filmov
tv
Resistivity and Resistance Formula, Conductivity, Temperature Coefficient, Physics Problems
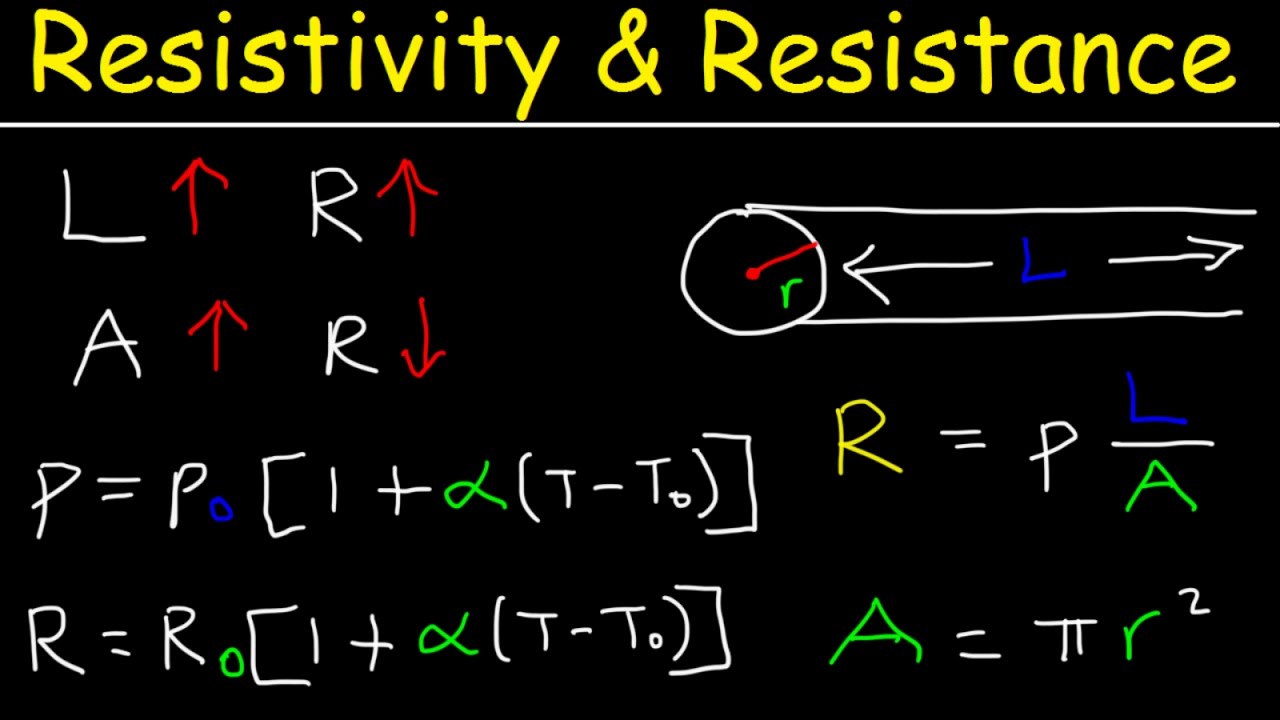
Показать описание
This physics video tutorial explains the concept of resistivity and resistance of electrical conductors like copper and silver as well as semiconductors such as silicon, germanium, and carbon graphite. It provides the formula to calculate the resistance of a metal or wire using resistivity. It discusses the inverse relationship between resistivity and conductivity as well the direct relationship between resistance and temperature. Electrical conductors such as metals have a positive temperature coefficient of resistivity which means that as the temperature of a metal increases, the resistivity will increase and the conductivity will decrease. For metalloids or semiconductors, the opposite is true. These elements have a negative temperature coefficient which means that the resistance will decrease as the temperature increases which correlates to an increase in conductivity. The resistivity depends on the length of the wire as well as the cross sectional area. Long wires have more resistance and short wires conduct electricity better. Thick wires have less resistance than thin wires. This video shows you how to calculate the temperature by simply measuring the current in a metal using a known voltage which has practical applications in digital thermometers.
Electric Current In Circuits:
The Electric Battery:
Ohm's Law Problems:
Resistor Color Code:
______________________________
Internal Resistance of a Battery:
Electromotive Force of a Battery:
Drift Velocity and Current Density:
Potential Difference Between Two Points:
Alternating Current Vs Direct Current:
______________________________
Schematic Diagrams & Symbols:
Open, Closed, and Short Circuits:
Resistors In Series:
Resistors In Parallel:
Physics PDF Worksheets:
Electric Current In Circuits:
The Electric Battery:
Ohm's Law Problems:
Resistor Color Code:
______________________________
Internal Resistance of a Battery:
Electromotive Force of a Battery:
Drift Velocity and Current Density:
Potential Difference Between Two Points:
Alternating Current Vs Direct Current:
______________________________
Schematic Diagrams & Symbols:
Open, Closed, and Short Circuits:
Resistors In Series:
Resistors In Parallel:
Physics PDF Worksheets:
Комментарии
 0:21:35
0:21:35
 0:02:54
0:02:54
 0:12:02
0:12:02
 0:11:08
0:11:08
 0:09:30
0:09:30
 0:04:38
0:04:38
 0:06:59
0:06:59
 0:07:35
0:07:35
 0:11:08
0:11:08
 0:28:32
0:28:32
 0:03:01
0:03:01
 0:03:50
0:03:50
 0:09:53
0:09:53
 0:11:25
0:11:25
 0:05:19
0:05:19
 0:01:51
0:01:51
 0:43:29
0:43:29
 0:00:15
0:00:15
 0:14:00
0:14:00
 0:05:34
0:05:34
 0:25:04
0:25:04
 0:00:56
0:00:56
 0:00:58
0:00:58
 0:00:17
0:00:17