filmov
tv
Cellular Metabolism - All Enzymes are NOT Proteins!!!!???

Показать описание
#ElectronTransportChain
#ShimekitTadele
chapter 4
general biology chapter 4
cellular metabolism
#biochemistry
#metabolism
#enzymes
classification of enzymes
six classes of enzymes
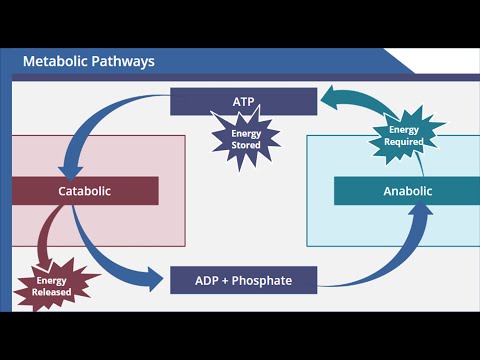
sum of chemical reactions
catabolic reactions
#catabolism
anabolic reactions
metabolic pathway
#metabolites
glycolysis
TCA cycle
glycolysis pathways
TCA cycle pathways
ATP
induced fit
lock and key
Chemical nature of enzymes
#cofactors
#apoenzyme
#holoenzyme
Simple enzymes
Conjugate Enzymes
prosthetic group
cytochromes
#coenzyme
#Metallo-enzymes
#Isoenzymes
#Isozymes
Classes of enzymes based on the substrate they act up on
Oxidation reduction
Transfer of electrons
oxidoreductases
oxidoreductase
Group transfer
Transferases
Transferase
Hydrolysis
Hydrolases
Hydrolase
non Hydrolysis cleavage
Lyases
Lyase
Isomerization & rearrangements
Isomerases
Isomerase
Ligation using energy from ATP
Ligases
Ligase
Mechanisms of enzyme action
enzyme– substrate complex
electrostatic and hydrophobic forces
Hydrophobic
Factors affecting enzymatic activities
enzyme’s Optimum Temperature
causes a change in shape of the enzyme
Different enzymes have different optimum pH
Substrate concentration and enzyme concentration
Changing the concentration of a substance only affects the rate of reaction if it is the limiting factor
Substrate concentration
Enzyme concentration
Enzyme inhibitors
Reversible inhibition
Competitive inhibition
Noncompetitive inhibition
Activators in enzymes
Irreversible inhibition
electrons move along the mitochondrial membrane from one protein to another.
hydrogen ions (H+) move from mitochondrial matrix to inter-membrane space.
hydrogen ions (H+) then diffuse down their concentration gradient back across the membrane and into the matrix through ATP synthase molecules in chemiosmosis
Protons and electrons are transferred to oxygen to form water
Electron Transport Chain
final step in the break-down of glucose
It also is the point at which most of the ATP is produced.
High-energy electrons and hydrogen ions from NADH and FADH2 produced in the Krebs cycle are used to convert ADP to ATP
#ShimekitTadele
chapter 4
general biology chapter 4
cellular metabolism
#biochemistry
#metabolism
#enzymes
classification of enzymes
six classes of enzymes
sum of chemical reactions
catabolic reactions
#catabolism
anabolic reactions
metabolic pathway
#metabolites
glycolysis
TCA cycle
glycolysis pathways
TCA cycle pathways
ATP
induced fit
lock and key
Chemical nature of enzymes
#cofactors
#apoenzyme
#holoenzyme
Simple enzymes
Conjugate Enzymes
prosthetic group
cytochromes
#coenzyme
#Metallo-enzymes
#Isoenzymes
#Isozymes
Classes of enzymes based on the substrate they act up on
Oxidation reduction
Transfer of electrons
oxidoreductases
oxidoreductase
Group transfer
Transferases
Transferase
Hydrolysis
Hydrolases
Hydrolase
non Hydrolysis cleavage
Lyases
Lyase
Isomerization & rearrangements
Isomerases
Isomerase
Ligation using energy from ATP
Ligases
Ligase
Mechanisms of enzyme action
enzyme– substrate complex
electrostatic and hydrophobic forces
Hydrophobic
Factors affecting enzymatic activities
enzyme’s Optimum Temperature
causes a change in shape of the enzyme
Different enzymes have different optimum pH
Substrate concentration and enzyme concentration
Changing the concentration of a substance only affects the rate of reaction if it is the limiting factor
Substrate concentration
Enzyme concentration
Enzyme inhibitors
Reversible inhibition
Competitive inhibition
Noncompetitive inhibition
Activators in enzymes
Irreversible inhibition
electrons move along the mitochondrial membrane from one protein to another.
hydrogen ions (H+) move from mitochondrial matrix to inter-membrane space.
hydrogen ions (H+) then diffuse down their concentration gradient back across the membrane and into the matrix through ATP synthase molecules in chemiosmosis
Protons and electrons are transferred to oxygen to form water
Electron Transport Chain
final step in the break-down of glucose
It also is the point at which most of the ATP is produced.
High-energy electrons and hydrogen ions from NADH and FADH2 produced in the Krebs cycle are used to convert ADP to ATP
 0:03:57
0:03:57
 0:06:51
0:06:51
 0:08:47
0:08:47
 0:09:18
0:09:18
 0:05:47
0:05:47
 0:08:23
0:08:23
 0:10:33
0:10:33
 0:18:18
0:18:18
 0:04:26
0:04:26
 0:32:02
0:32:02
 0:34:45
0:34:45
 0:00:51
0:00:51
 0:14:02
0:14:02
 0:04:37
0:04:37
 0:13:26
0:13:26
 0:04:40
0:04:40
 0:04:22
0:04:22
 0:19:33
0:19:33
 0:43:17
0:43:17
 0:01:43
0:01:43
 0:22:34
0:22:34
 0:34:33
0:34:33
 0:08:16
0:08:16
 0:05:06
0:05:06