filmov
tv
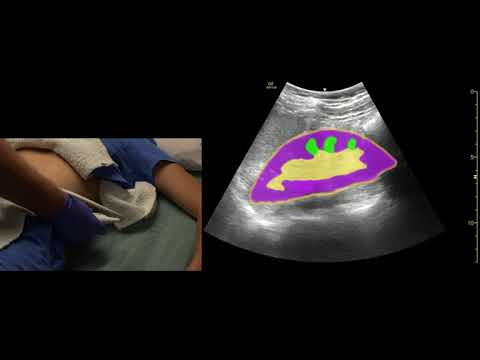
Ultrasound Video showing Bilateral renal parenchymal disease, pleural effusion, and ascites.

Показать описание
This video shows Chronic kidney disease (CKD), bilateral renal parenchymal disease, bilateral pleural effusion, and ascites.
Chronic kidney disease (CKD) is one of the common causes of renal failure. As ultrasonographic findings like echogenicity, longitudinal length, parenchymal, and cortical thickness represent irreversible changes, ultrasonography is a better imaging modality when it comes to ascertaining the progression of the disease.
The renal parenchyma is the functional part of the kidney that includes the renal cortex (the outermost part of the kidney) and the renal medulla. Renal parenchyma disease describes medical conditions that damage these parts of the kidney. These diseases may be congenital, hereditary or acquired.
The bilateral renal parenchymal disease" is a doctor term for scarring changes in the substance of both kidneys. The most common cause of the renal parenchymal disease is high blood pressure or diabetes.
Chronic kidney disease is a slow and progressive loss of kidney function over a period of several years. Eventually, a person will develop permanent kidney failure. As kidney failure advances and the organ's function is severely impaired, dangerous levels of waste and fluid can rapidly build up in the body.
The most common signs and symptoms of chronic kidney disease include:
Anemia.
Blood in the urine.
Dark urine.
Decreased mental alertness.
Decreased urine output.
Edema - swollen feet, hands, and ankles (face if edema is severe)
Fatigue (tiredness)
Hypertension (high blood pressure).
How to know about the function of Kidneys--Two Simple Tests
Urine Test called ACR. ACR stands for “albumin-to-creatinine ratio.” Urine will be tested for albumin. Albumin is a type of protein.
Blood Test to estimate your GFR. Blood will be tested for a waste product called creatinine. Creatinine comes from muscle tissue.
Five Stages of Kidney Disease
Stage 1 with normal or high GFR (GFR more than 90 mL/min)
Stage 2 Mild CKD (GFR = 60-89 mL/min)
Stage 3A Moderate CKD (GFR = 45-59 mL/min)
Stage 3B Moderate CKD (GFR = 30-44 mL/min.
Stage 4 Severe CKD (GFR = 15-29 mL/min)
Stage 5 End Stage CKD (GFR nore than15 mL/min)
6 Tips May Help CKD Patients Reduce Protein Intake
Do not add salt during cooking or at the table.
Avoid salami, sausages, cheese, dairy products, and canned foods.
Replace noodles and bread with low protein alternatives.
Eat 4–5 servings of fruits and vegetables daily.
Meat, fish, or eggs are allowed once a day in a reasonable quantity.
Chronic kidney disease (CKD) is one of the common causes of renal failure. As ultrasonographic findings like echogenicity, longitudinal length, parenchymal, and cortical thickness represent irreversible changes, ultrasonography is a better imaging modality when it comes to ascertaining the progression of the disease.
The renal parenchyma is the functional part of the kidney that includes the renal cortex (the outermost part of the kidney) and the renal medulla. Renal parenchyma disease describes medical conditions that damage these parts of the kidney. These diseases may be congenital, hereditary or acquired.
The bilateral renal parenchymal disease" is a doctor term for scarring changes in the substance of both kidneys. The most common cause of the renal parenchymal disease is high blood pressure or diabetes.
Chronic kidney disease is a slow and progressive loss of kidney function over a period of several years. Eventually, a person will develop permanent kidney failure. As kidney failure advances and the organ's function is severely impaired, dangerous levels of waste and fluid can rapidly build up in the body.
The most common signs and symptoms of chronic kidney disease include:
Anemia.
Blood in the urine.
Dark urine.
Decreased mental alertness.
Decreased urine output.
Edema - swollen feet, hands, and ankles (face if edema is severe)
Fatigue (tiredness)
Hypertension (high blood pressure).
How to know about the function of Kidneys--Two Simple Tests
Urine Test called ACR. ACR stands for “albumin-to-creatinine ratio.” Urine will be tested for albumin. Albumin is a type of protein.
Blood Test to estimate your GFR. Blood will be tested for a waste product called creatinine. Creatinine comes from muscle tissue.
Five Stages of Kidney Disease
Stage 1 with normal or high GFR (GFR more than 90 mL/min)
Stage 2 Mild CKD (GFR = 60-89 mL/min)
Stage 3A Moderate CKD (GFR = 45-59 mL/min)
Stage 3B Moderate CKD (GFR = 30-44 mL/min.
Stage 4 Severe CKD (GFR = 15-29 mL/min)
Stage 5 End Stage CKD (GFR nore than15 mL/min)
6 Tips May Help CKD Patients Reduce Protein Intake
Do not add salt during cooking or at the table.
Avoid salami, sausages, cheese, dairy products, and canned foods.
Replace noodles and bread with low protein alternatives.
Eat 4–5 servings of fruits and vegetables daily.
Meat, fish, or eggs are allowed once a day in a reasonable quantity.
Комментарии
 0:06:02
0:06:02
 0:06:37
0:06:37
 0:04:46
0:04:46
 0:01:13
0:01:13
 0:03:02
0:03:02
 0:03:01
0:03:01
 0:02:55
0:02:55
 0:02:04
0:02:04
 0:01:08
0:01:08
 0:05:36
0:05:36
 0:02:14
0:02:14
 0:05:13
0:05:13
 0:06:02
0:06:02
 0:02:33
0:02:33
 0:04:33
0:04:33
 0:06:37
0:06:37
 0:30:36
0:30:36
 0:08:50
0:08:50
 0:00:47
0:00:47
 0:14:29
0:14:29
 0:00:14
0:00:14
 0:00:18
0:00:18
 0:04:22
0:04:22
 0:02:44
0:02:44