filmov
tv
ATP: Adenosine triphosphate | Energy and enzymes | Biology | Khan Academy

Показать описание
Learn more about ATP: how it stores energy, and how that energy is released when it's converted to ATP and phosphate.
Biology on Khan Academy: Life is beautiful! From atoms to cells, from genes to proteins, from populations to ecosystems, biology is the study of the fascinating and intricate systems that make life possible. Dive in to learn more about the many branches of biology and why they are exciting and important. Covers topics seen in a high school or first-year college biology course.
About Khan Academy: Khan Academy offers practice exercises, instructional videos, and a personalized learning dashboard that empower learners to study at their own pace in and outside of the classroom. We tackle math, science, computer programming, history, art history, economics, and more. Our math missions guide learners from kindergarten to calculus using state-of-the-art, adaptive technology that identifies strengths and learning gaps. We've also partnered with institutions like NASA, The Museum of Modern Art, The California Academy of Sciences, and MIT to offer specialized content.
For free. For everyone. Forever. #YouCanLearnAnything
Biology on Khan Academy: Life is beautiful! From atoms to cells, from genes to proteins, from populations to ecosystems, biology is the study of the fascinating and intricate systems that make life possible. Dive in to learn more about the many branches of biology and why they are exciting and important. Covers topics seen in a high school or first-year college biology course.
About Khan Academy: Khan Academy offers practice exercises, instructional videos, and a personalized learning dashboard that empower learners to study at their own pace in and outside of the classroom. We tackle math, science, computer programming, history, art history, economics, and more. Our math missions guide learners from kindergarten to calculus using state-of-the-art, adaptive technology that identifies strengths and learning gaps. We've also partnered with institutions like NASA, The Museum of Modern Art, The California Academy of Sciences, and MIT to offer specialized content.
For free. For everyone. Forever. #YouCanLearnAnything
Комментарии
 0:07:02
0:07:02
 0:05:52
0:05:52
 0:09:46
0:09:46
 0:00:50
0:00:50
 0:01:54
0:01:54
 0:01:56
0:01:56
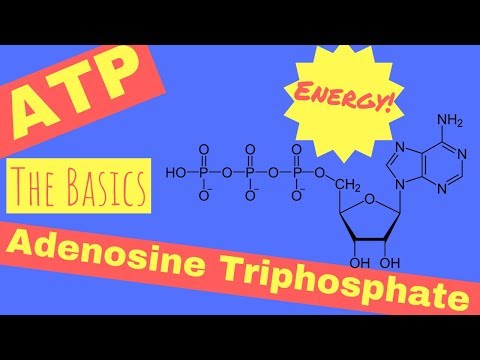 0:02:05
0:02:05
 0:06:19
0:06:19
 0:00:43
0:00:43
 0:03:27
0:03:27
 0:04:48
0:04:48
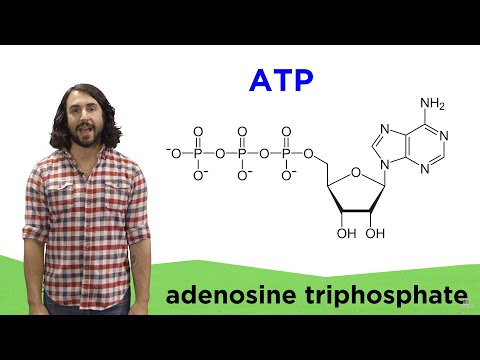 0:04:22
0:04:22
 0:13:26
0:13:26
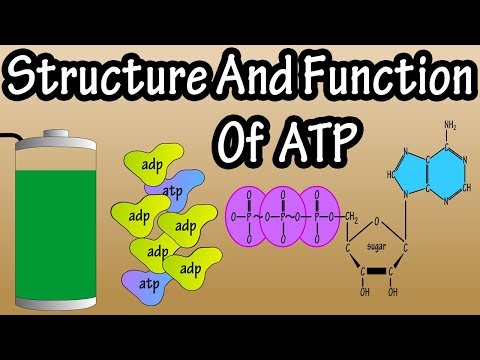 0:01:41
0:01:41
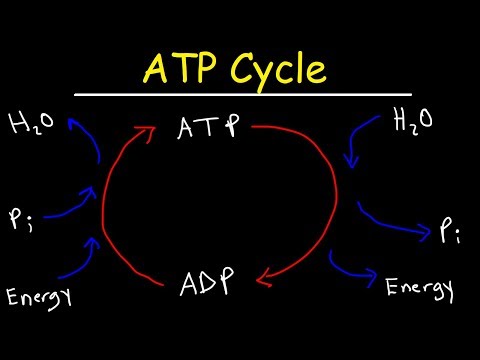 0:05:12
0:05:12
 0:06:23
0:06:23
 0:02:57
0:02:57
 0:05:08
0:05:08
 0:02:05
0:02:05
 0:10:16
0:10:16
 0:13:35
0:13:35
 0:03:15
0:03:15
 0:04:36
0:04:36
 0:04:06
0:04:06