filmov
tv
Introduction to lexical analyzer

Показать описание
introduction to lexical analysis (scanning) with code example
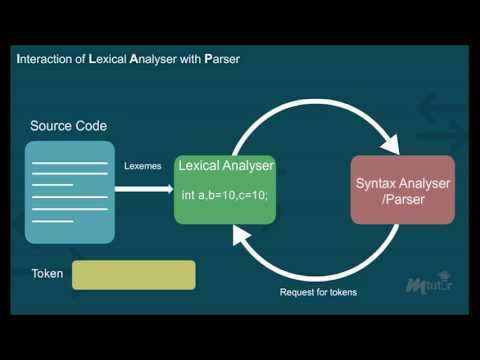
lexical analysis, often called scanning or tokenization, is the first phase of a compiler. its primary role is to read the source code as a stream of characters and convert it into a stream of tokens. these tokens are the basic building blocks of the programming language. think of it like breaking down a sentence into individual words and identifying their type (noun, verb, etc.).
**why is lexical analysis important?**
* **simplifies parsing:** by grouping characters into meaningful tokens, the parser (the next phase of the compiler) can work with a higher-level abstraction, making its job significantly easier. instead of dealing with individual characters, the parser deals with identifiers, keywords, operators, etc.
* **removes irrelevant information:** the lexical analyzer typically removes whitespace, comments, and other irrelevant characters from the source code, making subsequent phases more efficient.
* **error detection:** the lexical analyzer can detect certain lexical errors, such as invalid characters or improperly formed identifiers, early in the compilation process.
* **source code abstraction:** it provides a layer of abstraction between the character-level representation of the source code and the higher-level syntactic structure.
* **improved code maintainability:** by isolating the code responsible for recognizing basic language elements, it makes the compiler code easier to understand and maintain.
**key concepts in lexical analysis:**
1. **tokens:** tokens are the fundamental building blocks identified by the lexical analyzer. each token represents a logically cohesive unit of the source code. examples include:
* `identifier`: variable names, function names (e.g., `x`, `myvariable`, `calculatesum`)
* `integer_literal`: integer numbers (e.g., `123`, `0`, `-456`)
* `float_literal`: floating-point numbers (e.g., `3.14`, `-0.5`, `1.0e-6`)
* `string_litera ...
#LexicalAnalyzer #CompilerDesign #python
lexical analyzer
tokenization
syntax analysis
compiler design
lexical analysis
tokens
regular expressions
finite automata
programming languages
parser
source code
scanning
language processing
code compilation
lexical tokens
lexical analysis, often called scanning or tokenization, is the first phase of a compiler. its primary role is to read the source code as a stream of characters and convert it into a stream of tokens. these tokens are the basic building blocks of the programming language. think of it like breaking down a sentence into individual words and identifying their type (noun, verb, etc.).
**why is lexical analysis important?**
* **simplifies parsing:** by grouping characters into meaningful tokens, the parser (the next phase of the compiler) can work with a higher-level abstraction, making its job significantly easier. instead of dealing with individual characters, the parser deals with identifiers, keywords, operators, etc.
* **removes irrelevant information:** the lexical analyzer typically removes whitespace, comments, and other irrelevant characters from the source code, making subsequent phases more efficient.
* **error detection:** the lexical analyzer can detect certain lexical errors, such as invalid characters or improperly formed identifiers, early in the compilation process.
* **source code abstraction:** it provides a layer of abstraction between the character-level representation of the source code and the higher-level syntactic structure.
* **improved code maintainability:** by isolating the code responsible for recognizing basic language elements, it makes the compiler code easier to understand and maintain.
**key concepts in lexical analysis:**
1. **tokens:** tokens are the fundamental building blocks identified by the lexical analyzer. each token represents a logically cohesive unit of the source code. examples include:
* `identifier`: variable names, function names (e.g., `x`, `myvariable`, `calculatesum`)
* `integer_literal`: integer numbers (e.g., `123`, `0`, `-456`)
* `float_literal`: floating-point numbers (e.g., `3.14`, `-0.5`, `1.0e-6`)
* `string_litera ...
#LexicalAnalyzer #CompilerDesign #python
lexical analyzer
tokenization
syntax analysis
compiler design
lexical analysis
tokens
regular expressions
finite automata
programming languages
parser
source code
scanning
language processing
code compilation
lexical tokens
 0:14:59
0:14:59
 0:08:28
0:08:28
 0:05:35
0:05:35
 0:09:55
0:09:55
 0:05:08
0:05:08
 0:07:03
0:07:03
 0:11:45
0:11:45
 0:09:10
0:09:10
 0:19:02
0:19:02
 0:09:22
0:09:22
 0:17:59
0:17:59
 0:07:14
0:07:14
 0:18:20
0:18:20
 0:18:53
0:18:53
 0:11:16
0:11:16
 0:14:20
0:14:20
 0:10:32
0:10:32
 0:19:51
0:19:51
 0:19:12
0:19:12
 0:01:22
0:01:22
 0:10:06
0:10:06
 0:06:12
0:06:12
 0:10:15
0:10:15
 0:05:19
0:05:19