filmov
tv
Difference between Aponeurosis and Tendon

Показать описание
Aponeurosis vs tendon
On dissecting a human body, one comes across various structures in and around the muscles apart from blood vessels, bones and nerves. Aponeuroses, fasciae, ligaments and tendons are structures seen along with muscles. Fasciae are the auxillary tissues that connect muscle to muscle while ligaments are connective tissues that connect one bone to another bone. Aponeuroses and tendons are connective tissues that connect muscles to bones.
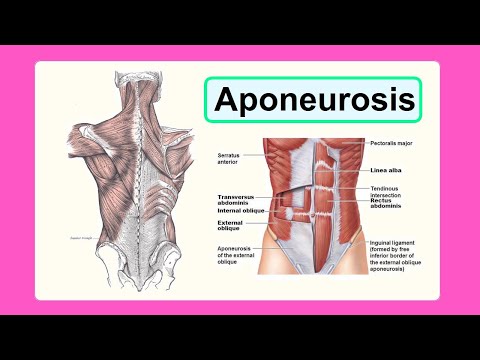
Aponeurosis is an extremely delicate, thin sheath-like structure, which attaches muscles to the bones whereas tendons are tough, rounded cord-like structures which are extensions of the muscle. Normally, tendons allow the attachment of the muscle from its originating bone to the bone on which it ends. An aponeurosis has the property of recoiling and hence, it functions like a spring; whenever the muscle expands or contracts, it bears all the extra pressure and tension. Likewise, a tendon has capacity for a lot of endurance to stretching and they allow the proper contraction of the muscle by providing strength and support. Aponeurosis is a white, transparent sheath, a flat structure like a sheet whereas a tendon is a white, shiny and glazed, rope-like tough structure.
A tendon is extremely important for muscle attachments and is present wherever the muscle has to exert force of contraction across a joint or if the bone of insertion is distant. The tendon is a collagenous tissue which is relatively flexible and thus can be wound across the joint. The aponeurosis of the abdomen called the obliqus externus abdominis is one such muscle which is entirely aponeurotic in structure. A tendon is so flexible and has such tremendous tensile strength that while performing an action, the muscle stretches almost minimally or remains the same, but the tendon stretches and contracts, thus allowing more storage of energy in the muscle. When a muscle contracts or shortens, the tendon which is present pulls the bone where the muscle is inserted, bringing about the desired movement. Tendon is thus, the effective structure that transmits the force of the contraction to the bone. Since a tendon is thick like a cord, it provides immense stability to the articulating joint. Aponeuroses are supplied sparsely with blood vessels.
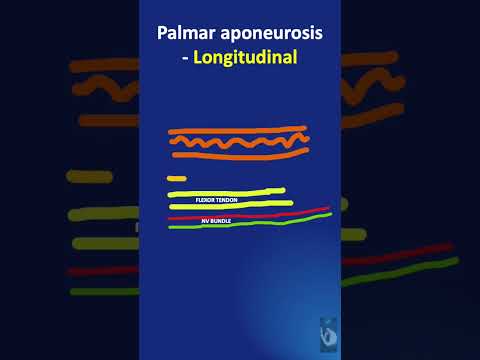
Tendon injuries are much more common than injuries to aponeuroses, especially the Achilles’ tendon, which is the strongest tendon in the human body. It has weight bearing properties too. Tendinitis is an inflammatory injury of the tendon whereas; tendinosis is a non-inflammatory injury to the tendon. Injuries to tendons are commonly seen in sportsmen due to the recurrent weight bearing strain on fixed group of muscles. While walking, the plantar aponeurosis mainly functions to raise the heel and bring the toe down, enabling stability of the arches of the foot.
Also, the aponeurosis acts as a shock absorber and thereby allows the bones of the foot to bear all the weight of the body without getting shorn. Certain examples of aponeurosis are the anterior abdominal aponeurosis, posterior lumbar aponeurosis, etc.
#aponeurosis #tendon #aponeurosisvstendon #aponeurosisandtendon #differencebetweenaponeurosisandtendon #whatisaponeurosis #whatistendon #aponeurosisanatomy #tendonanatomy
Комментарии
 0:04:25
0:04:25
 0:01:27
0:01:27
 0:04:09
0:04:09
 0:00:47
0:00:47
 0:02:44
0:02:44
 0:00:21
0:00:21
 0:07:29
0:07:29
 0:09:12
0:09:12
 0:10:19
0:10:19
 0:05:01
0:05:01
 0:14:04
0:14:04
 0:01:32
0:01:32
 0:02:48
0:02:48
 0:06:20
0:06:20
 0:00:55
0:00:55
 0:01:29
0:01:29
 0:00:54
0:00:54
 0:02:07
0:02:07
 0:00:10
0:00:10
 0:08:09
0:08:09
 0:00:59
0:00:59
 0:00:59
0:00:59
 0:11:21
0:11:21
 0:01:38
0:01:38