filmov
tv
Show f(z)={x³(1+i)-y³(1-i)}/(x² + y²) ,f(0) = 0 continuous & C-R eq are satisfy yet f'(0) not exist.
Показать описание
Complex Analysis Theorem from Analytic function
Statement/Theorem /Prove that :-
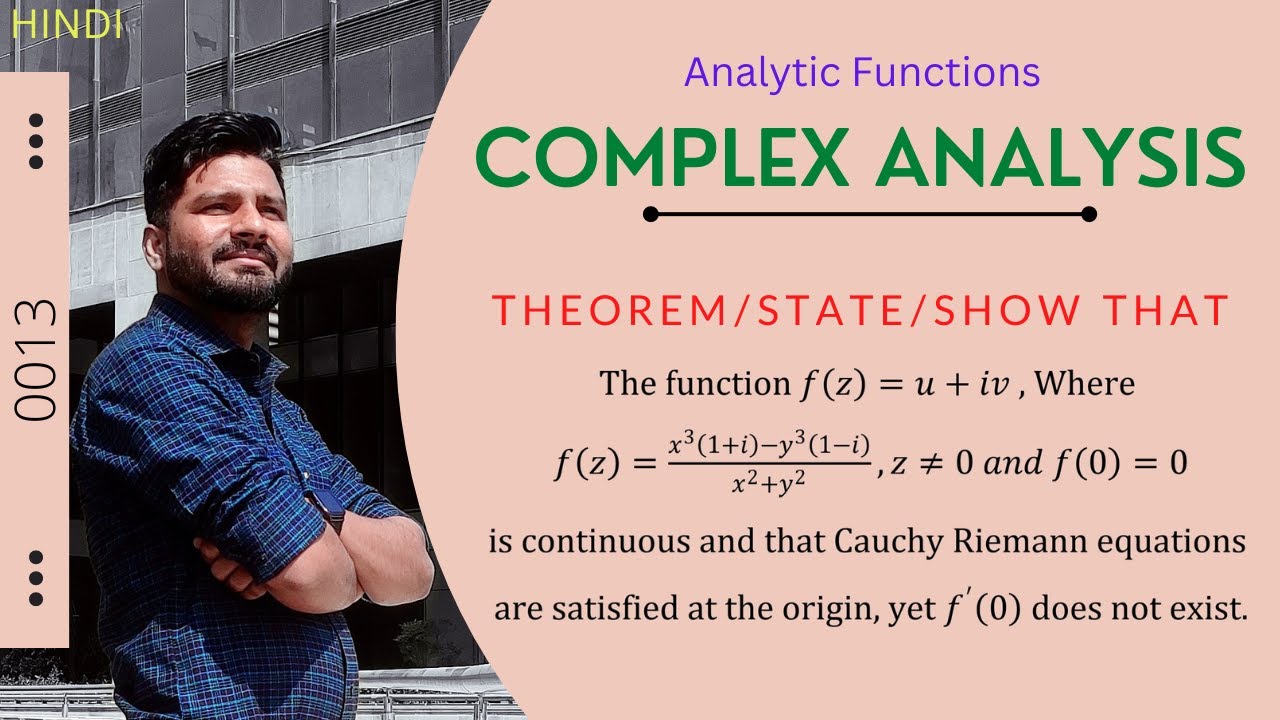
Show that the function f(z) = u+iv, where
f(z) = {x³(1+i)-y³(1-i)}/(x² + y²) , z ≠ 0 and f(0) = 0
is continuous and that Cauchy-Riemann equations are satisfited at the origin, yet f'(0) does not exist.
Solution/ Proof:-
We have
f(z) = {x³(1+i)-y³(1-i)}/(x² + y²)
⇒u+iv = {(x³-y³)+i(x³+y³)}/(x² + y²)
⇒u= (x³-y³)/(x² + y²) and v=(x³+y³)/(x² + y²)
By definition of Continuity
lim z→z₀ f(z) = lim z→z₀ {x³(1+i)-y³(1-i)}/(x² + y²)
lim z→z₀ f(z) = lim ₓ→ₓ₀ , ᵧ→ᵧ₀ {x³(1+i)-y³(1-i)}/(x² + y²)
lim z→z₀ f(z) = {x₀³(1+i)-y₀³(1-i)}/(x₀² + y₀²)
lim z→z₀ f(z) = f(z₀)
Hence f(z) is continuous.
