filmov
tv
Basic Types of Radiation: Alpha, Beta & Gamma

Показать описание
Few things cause as much fear as radiation, there are countless horror movies that use radiation as a plot device to turn some mild mannered man into a huge angry monster -- Godzilla, the Hulk, the 50 foot woman, Spider man, even Superman's power's were caused by cosmic radiation. Radiation is like congress and spending cuts, it sounds good on TV but the facts are much different than what you see.
In fact, as a hazardous material technician, I would MUCH rather deal with a radiological release than any other hazardous material for several reasons.
Radiological contamination is much easier to find with instruments than the typical hazardous chemical.
Due to the nature of radiological materials, I can protect myself with a basic knowledge of chemistry. The inverse square law helps me know how close I can get without injury. We can also create shielding to protect me from radiological exposure. As a matter of fact in many of the most common radiological exposures can be dealt with without wearing protective gear other than a dust mask and a paper suit.
Rain and other environmental factors can make a chemical spill much worse. For example moisture can turn chlorine gas into hydrochloric acid or hypochlorous acid; where as a radiological material's properties are not changed by the weather making it a lot more predictable.
However, the purpose of this article is not to be a cheerleader for radiation, but rather to give a simple explanation of the types of radiation most commonly encountered by a citizen.
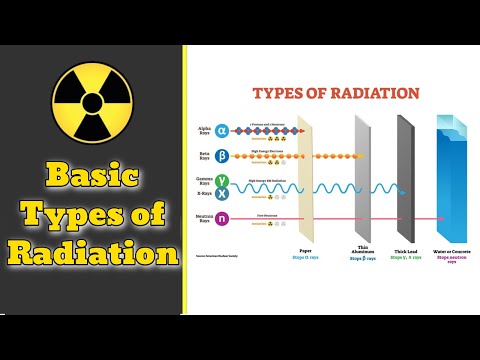
Basically radiation is energy travelling through material. Light, heat, radio and microwaves are all radiating out from their sources. Radiation is all around you, but that radiation is divided into two basic classes, ionizing and non-iodizing radiation.
If the radiation that has enough energy to knock around atoms in a molecule and cause them to vibrate, but not enough to actually kick electrons out of the molecule, is referred to as ""non-ionizing radiation."" Examples of this kind of radiation include visible light and microwaves.
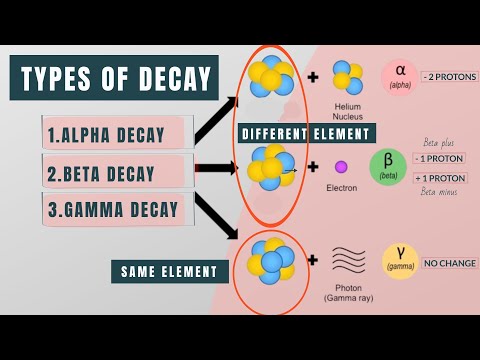
If the radiation is powerful to bounce electrons out from their atoms it is "ionizing" because it creates ions. When we thing our "radiation" this is the type we normally thing about.
In fact, as a hazardous material technician, I would MUCH rather deal with a radiological release than any other hazardous material for several reasons.
Radiological contamination is much easier to find with instruments than the typical hazardous chemical.
Due to the nature of radiological materials, I can protect myself with a basic knowledge of chemistry. The inverse square law helps me know how close I can get without injury. We can also create shielding to protect me from radiological exposure. As a matter of fact in many of the most common radiological exposures can be dealt with without wearing protective gear other than a dust mask and a paper suit.
Rain and other environmental factors can make a chemical spill much worse. For example moisture can turn chlorine gas into hydrochloric acid or hypochlorous acid; where as a radiological material's properties are not changed by the weather making it a lot more predictable.
However, the purpose of this article is not to be a cheerleader for radiation, but rather to give a simple explanation of the types of radiation most commonly encountered by a citizen.
Basically radiation is energy travelling through material. Light, heat, radio and microwaves are all radiating out from their sources. Radiation is all around you, but that radiation is divided into two basic classes, ionizing and non-iodizing radiation.
If the radiation that has enough energy to knock around atoms in a molecule and cause them to vibrate, but not enough to actually kick electrons out of the molecule, is referred to as ""non-ionizing radiation."" Examples of this kind of radiation include visible light and microwaves.
If the radiation is powerful to bounce electrons out from their atoms it is "ionizing" because it creates ions. When we thing our "radiation" this is the type we normally thing about.
Комментарии
 0:03:17
0:03:17
 0:04:37
0:04:37
 0:00:48
0:00:48
 0:10:45
0:10:45
 0:09:23
0:09:23
 0:02:55
0:02:55
 0:04:20
0:04:20
 0:07:37
0:07:37
 0:28:55
0:28:55
 0:18:34
0:18:34
 0:08:08
0:08:08
 0:10:50
0:10:50
 0:02:46
0:02:46
 0:11:15
0:11:15
 0:05:34
0:05:34
 0:00:08
0:00:08
 0:04:54
0:04:54
 0:01:00
0:01:00
 0:09:04
0:09:04
 0:15:57
0:15:57
 0:02:16
0:02:16
 0:05:31
0:05:31
 0:00:15
0:00:15
 0:52:57
0:52:57