filmov
tv
Liver Infections | Surgery Video Lectures | Medical Student Education | V-Learning

Показать описание
-------------------------------------------------------------
Lecture Duration - 00:44:19
Release Date - January 2020
General Surgery Lectures Collection -
-------------------------------------------------------------
The viruses that cause liver damage can be spread through Blood or semen, contaminated food or water, or close contact with a person who is infected. Ascending bacterial infection of the biliary tract is usually associated with obstruction and presents with clinical jaundice, rigors and a tender right upper quadrant (Charcot’s triad). The diagnosis is confirmed by the finding of dilated bile ducts on ultrasound, an obstructive picture of liver function tests and the isolation of an organism from the Blood on culture.
The condition is a medical emergency, and delay in appropriate treatment results in multiorgan failure secondary to septicaemia. Once the diagnosis has been confirmed, the patient should be commenced on a first-line broad spectrum antibiotic and rehydrated, and arrangements should be made for urgent endoscopic or percutaneous transhepatic drainage of the biliary tree. Biliary stone disease is a common predisposing factor, and the causative ductal stones may be removed at the time of endoscopic cholangiography by endoscopic sphincterotomy.
The aetiology of a pyogenic liver abscess is unexplained in the majority of patients. Common causes include biliary stone disease and other causes of intra-abdominal sepsis, including appendicitis and diverticular disease. The diagnosis is suggested by the finding of a multiloculated cystic mass on ultrasound or CT scan. The most common organisms are Streptococcus milleri and Escherichia coli, but other enteric organisms such as Streptococcus faecalis, Klebsiella and Proteus vulgaris also occur, and mixed growths are common.
-------------------------------------------------------------
1300+ Medical Courses Lectures.
-------------------------------------------------------------
In Amebiasis, the amoebic cyst is ingested and develops into the trophozoite form in the colon, and then passes through the bowel wall and to the liver via the portal Blood. Diagnosis is by isolation of the parasite from the liver lesion or the stool and confirming its nature by microscopy.
Hydatid Liver Disease’s diagnosis, Percutaneous Treatment (PAIR) and Surgical Treatment are explained in the end of this lecture.
-------------------------------------------------------------
-------------------------------------------------------------
 0:01:59
0:01:59
 0:05:05
0:05:05
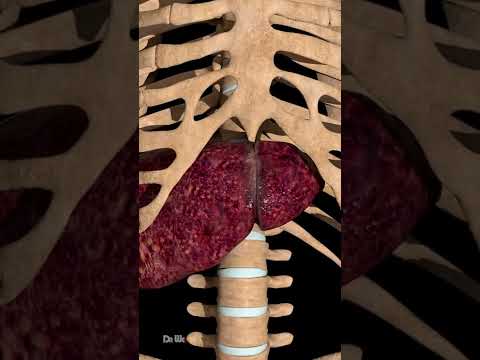 0:00:31
0:00:31
 0:00:53
0:00:53
 0:26:53
0:26:53
 0:07:11
0:07:11
 0:06:30
0:06:30
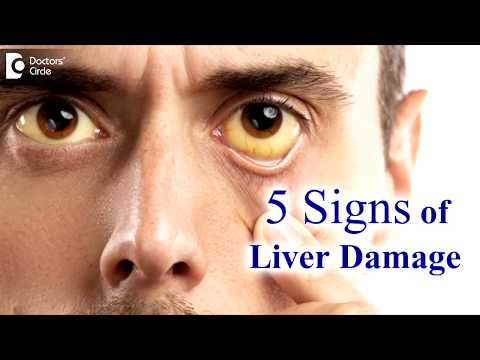 0:01:20
0:01:20
 0:08:04
0:08:04
 0:09:48
0:09:48
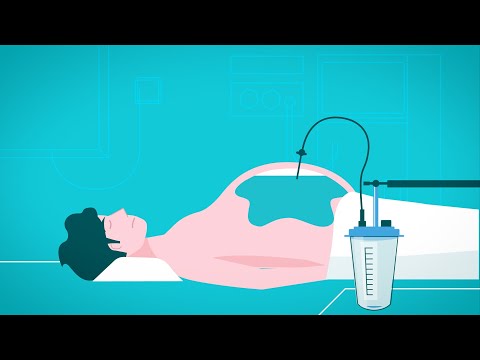 0:01:51
0:01:51
 0:01:50
0:01:50
 0:01:36
0:01:36
 0:04:07
0:04:07
 0:01:01
0:01:01
 0:01:54
0:01:54
 0:02:14
0:02:14
 0:11:37
0:11:37
 0:07:17
0:07:17
 0:07:44
0:07:44
 0:03:18
0:03:18
 0:01:46
0:01:46
 0:05:35
0:05:35
 0:09:28
0:09:28