filmov
tv
Evaluating Limits with Fractions | Limits and Fractions | Calculus
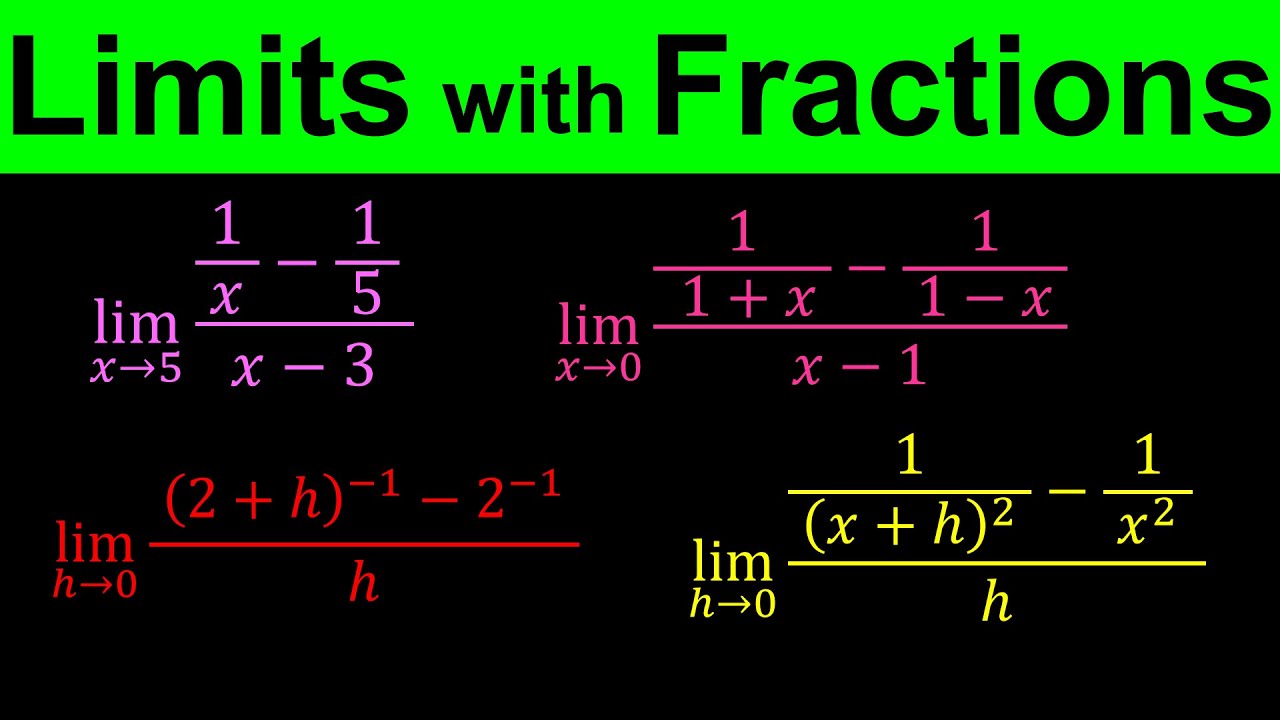
Показать описание
In this calculus video I am gonna show you how to find the limits involving rational expressions. To find these type of limits simply multiply top and botton by the common denominator. We will learn this by doing lots of examples.
In mathematics, the limit of a function is a fundamental concept in calculus and analysis concerning the behavior of that function near a particular input.
Formal definitions, first devised in the early 19th century, are given below. Informally, a function f assigns an output f(x) to every input x. We say that the function has a limit L at an input p, if f(x) gets closer and closer to L as x moves closer and closer to p. More specifically, when f is applied to any input sufficiently close to p, the output value is forced arbitrarily close to L. On the other hand, if some inputs very close to p are taken to outputs that stay a fixed distance apart, then we say the limit does not exist.
The notion of a limit has many applications in modern calculus. In particular, the many definitions of continuity employ the concept of limit: roughly, a function is continuous if all of its limits agree with the values of the function. The concept of limit also appears in the definition of the derivative: in the calculus of one variable, this is the limiting value of the slope of secant lines to the graph of a function.
In mathematics, the limit of a function is a fundamental concept in calculus and analysis concerning the behavior of that function near a particular input.
Formal definitions, first devised in the early 19th century, are given below. Informally, a function f assigns an output f(x) to every input x. We say that the function has a limit L at an input p, if f(x) gets closer and closer to L as x moves closer and closer to p. More specifically, when f is applied to any input sufficiently close to p, the output value is forced arbitrarily close to L. On the other hand, if some inputs very close to p are taken to outputs that stay a fixed distance apart, then we say the limit does not exist.
The notion of a limit has many applications in modern calculus. In particular, the many definitions of continuity employ the concept of limit: roughly, a function is continuous if all of its limits agree with the values of the function. The concept of limit also appears in the definition of the derivative: in the calculus of one variable, this is the limiting value of the slope of secant lines to the graph of a function.
Комментарии
 0:11:42
0:11:42
 0:03:25
0:03:25
 0:19:46
0:19:46
 0:02:47
0:02:47
 0:03:12
0:03:12
 0:10:06
0:10:06
 0:04:25
0:04:25
 0:11:35
0:11:35
 0:02:45
0:02:45
 0:03:40
0:03:40
 0:04:58
0:04:58
 0:01:56
0:01:56
 0:16:51
0:16:51
 0:14:24
0:14:24
 0:02:30
0:02:30
 0:19:48
0:19:48
 0:12:38
0:12:38
 0:04:31
0:04:31
 0:01:40
0:01:40
 0:00:56
0:00:56
 0:01:30
0:01:30
 0:08:00
0:08:00
 0:02:51
0:02:51
 0:06:00
0:06:00