filmov
tv
Static Equilibrium

Показать описание
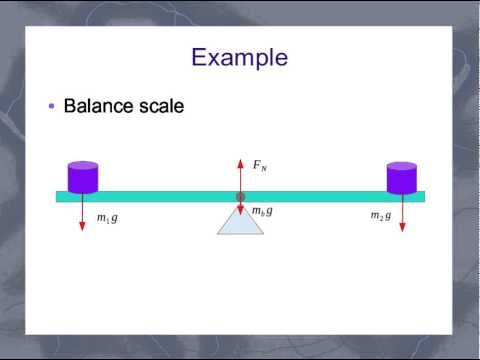
Newton’s 2nd Law states that the sum of the external forces on an object are equal to the product of the object’s mass and acceleration. An object is in static equilibrium when the sum of the forces on the object is zero. In this demonstration, a mass is hung from a string between two pulleys of negligible mass, and two unequal masses are hung from each end of the string. The heavier of the two end masses provides a larger tension in the string, and thus, the center mass will reach static equilibrium closer to the side suspending the heavier mass. When the configuration is repeated with equal end masses, the center mass reaches equilibrium at the center of the pulleys.
 0:07:28
0:07:28
 0:06:24
0:06:24
 0:10:21
0:10:21
 0:11:56
0:11:56
 0:09:08
0:09:08
 0:07:04
0:07:04
 0:05:59
0:05:59
 0:10:54
0:10:54
 11:41:08
11:41:08
 0:03:25
0:03:25
 0:11:32
0:11:32
 0:09:34
0:09:34
 0:08:38
0:08:38
 0:03:48
0:03:48
 0:09:46
0:09:46
 0:09:13
0:09:13
 0:04:34
0:04:34
 0:09:13
0:09:13
 0:10:09
0:10:09
 0:00:39
0:00:39
 0:09:10
0:09:10
 0:12:34
0:12:34
 0:11:40
0:11:40
 0:14:30
0:14:30