filmov
tv
Understanding I2C

Показать описание
This video provides a brief technical overview of the I2C protocol and how it is used to transfer digital information.
Timeline:
00:00 Introduction
00:14 About I2C
01:00 Basic I2C topology
01:36 Overview of I2C frames
02:10 Start condition
02:51 Slave address
03:36 Aside: timing relationship between SDA and SCL
04:16 Read / write bit
04:51 Ack(knowledge) bit
05:32 Data byte(s)
06:06 Multiple data bytes
06:48 Stop condition
07:28 About “open drain”
08:14 Pull up resistor values
08:56 Modes / speeds
09:54 Summary
Timeline:
00:00 Introduction
00:14 About I2C
01:00 Basic I2C topology
01:36 Overview of I2C frames
02:10 Start condition
02:51 Slave address
03:36 Aside: timing relationship between SDA and SCL
04:16 Read / write bit
04:51 Ack(knowledge) bit
05:32 Data byte(s)
06:06 Multiple data bytes
06:48 Stop condition
07:28 About “open drain”
08:14 Pull up resistor values
08:56 Modes / speeds
09:54 Summary
Understanding I2C
How I2C Communication Works and How To Use It with Arduino
Basics of I2C communication | Hardware implementation of I2C bus
Electronic Basics #19: I2C and how to use it
I2C Frame structure Understanding | I2C data transmission
I2C Addresses - Collin’s Lab Notes #adafruit #collinslabnotes
PROTOCOLS: UART - I2C - SPI - Serial communications #001
What is I2C, Basics for Beginners
What Is...I2C?
Inter-Integrated Circuit (I2C) Basics
I2C introduction: The protocol
I2C Protocol Explained: Basics, Interface, Clock Stretching, and Communication
How SPI & I2C Work - Communication Protocols | Embedded Systems Explained
Understanding I2C Communication with OLED Display: STM32 Microcontroller Programming Deep Dive
I3C vs I2C Protocol | Difference between I3C Protocol and I2C Protocol
I2C and SPI on a PCB Explained!
Inter-Integrated Circuit (I2C) Part-1 Explained in Hindi l Embedded And Real time Operating System
I2C Part 1 - Using 2 Arduinos
I2C vs SPI Protocol | Difference between I2C Protocol and SPI Protocol
Understanding I2C
What is I2C communication protocol ? #embedded #electronics #engineering
I2C protocol overview
Understand the I2C Bus, Tutorial
I2C Communication Simplified: A Quick Guide
Комментарии
 0:10:58
0:10:58
 0:09:57
0:09:57
 0:06:48
0:06:48
 0:06:09
0:06:09
 0:10:26
0:10:26
 0:01:00
0:01:00
 0:11:58
0:11:58
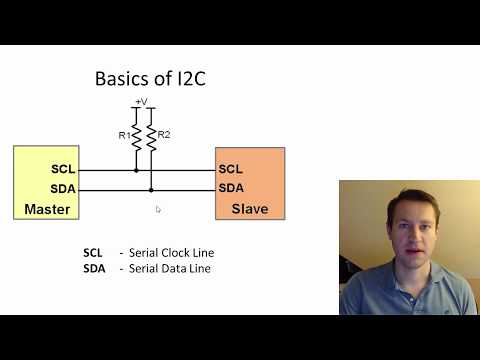 0:18:30
0:18:30
 0:06:25
0:06:25
 0:25:29
0:25:29
 0:15:47
0:15:47
 0:13:31
0:13:31
 0:10:03
0:10:03
 1:41:20
1:41:20
 0:01:26
0:01:26
 0:15:34
0:15:34
 0:07:24
0:07:24
 0:25:51
0:25:51
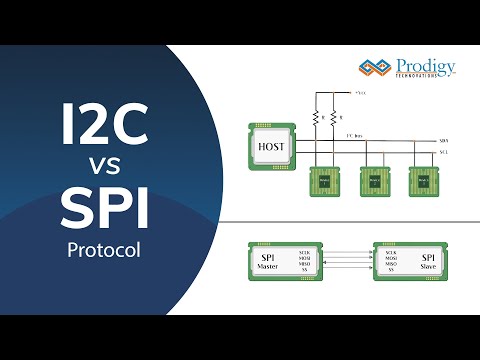 0:01:23
0:01:23
 0:07:22
0:07:22
 0:01:00
0:01:00
 0:09:13
0:09:13
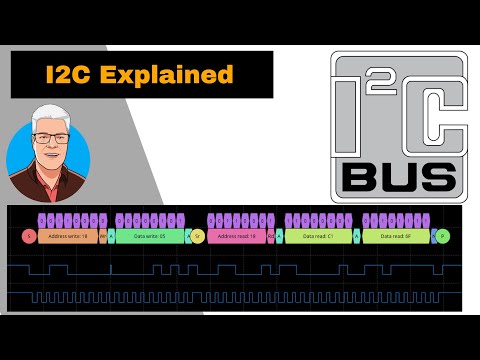 0:30:41
0:30:41
 0:01:41
0:01:41