filmov
tv
Atomic Structure (Bohr Model) for Oxygen (O)
Показать описание
In this video we'll look at the atomic structure and Bohr model for the Oxygen atom (O).
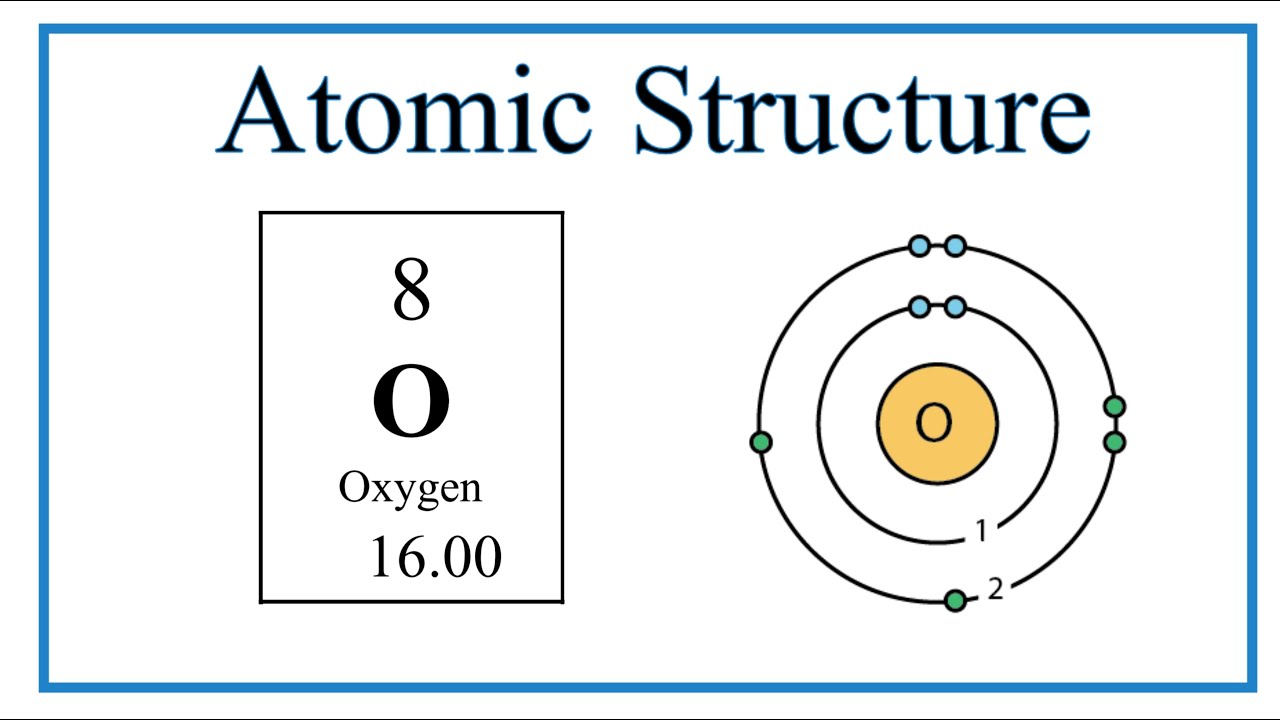
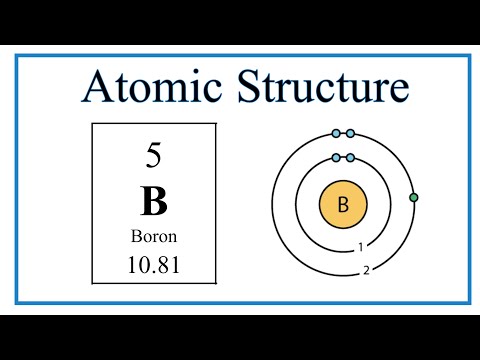
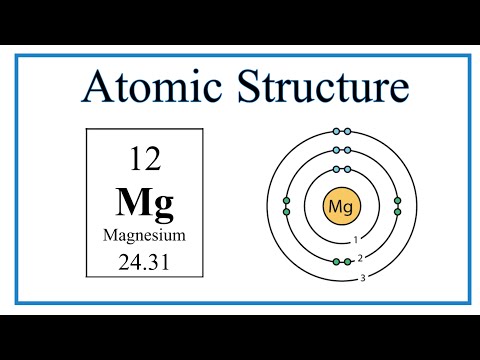
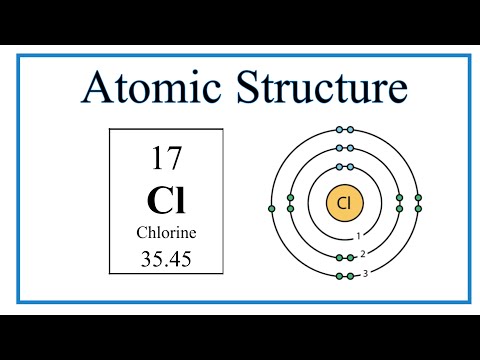
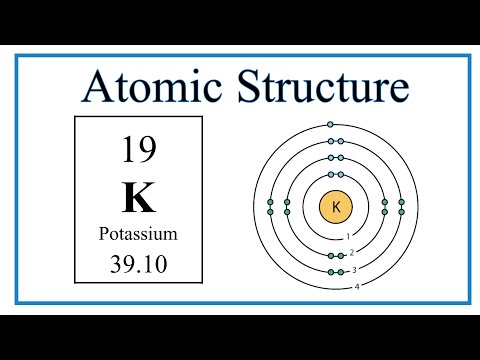
We’ll use a Bohr diagram to visually represent where the electrons are around the nucleus of the Oatom. Electrons are placed in energy levels in a predictable pattern. The first energy level can hold two valence electrons, and the second and third can each hold eight electrons.
Using the atomic number for Oxygen we can find the total number of electrons for the atom. We then place these in energy levels in our diagram.
The Periodic Table can also be used to determine where the electrons should go in our Bohr model. We could also write the electron configuration to show the arrangement of electrons. Electron configurations can provide a higher degree of detail about the arrangement of electrons within each energy level.
Bohr diagrams (models) are useful because the allow us to clearly see the arraignment of electrons around the nucleus. In particular, the electrons in the highest energy level are the most important since these are the electrons involved in chemical bonding. We call these valence electrons.
Bohr Diagram Image:
We’ll use a Bohr diagram to visually represent where the electrons are around the nucleus of the Oatom. Electrons are placed in energy levels in a predictable pattern. The first energy level can hold two valence electrons, and the second and third can each hold eight electrons.
Using the atomic number for Oxygen we can find the total number of electrons for the atom. We then place these in energy levels in our diagram.
The Periodic Table can also be used to determine where the electrons should go in our Bohr model. We could also write the electron configuration to show the arrangement of electrons. Electron configurations can provide a higher degree of detail about the arrangement of electrons within each energy level.
Bohr diagrams (models) are useful because the allow us to clearly see the arraignment of electrons around the nucleus. In particular, the electrons in the highest energy level are the most important since these are the electrons involved in chemical bonding. We call these valence electrons.
Bohr Diagram Image:
Комментарии
 0:01:59
0:01:59
 0:04:50
0:04:50
 0:01:59
0:01:59
 0:05:05
0:05:05
 0:21:44
0:21:44
 0:02:01
0:02:01
 0:01:55
0:01:55
 0:06:21
0:06:21
 0:43:58
0:43:58
 0:02:01
0:02:01
 0:02:20
0:02:20
 0:02:07
0:02:07
 0:01:51
0:01:51
 0:01:59
0:01:59
 0:27:12
0:27:12
 0:01:59
0:01:59
 0:02:10
0:02:10
 0:02:03
0:02:03
 0:02:05
0:02:05
 0:06:48
0:06:48
 0:07:04
0:07:04
 0:01:59
0:01:59
 1:12:19
1:12:19
 0:02:21
0:02:21