become synonyms. Note that synonyms are defined with respect to certain senses of words; for instance, ‘he expired’ means the same as ‘he died’, yet 'my passport has expired' cannot be replaced by 'my passport has died'.
𝐀𝐧𝐭𝐨𝐧𝐲𝐦𝐲
Antonym is a word having a meaning opposite to that of another word. Antonymy is the sense relation that exists between words which are opposite in meaning; for example, male : female, long : short, up : down, precede : follow etc.
𝐇𝐲𝐩𝐨𝐧𝐲𝐦𝐲
In linguistics, a specific term used to designate a member of a class.
For instance, oak is a hyponym of tree, and dog is a hyponym of animal. Then scarlet, vermilion, carmine, and crimson are all hyponyms of red (their hypernym), which is, in turn, a hyponym of colour. The opposite of a hyponym is a hypernym.
𝐌𝐞𝐫𝐨𝐧𝐲𝐦𝐲
The semantic relation that holds between a part and the whole. Cover, page, for example, are meronyms of book. Meronymy is somewhat similar to hyponymy which is the semantic relation of being subordinate or belonging to a lower rank or class.
𝐏𝐨𝐥𝐲𝐬𝐞𝐦𝐲
It is the association of one word with two or more distinct meanings. A polyseme is a word or phrase with multiple meanings. Some examples Wood (a piece of a tree + a geographical area with many trees) Crane (a bird + a type of construction equipment)
Present (right now + the current moment + a gift + to show or display + to be physically somewhere) The opposite of polysemy is monosemy.
𝐇𝐨𝐦𝐨𝐧𝐲𝐦𝐲
It is the state or quality of a given word’s having the same spelling and the same sound or pronunciation as another word, but with a different meaning, as ‘race’ (tribe) and ‘race’ (running contest).
In other words in linguistics, a homonym is, in the strict sense, one of a group of words that share the same spelling and the same pronunciation but have different meanings. Examples of homonyms are the pair ‘stalk’ (part of a plant) and ‘stalk’ (follow/harass a person) and the pair ‘left’ (past tense of leave) and ‘left’ (opposite of right), the verb ‘bear’ (to carry or endure) and the noun ‘bear’ (the name of an animal).
Homophony: a phenomenon of two or more words having the same pronunciation but different meaning or spelling. e.g. sea : see, knew : new, some : sum, sun : son etc.
𝐌𝐞𝐭𝐨𝐧𝐲𝐦𝐲
Metonymy means calling something, not by its true name, but by something associated with it. The use of word crown for the king is an example of metonymy. Grey hair should be respected. (Old Man) These days I am reading Ghalib. (The Poetry of Ghalib)
𝐂𝐨𝐥𝐥𝐨𝐜𝐚𝐭𝐢𝐨𝐧
Collocation refers to the tendency for certain words to occur together. A word like ‘clear’, for example, can be found with a number of nouns, clear sky, clear conscience, clear idea, clear road. In each term clear has a slightly different meaning because of the word it is qualifying. It is an arrangement or juxtaposition of words or other elements, especially those that commonly co-occur, as dead serious, iron will, green with jealously etc.
Комментарии
 0:14:35
0:14:35
 0:12:38
0:12:38
 0:06:50
0:06:50
 0:04:20
0:04:20
 0:09:13
0:09:13
 0:10:39
0:10:39
 0:03:27
0:03:27
 0:13:54
0:13:54
 0:05:44
0:05:44
 0:25:09
0:25:09
 0:09:57
0:09:57
 0:12:06
0:12:06
 0:00:06
0:00:06
 0:11:56
0:11:56
 0:05:44
0:05:44
 0:07:10
0:07:10
 0:25:28
0:25:28
 0:23:55
0:23:55
 0:11:35
0:11:35
 0:00:19
0:00:19
 0:14:47
0:14:47
 0:05:10
0:05:10
 0:12:10
0:12:10
 0:19:14
0:19:14