filmov
tv
The Unbelievable Science of Twin Babies

Показать описание
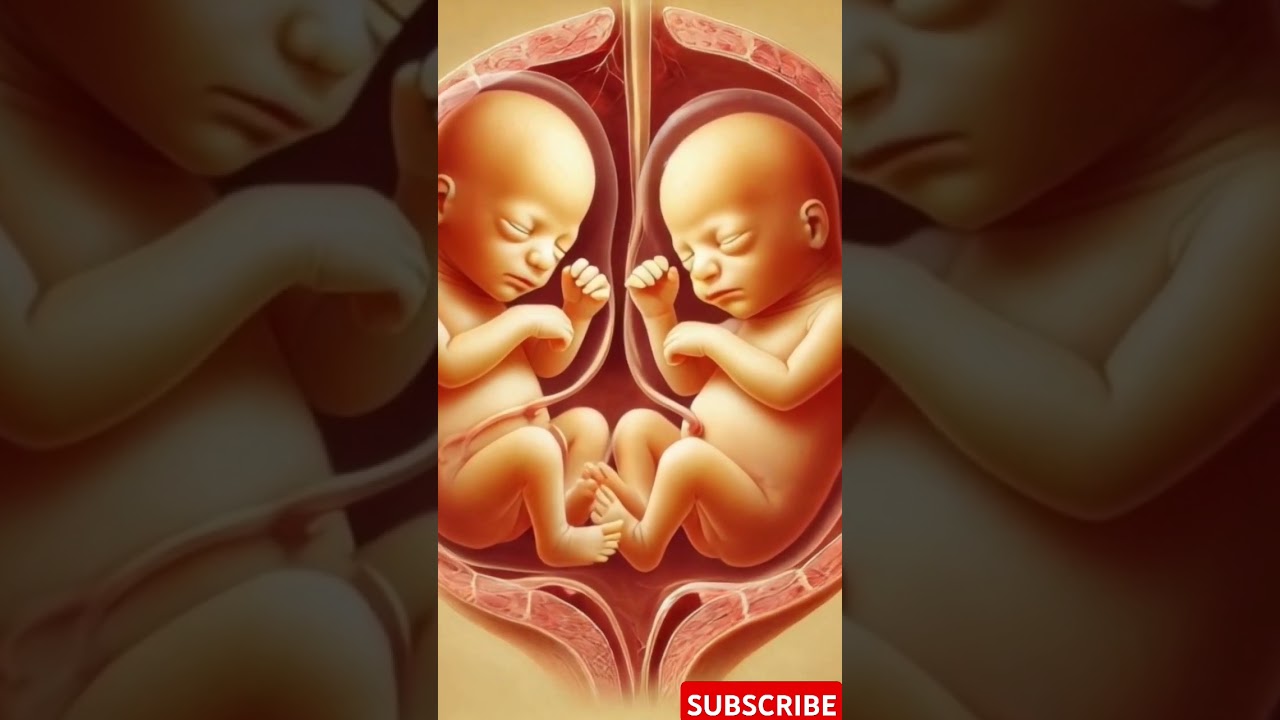
Twins are two offspring born from the same pregnancy. While they are common in many cultures, they occur in only about 1 in every 250 pregnancies naturally. Twins are broadly classified into two types:
1. Identical (monozygotic) twins: These twins form when a single fertilized egg splits into two embryos. They share 100% of their DNA and are always the same sex.
2. Fraternal (dizygotic) twins: These result from two separate eggs fertilized by two different sperm cells. They share about 50% of their DNA, similar to regular siblings, and can be of the same or different sexes.
---
2. The Formation of Twins
Identical Twins
The process begins when a single zygote divides into two embryos during the first 14 days after fertilization. Depending on when this division occurs, identical twins may share:
Separate placentas and amniotic sacs (if the split occurs very early).
A shared placenta but separate sacs (if the split is slightly later).
A single placenta and sac (if the split is very late, which is rare and can lead to complications like conjoined twins).
Fraternal Twins
In contrast, fraternal twins occur when a woman releases two eggs during ovulation, and each is fertilized by a separate sperm. Factors that increase the likelihood of fraternal twins include maternal age, heredity, fertility treatments, and ethnicity.
---
3. The Role of Genetics in Twinning
Identical Twins
The formation of identical twins appears to be a random event, not influenced by genetics or environmental factors. It’s nature’s spontaneous duplication process.
Fraternal Twins
Fraternal twinning, however, has a strong genetic component. Women with a family history of fraternal twins are more likely to release multiple eggs during ovulation. Interestingly, this predisposition does not apply to men, as they do not ovulate.
---
4. Twin Studies and Their Importance
Twin studies have revolutionized our understanding of nature versus nurture. By comparing identical and fraternal twins, scientists can determine how much of a trait is influenced by genetics versus environment.
Key Findings
Intelligence: About 50-80% of intelligence is heritable, with identical twins showing more similarity in IQ than fraternal twins.
Personality: Traits like introversion and extraversion are partly genetic but also shaped by environment.
Health: Studies on twins have uncovered genetic predispositions to diseases like diabetes, cancer, and schizophrenia.
---
5. The Twin Bond
Twins share an unparalleled bond that begins in the womb. Studies using ultrasound have shown that twins interact as early as 14 weeks into pregnancy. This bond continues throughout life, often leading to stronger emotional connections compared to regular siblings.
Twin Telepathy
One of the most intriguing phenomena associated with twins is "twin telepathy." While there is no scientific evidence to support true telepathy, many twins report a heightened intuition or understanding of each other’s thoughts and feelings.
---
6. Challenges Unique to Twins
While being a twin has its perks, it also comes with unique challenges.
Twin-to-Twin Transfusion Syndrome (TTTS)
This condition affects identical twins who share a placenta. Blood flow between the twins can become unbalanced, leading to complications. Modern medical interventions like laser surgery have significantly improved outcomes for TTTS.
Identity and Individuality
Twins, especially identical ones, may struggle to establish their own identities. Being constantly compared can lead to pressure to conform or compete. Parents and educators play a crucial role in fostering individuality.
Health Risks
Twin pregnancies are considered high-risk. Complications like preterm birth, low birth weight, and gestational diabetes are more common. Twins themselves may also face health challenges early in life due to these factors.
---
7. Fascinating Facts About Twins
1. Twin Birth Rates Are Rising: The rate of twin births has increased by over 30% since the 1980s, largely due to fertility treatments and delayed motherhood.
2. Mirror Twins: In rare cases, identical twins can develop as mirror images of each other, with features like birthmarks or dominant hands reversed.
#multiples talk #science kit #twin genetics #fraternal twins #twin #non identical twins in womb #identical twins #twin studies #twin babies #twin science #twins #monozygotic twins #baby development #unbelievable twins #twin phenomena
Комментарии
 0:00:06
0:00:06
 0:03:31
0:03:31
 0:00:38
0:00:38
 0:06:59
0:06:59
 0:06:56
0:06:56
 0:00:08
0:00:08
 0:03:48
0:03:48
 0:03:31
0:03:31
 0:00:47
0:00:47
 0:00:57
0:00:57
 0:00:37
0:00:37
 0:00:54
0:00:54
 0:00:59
0:00:59
 0:08:12
0:08:12
 0:00:51
0:00:51
 0:00:45
0:00:45
 0:00:38
0:00:38
 0:00:08
0:00:08
 0:02:21
0:02:21
 0:14:29
0:14:29
 0:00:24
0:00:24
 0:00:38
0:00:38
 0:00:13
0:00:13
 0:05:40
0:05:40