filmov
tv
Protein Synthesis ( Part 1) : Transcription and eukaryotic mRNA processing

Показать описание
This video gives a brief information about prokaryotic and eukaryotic transcription (initiation, elongation and termination), eukaryotic mRNA processing, translation and protein synthesis.
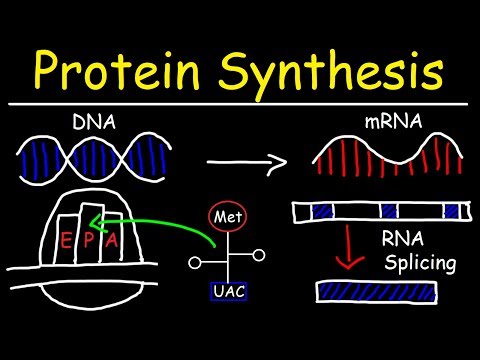
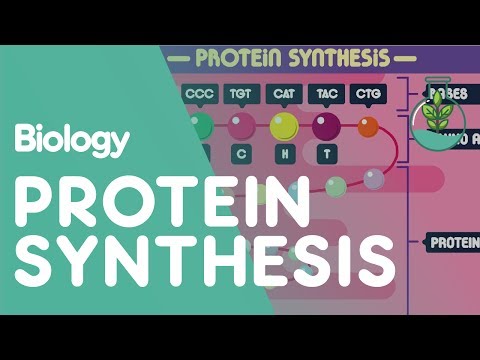
The production of proteins (protein synthesis) consists of transcription and translation processes.
Transcription means the information within the gene is transferred into mRNA
Translation is the process by which the information in mRNA is used to make proteins.
mRNA processing is required before the mRNA leaves the nucleus for translation.
mRNA processing: 5'capping, poly-A tail and splicing
Subscribe my channel:
Related videos:
Protein Synthesis ( Part 2) :Translation in eukaryotes and prokaryotes:
In eukaryotes, genetic information is stored in the nucleus. Transcription takes place in the nucleus and translation takes place in the cytoplasm.
In prokaryotic cells, there is no nucleus, so both transcription and translation take place in the cytoplasm.
During transcription, genetic information in a gene is transferred into a message (messenger RNA). This mRNA then leaves the nucleus, goes to ribosome in the cytoplasm to initiate translation.
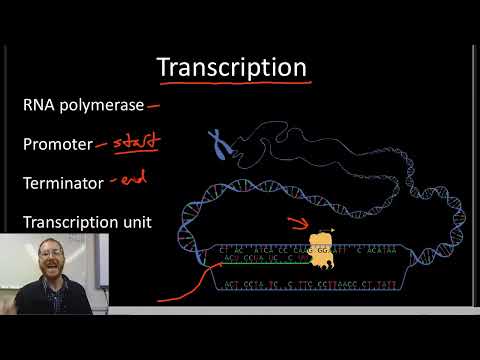
Transcription takes place in 3 steps: initiation, elongation and termination.
Initiation is the first step of transcription. During this process, an enzyme called RNA polymerase binds to promoter region which signals the DNA to unwind so that the RNA polymerase can read the bases in the template strand of DNA.
Elongation is the step where nucleotides are added to mRNA.
5' capping initated during elongation.
RNA triphosphatase removes one of the terminal phosphate groups.
Guanylyl transferase enzyme carries a reaction between alpha phosphate of GTP and terminal phosphate group.
Once guanine is attached, methyl transferase enzyme adds a methyl group to the guanine nucleotide which leads to the formation of 5' cap which helps in the recruitment of mRNA to the ribosome.
Termination is the step which the mRNA is complete and detaches from the DNA and RNA polymerase.
When the end of the gene is transcribed into mRNA, two proteins called CstF and CPSF are recruited to RNA by C-terminal domain of the RNA polymerase.
CstF: Cleavage Stimulating Factor
CPSF: Cleavage and polyadenylation specificity factor.
CstF cleaves the mRNA and dissociates from the coplex.
CPSF recruits Poly A Polymerase enzyme which adds Adenine residues to the 3'end of mRNA forming Poly-A tail.
Poly A binding proteins protein the poly-A tail from degradation.
The resulting pre-mRNA contains exons and introns. Introns do not code for protein and they are spliced out by spliceosomes and exons are joined together. The resulting mRNA is now called mature mRNA. mature mRNA now ready to leave the nucleus for another process known as translation.
LifeSciences Study Guide
Protein, Protein synthesis, Polypeptide chain, transcription, mRNA processing, translation, eukaryotic transcription, prokaryotic transcription mRNA processing in eukaryotes, transcription initiation, transcription elongation, transcription termination, transcription factors, transcription bacteria, transcription humans, DNA, mRNA, protein, Sintesi proteica, human, bacteria DNA, Biosynthèse des protéines, Biosíntesis proteica, protein production, transcription and translation, pre-mRNA, mature mRNA, transcription biology, life sciences, rna transcription, molecular biology, rna interference, rna seq, rna polymerase, Transkripsiyon, Trascrizione (biologia), Transcription (biologie), Transkription (Biologie), Μεταγραφή (βιολογία), biological sciences, biochemistry, translation bacteria, protein synthesis video, protein synthesis animation, protein synthesis in bacteria, protein synthesis in eukaryotes, protein synthesis in prokaryotes, ribosome, rRNA, tRNA, mRNA, enzymes. #proteinsynthesis #transcription #RNA #protein #DNA #enzyme #RNA #mRNA #DNAanalysis #rnatranscription
#molecularbiology #simplebiology #biology #tutorial
protein synthesis in eukaryotes, protein synthesis in prokaryotes, protein synthesis bacteria, Protein biosynthesis, biology paper 1, free science lessons biology paper 1,
#protein #translation #proteinsynthesis #simplebiology #tutorial #molecularbiology #biologytutorial #transcription #DNA #RNA #lesson, a level biology, gcse biology, cell biology, biology revision, #revision #biology, #GCSE #ALEVELBIOLOGY protein synthesis a level biology, medical exam, molecular biology lecture, #education #lecture #tutorial #proteintutorial
education animation, educational, education videos, education connection, education hub
Protein, Protein sentezi, Polipeptit zinciri, transkripsiyon, mRNA işleme, translasyon, ökaryotik transkripsiyon, prokaryotik transkripsiyon Ökaryotlarda mRNA işleme,
The production of proteins (protein synthesis) consists of transcription and translation processes.
