filmov
tv
Composite tolerances explained

Показать описание
How tolerance zone mobility for a pattern of features is defined by the lower tier of a composite position callout is introduced.
Composite tolerances explained
GD&T: Position, Composite vs Two Single Segment
GD&T Q&A: Composite vs Two Single Segment Position, Single Datum Reference.
GD&T ASME Y14.5 Composite Position Tolerance Practical Explanation
GD&T: Composite Profile Example, Three Segment Feature Control Frame Explained
Composite Position vs Multiple Single Segment Tolerances
GD&T Tutorial 28.15 : Composite Positional Tolerance
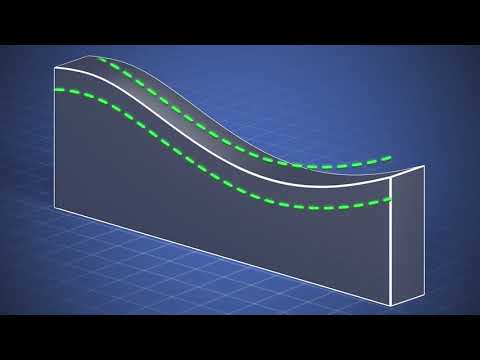
Composite Profile Tolerance applied to a Curved Surface
Understanding GD&T
Position in GD&T #tolerance #position #GD&T
Ch. 9 Composite Position Tolerances - 2
Ch. 9 Composite Position Tolerances - 1
GD&T COMPOSITE POSITION TOLERANCING
GD&T Composite Position Lesson 13 - NO MATH
GD&T: Composite Profile With 'Individually'
Tolerance Zones for Patterns (Composite Tolerance), PLTZF and FRTZF
Composite Tolerances in Geometric tolerances
GD&T Composite vs. Multiple Single-Segment Lesson 14 - NO MATH
GD & T: Profile Tolerances
Improved Composite Geometric Tolerances GTOLS in Detailed Drawings
Composite ProfileTolerance Frame
improved composite geometric tolerances gtols in detailed drawings
GD&T: Profile vs Flatness
Composite Positional Tolerancing
Комментарии
 0:05:56
0:05:56
 0:07:16
0:07:16
 0:06:02
0:06:02
 0:05:46
0:05:46
 0:04:17
0:04:17
 0:14:20
0:14:20
 0:03:42
0:03:42
 0:06:04
0:06:04
 0:29:32
0:29:32
 0:00:56
0:00:56
 0:17:08
0:17:08
 0:38:15
0:38:15
 0:08:05
0:08:05
 0:15:07
0:15:07
 0:08:44
0:08:44
 0:13:51
0:13:51
 0:22:50
0:22:50
 0:07:55
0:07:55
 0:01:44
0:01:44
 0:01:14
0:01:14
 0:09:19
0:09:19
 0:00:51
0:00:51
 0:07:03
0:07:03
 0:26:31
0:26:31