filmov
tv
Repeat Expansion Diagnostic Techniques Part 2 - Repeat Primed PCR
Показать описание
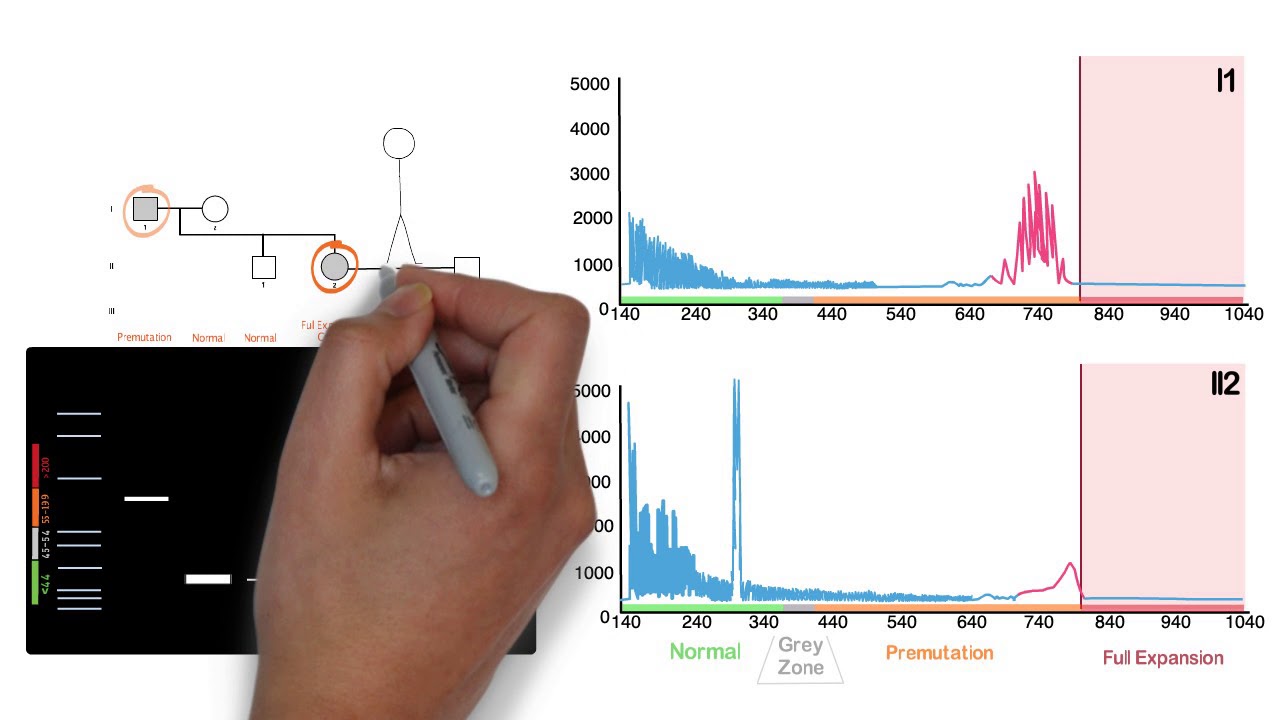
This is Part 2 of a 2-part series about molecular diagnostic testing for repeat expansion disorders. In this video, triplet-primed PCR is explained using Fragile-X disorder (FMR1) as an illustrative example.
Repeat Expansion Diagnostic Testing: Part 2 - Triplet-Primed PCR by Navneet Aujla and Talia Silver is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
Video generated using VideoScribe
Repeat Expansion Diagnostic Testing: Part 2 - Triplet-Primed PCR by Navneet Aujla and Talia Silver is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
Video generated using VideoScribe
Repeat Expansion Diagnostic Techniques Part 1: Southern Blot
Repeat Expansion Diagnostic Techniques Part 2 - Repeat Primed PCR
Multiplex, Long-Read Sequencing of Ataxia Repeat Expansions
Repeat Expansions
Evaluation of Triplet Repeat Primed PCR to Diagnose Fragile X Syndrome (Ann Lab Med)
Identifying repeat expansions in short read sequencing: Compassion of tools
Ira Deveson: Towards comprehensive genetic diagnosis of repeat expansion disorders
Long-range PCR & long-read sequencing: Tandem technologies for tackling genes in carrier screeni...
Trinucleotide Repeat Disorders
Webinar 28: Repeat Expansion diseases assessment with WGS
USMLE-Rx Express Video of the Week: Trinucleotide repeat expansion diseases
E14.1 Recent Advances in the Identification and Characterization of Expanded Repeats
Trinucleotide Repeats
Trinucleotide Repeat Expansion Diseases: A Comprehensive Review in Q&A Format
Long-read Sequencing and Optical Mapping of ATXN10 Repeat Expansion
Constitutional genetic disease diagnosis: Solving microarray, panel and exome negative cases
Enabling neurological disease research via DNA fragment analysis on the new SeqStudio genetic..
Detection of Familial Adult Myoclonic Epilepsy Type 3 Repeat Expansion Using Optical Genome Mapping
Short Tandem Repeat Expansions are Under-Appreciated in Rare Disease Diagnosis
Long-read Sequencing to Assess an Expanded Repeat in C9orf72
Applying targeted long-read sequencing to assess an expanded repeat in C9orf72
USMLE: Trinucleotide Repeat Expansion Mnemonic || USMLE BOOSTER MD #usmle
Huntington Disease: Presymptomatic to Diagnostic Testing and Care
Triplet Primed PCR part -2 l #tripletprimedpcr #pcr
Комментарии
 0:09:50
0:09:50
 0:09:21
0:09:21
 0:22:29
0:22:29
 0:02:49
0:02:49
 0:02:09
0:02:09
 0:25:21
0:25:21
 0:20:59
0:20:59
 0:30:45
0:30:45
 0:01:44
0:01:44
 0:44:37
0:44:37
 0:05:56
0:05:56
 0:17:07
0:17:07
 0:13:00
0:13:00
 0:07:33
0:07:33
 0:24:17
0:24:17
 0:15:42
0:15:42
 0:58:31
0:58:31
 0:15:18
0:15:18
 0:59:18
0:59:18
 0:24:26
0:24:26
 0:25:45
0:25:45
 0:05:09
0:05:09
 0:47:12
0:47:12
 0:12:28
0:12:28