filmov
tv
Photochemical Smog (Animation)

Показать описание
#PhotochemicalSmog #AnimatedChemistry #KineticSchool
More videos:
What is Greenhouse Effect? Explained.
Layers of the Atmosphere
How Lightning Forms
How Satellite Works
Acid Rain
Sources of Air Pollution
Air Pollution
How Battery Works
Corrosion : Factors Affecting Corrosion (Chapter 1)
Corrosion : Dry or Chemical Corrosion (Chapter 2)
Corrosion : Electrochemical Cell or Corrosion Cell (Chapter 3)
Corrosion : Types of Electrochemical Cells (Chapter 4)
Corrosion : Rusting of Iron (Chapter 5)
Formation of Photochemical smog:
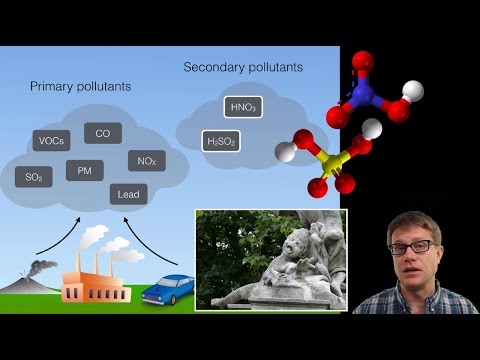
"Smog" is a mixture of fog and smog which occurs in some busy industrial cities.
Smoke + Fog = SMOG
Smog is of two types:
1. Classical Smog.
2. Photochemical Smog.
Classical Smog, is produced by the combustion or burning of fossil fuels like coal, petrol or gasoline etc., and caused by a mixture of smoke and SO2, present in air.
Classical smog also known as London Smog.
• It’s also reducing in nature.
• It occurs in cool, humid climate.
• Major Constituents are smoke, fog and sulfur dioxide.
• It can occur both during the day and at night.
In December 1952, London was trapped in a deadly cloud of fog and pollution for five days.
At the time, the city ran on cheap coal for everything from generating power to heating homes.
which was the result of classical smog.
Photochemical smog is a type of smog produced when ultraviolet light from the sun reacts with nitrogen oxides (NOx) and volatile organic compounds (VOCs) in the atmosphere.
• It is also referred to as "Summer Smog" or "Los Angeles Smog".
• It is an Oxidising Smog and visible as a Brown Haze.
• It only happens in the presence of sunlight.
• Major Constituents are Hydrocarbons, O3, PAN and NOx.
• It is most prominent during the morning and afternoon.
photochemical smog formation is influenced by the weather conditions, such as
• Warm Sunny Days.
• Gentle Winds.
• Lower Level Inversion, which is also known as Thermal Inversion.
• Combustion of hydrocarbon and Nitrogen Oxides.
Sources of Photochemical smog’s pollutants.
•Volcanic eruption
• Forest fire
• Automobiles
• industry
• power plant
Reaction of Photochemical smog:
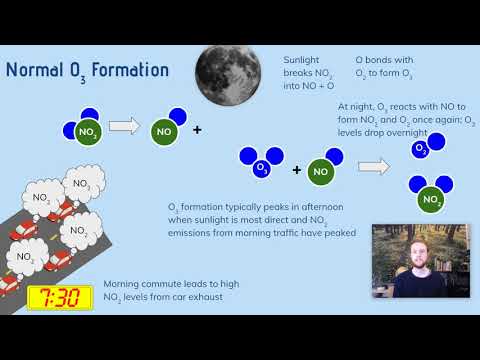
•Nitrogen (N₂) and Oxygen (O₂) combine in the combustion process to form Nitric Oxide (NO).
N₂ + O₂ = 2NO
•This Nitric Oxide (NO) oxidized in the atmosphere to produce Nitrogen Dioxide (NO₂).
2NO + O₂ = 2NO₂
•Sunlight breaks down Nitrogen Dioxide (NO₂) into Nitric Oxide (NO) and an Oxygen radical (O).
NO₂ + h𝝊 = NO + O
•The Oxygen radical (O) combines with molecular Oxygen (O₂) to form Ozone (O₃).
O₂ + O = O
•Ozone (O₃) is the main component of photochemical smog.
•NO can remove O₃ by reacting with it to form NO₂ and O₂ .
NO + O₃ = NO₂ + O₂
Alternative Reactions:
NO and NO₂ can also react with the hydrocarbons instead of O₃ to form other volatile compounds known as PAN (peroxyacetyl nitrate).
NO₂ + O₂ + Hydrocarbons + light → PAN
a) Reactive hydrocarbon (those with C=C group) from auto exhaust interact with O₃ to from a hydrocarbon free radical RCH₂•.
b) RCH₂• rapidly reacts with O₂ to from another free radical RCH₂O₂•.
c) RCH₂O₂• reacts with NO to produce NO₂ & the free radical RCH₂O•
d) This new free radical next interacts with O₂ to yield a stable aldehyde (RCHO), and hydroperoxyl radical (HO₂•).
e) HO₂• then reactive with another molecule of NO to give NO₂ & HO•.
f) HO• is extremely reactive & rapidly reacts with a stable hydrocarbon RCH ₃ to yield H₂O & regenerate the hydrocarbon free radical RCH₂•, thereby completing cycle.
Peroxyacetyl nitrate is also known as peroxyacyl nitrate.
Photochemical smog was first identified in Los Angeles in 1944.
In 2017, Photochemical smog to envelop large parts of Beijing.
