filmov
tv
Differential Equations, Lecture 3.9: The method of Frobenius

Показать описание
Differential Equations, Lecture 3.9: The method of Frobenius.
In the previous lecture, we saw how many 2nd ODEs have solutions that are power series. In this lecture, we learn when this is the case, which is due to a theorem of Frobenius. In particular, if the center x_0 of the power series is a so-called "ordinary point", then the ODE will have a power series solution. Otherwise, x_0 is said to be a "singular point," and there are two types of these. If x_0 is an "regular singular point", then there is a generalized power series solution, which is simply a power series times x^r, where r could be a negative number, fraction, or complex number. In this lecture, we learn what these mean, we discuss the radii of convergence of these solutions, and we conclude with an example of an ODE that has as generalized power series solution.
In the previous lecture, we saw how many 2nd ODEs have solutions that are power series. In this lecture, we learn when this is the case, which is due to a theorem of Frobenius. In particular, if the center x_0 of the power series is a so-called "ordinary point", then the ODE will have a power series solution. Otherwise, x_0 is said to be a "singular point," and there are two types of these. If x_0 is an "regular singular point", then there is a generalized power series solution, which is simply a power series times x^r, where r could be a negative number, fraction, or complex number. In this lecture, we learn what these mean, we discuss the radii of convergence of these solutions, and we conclude with an example of an ODE that has as generalized power series solution.
Differential Equation - 1st Order, Linear Form (3 of 9) General Solution of the Non-Homogenous Eqn.
Introduction to Slope Fields (Differential Equations 9)
Differential Equations: Lecture 2.2 Separable Equations
Differential equations, a tourist's guide | DE1
Homogeneous Differential Equations | Class 12 Maths | Lecture 3
Differential Equations: Lecture 4.3 Homogeneous Linear Equations with Constant Coefficients
First order, Ordinary Differential Equations.
Differential Equations, Lecture 3.3: The method of undetermined coefficients
CUET PG Maths Ordinary Differential Equations PYQs | CUET PG Mathematics Previous Year Questions
Differential equation introduction | First order differential equations | Khan Academy
First Order Linear Differential Equation & Integrating Factor (introduction & example)
When mathematicians get bored (ep1)
LECT 9 - UNIT 1 - LINEAR DIFFERENTIAL EQUATION (LDE) - ENGG MATHS 3 (M3) -SHORTCUT METHOD - SPPU
Oxford student reacts to India’s JEE Advanced exam paper *really hard* #shorts #viral #jeeadvanced
How REAL Men Integrate Functions
LINEAR DIFFERENTIAL EQUATION WITH CONSTANT COEFFICIENT |HIGHER ORDER|LECTURE 03|Particular Integral
5 simple unsolvable equations
👀 Asking GCSE Students (Hamdi) How Much They Physics They Know - Part 1 #Shorts
Differential Equations - Introduction, Order and Degree, Solutions to DE
Differential Equations: Lecture 2.4 Exact Equations
Order And Degree Of Differential Equations | Differential Equation Class 12
Differential Equation 1st Order and 1st Degree| Homogeneous Differential Equation
MIT Entrance Exam Problem from 1869 #Shorts #math #maths #mathematics #problem #MIT
Bill Gates Vs Human Calculator
Комментарии
 0:08:44
0:08:44
 0:34:18
0:34:18
 0:56:16
0:56:16
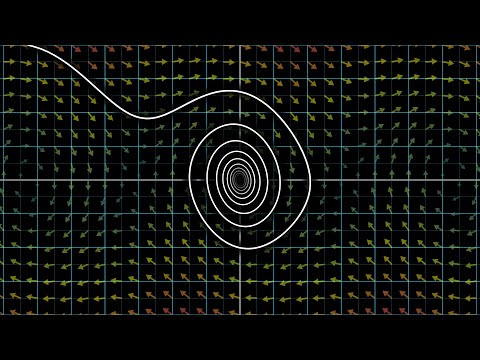 0:27:16
0:27:16
 0:19:58
0:19:58
 1:26:56
1:26:56
 0:48:35
0:48:35
 0:54:39
0:54:39
 0:58:14
0:58:14
 0:07:49
0:07:49
 0:20:34
0:20:34
 0:00:37
0:00:37
 0:33:33
0:33:33
 0:01:00
0:01:00
 0:00:35
0:00:35
 0:38:17
0:38:17
 0:00:50
0:00:50
 0:00:37
0:00:37
 0:34:59
0:34:59
 0:42:25
0:42:25
 0:01:55
0:01:55
 0:30:35
0:30:35
 0:00:48
0:00:48
 0:00:51
0:00:51