Now at origin (0,0)
(∂u/∂x)= lim ₓ→₀ {u(x,0)-u(0,0)}/x
= lim ₓ→₀ (x³/x²)/x
= lim ₓ→₀ x³/x³
= 1
(∂u/∂y)= lim ᵧ→₀ {u(0,y)-u(0,0)}/y
= lim ᵧ→₀ (-y³/y²)/y
= lim ᵧ→₀ (-y³/y³)
= -1
(∂v/∂x)= lim ₓ→₀ {v(x,0)-v(0,0)}/x
= lim ₓ→₀ (x³/x²)/x
= lim ₓ→₀ x³/x³
= 1
(∂v/∂y)= lim ᵧ→₀ {v(0,y)-v(0,0)}/y
= lim ᵧ→₀ (y³/y²)/y
= lim ᵧ→₀ y³/y³
= 1
Here
(∂v/∂x)=(∂v/∂y) and (∂v/∂x)=-(∂u/∂y)
∴ u and v satisfy Cauchy-Riemann equations at origin.
Now for existence of differentiability
f'(0)=lim z→o {f(z)-f(0)}/(z-0)
f'(0)=lim z→o {(x³-y³)+i(x³+y³)}/{(x² + y²)(x+iy)}
Along real axis
z=x , y=0 ⇒z→0 ∴ x→0
f'(0)=lim ₓ→₀ {(x³-0)+i(x³+0)}/x(x² +0)
=lim ₓ→₀ (x³+ix³)/x³
=(1+i)
Along imaginary axis
z=iy , x=0 ⇒z→0 ∴ y→0
f'(0)=lim ᵧ→₀ {(0-y³)+i(0+y³)}/(iy)(0 + y²)
=lim ₓ→₀ (-y³+iy³)/iy³
=(-1+i)/i
=(1+i)
Along a line curve y=x
f'(0)= lim z→o {(x³-x³)+i(x³+x³)}/{(x² + x²)(x+ix)}
f'(0)= lim z→o (0+i2x³)/{2x³(1+i)}
f'(0)= lim z→o (i2x³)/{2x³(1+i)}
f'(0)= i/(1+i)
f'(0)= (i+1)/2
This shows that f'(0) has different values Along difference curve
∴ f'(z) is not unique , Hence f'(0) does not exist.
Hence Proved...!!!
.
.
.
.
.
.
Kindly join us for CSIR-UGC National Eligibility Test (NET) for Junior Research Fellowship and Lecturer-ship COMMON SYLLABUS FOR PART 'B' AND 'C' MATHEMATICAL SCIENCE
.
.
.
.
.
All BSc, B.Tech, MSc, MA Mathematics students join with us A great platform to get knowledge in Mathematics and science... Stay tuned....for detailed videos on whole SYLLABUS with topic wise...
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
#complexanalysis #csirnet #analyticfunction
.
.
Videos links 🔥🔥🔥
Play List ( Complex Analysis)
Statement/Theorem /Prove that :-
Show that the function f(z) = u+iv, where
f(z) = {x³(1+i)-y³(1-i)}/(x² + y²) , z ≠ 0 and f(0) = 0
is continuous and that Cauchy-Riemann equations are satisfited at the origin, yet f'(0) does not exist.
Solution/ Proof:-
We have
f(z) = {x³(1+i)-y³(1-i)}/(x² + y²)
⇒u+iv = {(x³-y³)+i(x³+y³)}/(x² + y²)
⇒u= (x³-y³)/(x² + y²) and v=(x³+y³)/(x² + y²)
By definition of Continuity
lim z→z₀ f(z) = lim z→z₀ {x³(1+i)-y³(1-i)}/(x² + y²)
lim z→z₀ f(z) = lim ₓ→ₓ₀ , ᵧ→ᵧ₀ {x³(1+i)-y³(1-i)}/(x² + y²)
lim z→z₀ f(z) = {x₀³(1+i)-y₀³(1-i)}/(x₀² + y₀²)
lim z→z₀ f(z) = f(z₀)
Hence f(z) is continuous.
