filmov
tv
NASA | Aquarius Observations of Sea Surface Salinity

Показать описание
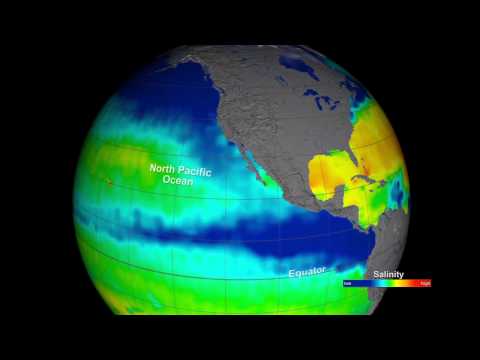
This visualization shows changes in global sea surface salinity, as measured by NASA's Aquarius instrument aboard the Aquarius/SAC-D spacecraft, from December 2011 through December 2012. Red represents areas of high salinity, while blue represents areas of low salinity. Aquarius is a focused effort to measure sea surface salinity and will provide the global view of salinity variability needed for climate studies. The mission is a collaboration between NASA and the Space Agency of Argentina (Comisión Nacional de Actividades Espaciales).
Like our videos? Subscribe to NASA's Goddard Shorts HD podcast:
Or find NASA Goddard Space Flight Center on Facebook:
Or find us on Twitter:
Like our videos? Subscribe to NASA's Goddard Shorts HD podcast:
Or find NASA Goddard Space Flight Center on Facebook:
Or find us on Twitter:
NASA | Aquarius Observations of Sea Surface Salinity
NASA | Aquarius Observations of Sea Surface Salinity
NASA| Aquarius: One Year Observing the Salty Seas
Aquarius Observations of Sea Surface Salinity
NASA | Aquarius Climate
NASA Aquarius Observations of Sea Surface Salinity
Aquarius: NASA's First Global Map of Ocean Salinity [1080p]
NASA | Aquarius Returns Global Maps of Soil Moisture
Robotically Exploring the Alien World of Earth's Deep Ocean with Dr. Richard Camilli
Sea Surface Salinity from Aquarius
Aquarius Nears on This Week @NASA
Aquarius maps soil moisture on This Week @NASA
Aquarius Satellite Sees Seas' Salt and More on This Week @NASA
NASA's Aquarius Mission Special Feature
NASA | Aquarius Climate
Aquarius Nears on This Week @NASA
Animation of Global Sea Surface Salinity from the NASA Aquarius/SAC-D Mission
Preparing for Armageddon - NASA Trains Underwater at Aquarius
Aquarius: Studying the Salt of the Sea
NASA | Aquarius Ocean Circulation
NASA Aquarius Data Training - Session #1 (4/7/16)
NASA | Aquarius Water Cycle
NASA Aquarius Data Training- Session #3 (4/21/16)
Sea Surface Salinity from NASA Aquarius (August 2011 - July 2014)
Комментарии
 0:00:30
0:00:30
 0:00:31
0:00:31
 0:03:18
0:03:18
 0:00:30
0:00:30
 0:02:14
0:02:14
 0:00:31
0:00:31
 0:00:20
0:00:20
 0:01:32
0:01:32
 1:00:30
1:00:30
 0:00:21
0:00:21
 0:10:07
0:10:07
 0:02:29
0:02:29
 0:10:28
0:10:28
 0:05:22
0:05:22
 0:02:14
0:02:14
 0:10:03
0:10:03
 0:00:45
0:00:45
 0:02:37
0:02:37
 0:02:24
0:02:24
 0:01:59
0:01:59
 1:21:59
1:21:59
 0:02:31
0:02:31
 1:10:24
1:10:24
 0:01:42
0:01:42