filmov
tv
Discrete Math II - 11.4.2 Spanning Trees - Breadth First Search

Показать описание
We continue our study of trees by examining spanning trees. Spanning trees are subgraphs of a graph that contain all vertices of the original graph. The resulting subgraph is a tree, so the graph is connected and contains no cycles.
In our second methodology, we will use a breadth-first search. That means that we will begin creating our spanning tree by choosing a specific vertex starting point, then connect ALL vertices adjacent to our starting vertex. Then, in order, we will connect each vertex adjacent to all those found in our first level, and so on, until all unvisited vertices have been visited.
Video Chapters:
Intro 0:00
Breadth-First Search 0:06
Practice With Me 2:12
Practice On Your Own 3:25
Up Next 4:41
In our second methodology, we will use a breadth-first search. That means that we will begin creating our spanning tree by choosing a specific vertex starting point, then connect ALL vertices adjacent to our starting vertex. Then, in order, we will connect each vertex adjacent to all those found in our first level, and so on, until all unvisited vertices have been visited.
Video Chapters:
Intro 0:00
Breadth-First Search 0:06
Practice With Me 2:12
Practice On Your Own 3:25
Up Next 4:41
Composition of relations | MISTAKE - explained RoS instead of SoR and vice versa | otherwise correct
Solving congruences, 3 introductory examples
Composition of Relation with Itself
Discrete Math - 1.4.2 Quantifiers
Discrete Math II - 8.5.1 The Principle of Inclusion-Exclusion
Discrete Math II - 6.5.1 Combinations with Repetition
Hasse Diagram with Example (Discrete Mathematics) Order relation & Lattice
Discrete Math II - 8.6.4 Apply the Principle of Inclusion Exclusion: Derangements
1st sem bca sep bnu |2nd sem bca nep bnu| unit 5| matrix |
Representation of Relations
Discrete Math II - 8.6.2 Apply the Principle of Inclusion-Exclusion: Linear Equation Model
Discrete Math II - 11.5.1 Minimum Spanning Trees: Prim's Algorithm
Relations||How to check relation is reflexive, symmetric or transitive?
Truth Table Tutorial - Discrete Mathematics Logic
functions explained in 17 seconds! (Algebra 1)
This chapter closes now, for the next one to begin. 🥂✨.#iitbombay #convocation
Types of Relations (Part 1)
Nested Quantifiers (Solved Example 1)
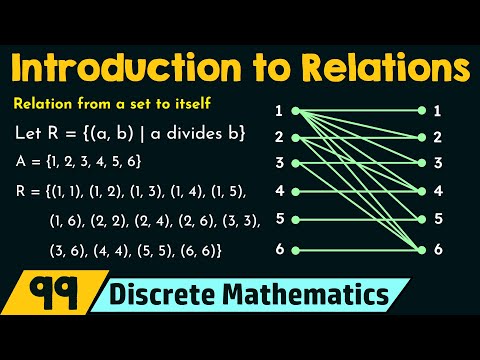
Introduction to Relations
Proof by Mathematical Induction - How to do a Mathematical Induction Proof ( Example 1 )
Venn Diagrams (A intersection B, A' union B')
MIT Entrance Exam Problem from 1869 #Shorts #math #maths #mathematics #problem #MIT
The Hardest Math Test
Equivalence Relation
Комментарии
 0:03:20
0:03:20
 0:03:51
0:03:51
 0:06:59
0:06:59
 0:15:47
0:15:47
 0:20:49
0:20:49
 0:19:06
0:19:06
 0:02:42
0:02:42
 0:09:02
0:09:02
 1:17:55
1:17:55
 0:05:51
0:05:51
 0:19:22
0:19:22
 0:13:03
0:13:03
 0:00:51
0:00:51
 0:07:51
0:07:51
 0:00:21
0:00:21
 0:00:16
0:00:16
 0:06:39
0:06:39
 0:07:34
0:07:34
 0:07:39
0:07:39
 0:07:32
0:07:32
 0:00:37
0:00:37
 0:00:48
0:00:48
 0:00:28
0:00:28
 0:06:29
0:06:29