Now at origin (0,0)
(∂u/∂x)= lim ₓ→₀ {u(x,0)-u(0,0)}/x
= lim ₓ→₀ (x³/x²)/x
= lim ₓ→₀ x³/x³
= 1
(∂u/∂y)= lim ᵧ→₀ {u(0,y)-u(0,0)}/y
= lim ᵧ→₀ (-y³/y²)/y
= lim ᵧ→₀ (-y³/y³)
= -1
(∂v/∂x)= lim ₓ→₀ {v(x,0)-v(0,0)}/x
= lim ₓ→₀ (x³/x²)/x
= lim ₓ→₀ x³/x³
= 1
(∂v/∂y)= lim ᵧ→₀ {v(0,y)-v(0,0)}/y
= lim ᵧ→₀ (y³/y²)/y
= lim ᵧ→₀ y³/y³
= 1
Here
(∂v/∂x)=(∂v/∂y) and (∂v/∂x)=-(∂u/∂y)
∴ u and v satisfy Cauchy-Riemann equations at origin.
Now for existence of differentiability
f'(0)=lim z→o {f(z)-f(0)}/(z-0)
f'(0)=lim z→o {(x³-y³)+i(x³+y³)}/{(x² + y²)(x+iy)}
Along real axis
z=x , y=0 ⇒z→0 ∴ x→0
f'(0)=lim ₓ→₀ {(x³-0)+i(x³+0)}/x(x² +0)
=lim ₓ→₀ (x³+ix³)/x³
=(1+i)
Along imaginary axis
z=iy , x=0 ⇒z→0 ∴ y→0
f'(0)=lim ᵧ→₀ {(0-y³)+i(0+y³)}/(iy)(0 + y²)
=lim ₓ→₀ (-y³+iy³)/iy³
=(-1+i)/i
=(1+i)
Along a line curve y=x
f'(0)= lim z→o {(x³-x³)+i(x³+x³)}/{(x² + x²)(x+ix)}
f'(0)= lim z→o (0+i2x³)/{2x³(1+i)}
f'(0)= lim z→o (i2x³)/{2x³(1+i)}
f'(0)= i/(1+i)
f'(0)= (i+1)/2
This shows that f'(0) has different values Along difference curve
∴ f'(z) is not unique , Hence f'(0) does not exist.
Hence Proved...!!!
.
.
.
.
.
.
Kindly join us for CSIR-UGC National Eligibility Test (NET) for Junior Research Fellowship and Lecturer-ship COMMON SYLLABUS FOR PART 'B' AND 'C' MATHEMATICAL SCIENCE
.
.
.
.
.
All BSc, B.Tech, MSc, MA Mathematics students join with us A great platform to get knowledge in Mathematics and science... Stay tuned....for detailed videos on whole SYLLABUS with topic wise...
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
#complexanalysis #csirnet #analyticfunction
.
.
Videos links 🔥🔥🔥
Play List ( Complex Analysis)
Комментарии
 0:14:07
0:14:07
 0:25:32
0:25:32
 0:28:11
0:28:11
 0:27:57
0:27:57
 0:19:31
0:19:31
 0:25:48
0:25:48
 0:37:43
0:37:43
 0:09:01
0:09:01
 0:36:53
0:36:53
 0:00:33
0:00:33
 0:07:57
0:07:57
 0:07:39
0:07:39
 0:05:19
0:05:19
 0:10:30
0:10:30
 0:11:49
0:11:49
 0:19:35
0:19:35
 0:37:36
0:37:36
 0:17:27
0:17:27
 0:06:34
0:06:34
 0:14:07
0:14:07
 0:05:47
0:05:47
 0:15:18
0:15:18
 0:07:52
0:07:52
 0:03:34
0:03:34