filmov
tv
Internal structure of a liquid crystal or LCD TV screen

Показать описание
In this episode the internal architecture of a liquid crystal display found in LCD TVs is discussed. The design of this type of screen requires an assembly of different parts such as polarizing filters, liquid crystal, electronic circuits and color filter.
Internal structure of a liquid crystal or LCD TV screen
LCD TV Repair Course, How Liquid Crystal Display Works | Internal Structure of LCD Screen
Internal Structure of Liquid Crystal Display | How LCD Screen Work #Short
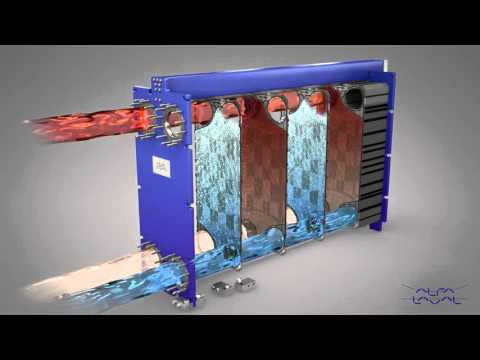
Alfa Laval liquid/liquid gasketed plate-and-frame heat exchanger
What is the internal structure of the liquid cooled energy storage system #energystorage #lifepo4
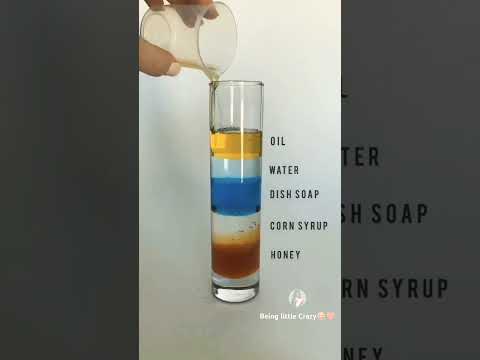
| colourful liquid density gradient | layers of liquid in glass |Awesome science experiment
What is the internal structure of the liquid cooled energy storage system #lithiumbattery #energy
Liquid Crystals pt1 Definitions
Earth's Interior: Structure of Earth | Physical Geography | UPSC CSE Geography Prelims & Ma...
Is Glass a Liquid?
What Liquid Is Really Inside a Level Tool (and Why It Matters)?
LIQUID PROPELLANT ROCKET ENGINE/liquid rocket 3d animation/construction working/ LEARN FROM THE BASE
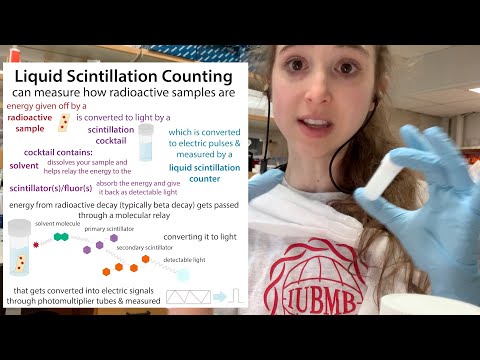
Liquid Scintillation Counting - a scintillating look inside of a way to measure radioactive decay!
liquid crystal display
Structure Of The Earth | The Dr. Binocs Show | Educational Videos For Kids
Tubeless Tire | The interesting Physics behind it
Jupiter's Secret Core: The Liquid Hydrogen Enigma #space
Water - Liquid Awesome: Crash Course Biology #2
KSG DYK - Which part of the earth's internal structure is in liquid state? #shorts #upscprelims
What's Inside Laptop LCD Display? What are the layers of a Liquid Crystal Display?
Liquid Crystal Display Television LCD TV (Basics, Types, Structure, Working, Pros & Cons) Explai...
internal structure of liquid pouch packing machine drinking water packaging equipment electric wire
Flooring Liquid Screed Overlay #shorts
liquid Crystal Display television LCD TV inside #lcdscreen #internal power supply
Комментарии
 0:09:45
0:09:45
 0:07:12
0:07:12
 0:00:11
0:00:11
 0:00:28
0:00:28
 0:00:19
0:00:19
 0:00:16
0:00:16
 0:00:30
0:00:30
 0:26:56
0:26:56
 0:34:03
0:34:03
 0:05:23
0:05:23
 0:00:41
0:00:41
 0:04:43
0:04:43
 0:20:53
0:20:53
 0:00:53
0:00:53
 0:03:13
0:03:13
 0:07:50
0:07:50
 0:00:24
0:00:24
 0:11:17
0:11:17
 0:00:59
0:00:59
 0:02:09
0:02:09
 0:10:52
0:10:52
 0:03:52
0:03:52
 0:00:09
0:00:09
 0:00:15
0:00:15