Transcription means the information within the gene is transferred into mRNA
Translation is the process by which the information in mRNA is used to make proteins.
mRNA processing is required before the mRNA leaves the nucleus for translation.
mRNA processing: 5'capping, poly-A tail and splicing
Subscribe my channel:
Related videos:
Protein Synthesis ( Part 2) :Translation in eukaryotes and prokaryotes:
In eukaryotes, genetic information is stored in the nucleus. Transcription takes place in the nucleus and translation takes place in the cytoplasm.
In prokaryotic cells, there is no nucleus, so both transcription and translation take place in the cytoplasm.
During transcription, genetic information in a gene is transferred into a message (messenger RNA). This mRNA then leaves the nucleus, goes to ribosome in the cytoplasm to initiate translation.
Transcription takes place in 3 steps: initiation, elongation and termination.
Initiation is the first step of transcription. During this process, an enzyme called RNA polymerase binds to promoter region which signals the DNA to unwind so that the RNA polymerase can read the bases in the template strand of DNA.
Elongation is the step where nucleotides are added to mRNA.
5' capping initated during elongation.
RNA triphosphatase removes one of the terminal phosphate groups.
Guanylyl transferase enzyme carries a reaction between alpha phosphate of GTP and terminal phosphate group.
Once guanine is attached, methyl transferase enzyme adds a methyl group to the guanine nucleotide which leads to the formation of 5' cap which helps in the recruitment of mRNA to the ribosome.
Termination is the step which the mRNA is complete and detaches from the DNA and RNA polymerase.
When the end of the gene is transcribed into mRNA, two proteins called CstF and CPSF are recruited to RNA by C-terminal domain of the RNA polymerase.
CstF: Cleavage Stimulating Factor
CPSF: Cleavage and polyadenylation specificity factor.
CstF cleaves the mRNA and dissociates from the coplex.
CPSF recruits Poly A Polymerase enzyme which adds Adenine residues to the 3'end of mRNA forming Poly-A tail.
Poly A binding proteins protein the poly-A tail from degradation.
The resulting pre-mRNA contains exons and introns. Introns do not code for protein and they are spliced out by spliceosomes and exons are joined together. The resulting mRNA is now called mature mRNA. mature mRNA now ready to leave the nucleus for another process known as translation.
LifeSciences Study Guide
Protein, Protein synthesis, Polypeptide chain, transcription, mRNA processing, translation, eukaryotic transcription, prokaryotic transcription mRNA processing in eukaryotes, transcription initiation, transcription elongation, transcription termination, transcription factors, transcription bacteria, transcription humans, DNA, mRNA, protein, Sintesi proteica, human, bacteria DNA, Biosynthèse des protéines, Biosíntesis proteica, protein production, transcription and translation, pre-mRNA, mature mRNA, transcription biology, life sciences, rna transcription, molecular biology, rna interference, rna seq, rna polymerase, Transkripsiyon, Trascrizione (biologia), Transcription (biologie), Transkription (Biologie), Μεταγραφή (βιολογία), biological sciences, biochemistry, translation bacteria, protein synthesis video, protein synthesis animation, protein synthesis in bacteria, protein synthesis in eukaryotes, protein synthesis in prokaryotes, ribosome, rRNA, tRNA, mRNA, enzymes. #proteinsynthesis #transcription #RNA #protein #DNA #enzyme #RNA #mRNA #DNAanalysis #rnatranscription
#molecularbiology #simplebiology #biology #tutorial
protein synthesis in eukaryotes, protein synthesis in prokaryotes, protein synthesis bacteria, Protein biosynthesis, biology paper 1, free science lessons biology paper 1,
#protein #translation #proteinsynthesis #simplebiology #tutorial #molecularbiology #biologytutorial #transcription #DNA #RNA #lesson, a level biology, gcse biology, cell biology, biology revision, #revision #biology, #GCSE #ALEVELBIOLOGY protein synthesis a level biology, medical exam, molecular biology lecture, #education #lecture #tutorial #proteintutorial
education animation, educational, education videos, education connection, education hub
Protein, Protein sentezi, Polipeptit zinciri, transkripsiyon, mRNA işleme, translasyon, ökaryotik transkripsiyon, prokaryotik transkripsiyon Ökaryotlarda mRNA işleme,
Комментарии
 0:03:58
0:03:58
 0:08:47
0:08:47
 0:10:55
0:10:55
 0:11:21
0:11:21
 0:08:49
0:08:49
 0:15:00
0:15:00
 0:12:30
0:12:30
 0:05:08
0:05:08
 1:17:01
1:17:01
 0:05:30
0:05:30
 0:06:50
0:06:50
 0:06:15
0:06:15
 0:08:54
0:08:54
 1:33:02
1:33:02
 0:07:55
0:07:55
 0:19:13
0:19:13
 0:00:59
0:00:59
 0:20:09
0:20:09
 0:01:00
0:01:00
 0:16:52
0:16:52
 0:50:49
0:50:49
 0:14:19
0:14:19
 0:42:43
0:42:43
 0:29:38
0:29:38