Otherwise, In November 2017, the air pollution spiked far beyond acceptable levels in Delhi.
Effects of Photochemical smog:
Photochemical smog's effects cause eye irritation, damage to the respiratory system and vegetation.
Music:
Creative Commons — Attribution 3.0 Unported — CC BY 3.0
More videos:
What is Greenhouse Effect? Explained.
Layers of the Atmosphere
How Lightning Forms
How Satellite Works
Acid Rain
Sources of Air Pollution
Air Pollution
How Battery Works
Corrosion : Factors Affecting Corrosion (Chapter 1)
Corrosion : Dry or Chemical Corrosion (Chapter 2)
Corrosion : Electrochemical Cell or Corrosion Cell (Chapter 3)
Corrosion : Types of Electrochemical Cells (Chapter 4)
Corrosion : Rusting of Iron (Chapter 5)
Formation of Photochemical smog:
"Smog" is a mixture of fog and smog which occurs in some busy industrial cities.
Smoke + Fog = SMOG
Smog is of two types:
1. Classical Smog.
2. Photochemical Smog.
Classical Smog, is produced by the combustion or burning of fossil fuels like coal, petrol or gasoline etc., and caused by a mixture of smoke and SO2, present in air.
Classical smog also known as London Smog.
• It’s also reducing in nature.
• It occurs in cool, humid climate.
• Major Constituents are smoke, fog and sulfur dioxide.
• It can occur both during the day and at night.
In December 1952, London was trapped in a deadly cloud of fog and pollution for five days.
At the time, the city ran on cheap coal for everything from generating power to heating homes.
which was the result of classical smog.
Photochemical smog is a type of smog produced when ultraviolet light from the sun reacts with nitrogen oxides (NOx) and volatile organic compounds (VOCs) in the atmosphere.
• It is also referred to as "Summer Smog" or "Los Angeles Smog".
• It is an Oxidising Smog and visible as a Brown Haze.
• It only happens in the presence of sunlight.
• Major Constituents are Hydrocarbons, O3, PAN and NOx.
• It is most prominent during the morning and afternoon.
photochemical smog formation is influenced by the weather conditions, such as
• Warm Sunny Days.
• Gentle Winds.
• Lower Level Inversion, which is also known as Thermal Inversion.
• Combustion of hydrocarbon and Nitrogen Oxides.
Sources of Photochemical smog’s pollutants.
•Volcanic eruption
• Forest fire
• Automobiles
• industry
• power plant
Reaction of Photochemical smog:
•Nitrogen (N₂) and Oxygen (O₂) combine in the combustion process to form Nitric Oxide (NO).
N₂ + O₂ = 2NO
•This Nitric Oxide (NO) oxidized in the atmosphere to produce Nitrogen Dioxide (NO₂).
2NO + O₂ = 2NO₂
•Sunlight breaks down Nitrogen Dioxide (NO₂) into Nitric Oxide (NO) and an Oxygen radical (O).
NO₂ + h𝝊 = NO + O
•The Oxygen radical (O) combines with molecular Oxygen (O₂) to form Ozone (O₃).
O₂ + O = O
•Ozone (O₃) is the main component of photochemical smog.
•NO can remove O₃ by reacting with it to form NO₂ and O₂ .
NO + O₃ = NO₂ + O₂
Alternative Reactions:
NO and NO₂ can also react with the hydrocarbons instead of O₃ to form other volatile compounds known as PAN (peroxyacetyl nitrate).
NO₂ + O₂ + Hydrocarbons + light → PAN
a) Reactive hydrocarbon (those with C=C group) from auto exhaust interact with O₃ to from a hydrocarbon free radical RCH₂•.
b) RCH₂• rapidly reacts with O₂ to from another free radical RCH₂O₂•.
c) RCH₂O₂• reacts with NO to produce NO₂ & the free radical RCH₂O•
d) This new free radical next interacts with O₂ to yield a stable aldehyde (RCHO), and hydroperoxyl radical (HO₂•).
e) HO₂• then reactive with another molecule of NO to give NO₂ & HO•.
f) HO• is extremely reactive & rapidly reacts with a stable hydrocarbon RCH ₃ to yield H₂O & regenerate the hydrocarbon free radical RCH₂•, thereby completing cycle.
Peroxyacetyl nitrate is also known as peroxyacyl nitrate.
Photochemical smog was first identified in Los Angeles in 1944.
In 2017, Photochemical smog to envelop large parts of Beijing.
Otherwise, In November 2017, the air pollution spiked far beyond acceptable levels in Delhi.
Effects of Photochemical smog:
Photochemical smog's effects cause eye irritation, damage to the respiratory system and vegetation.
Music:
Creative Commons — Attribution 3.0 Unported — CC BY 3.0
Комментарии
 0:08:20
0:08:20
 0:05:44
0:05:44
 0:04:22
0:04:22
 0:07:23
0:07:23
 0:03:53
0:03:53
 0:02:03
0:02:03
 0:03:33
0:03:33
 0:17:21
0:17:21
 0:01:45
0:01:45
 0:00:45
0:00:45
 0:01:57
0:01:57
 0:00:42
0:00:42
 0:14:56
0:14:56
 0:02:23
0:02:23
 0:11:55
0:11:55
 0:08:52
0:08:52
 0:05:26
0:05:26
 0:12:57
0:12:57
 0:14:45
0:14:45
 0:00:11
0:00:11
 0:09:25
0:09:25
 0:30:03
0:30:03
 0:04:04
0:04:04
 0:03:22
0:03:22