filmov
tv
Posterior Triangle Of The Neck - Everything You Need To Know - Dr. Nabil Ebraheim

Показать описание
Dr. Ebraheim’s educational animated video describes the posterior triangle of the neck.
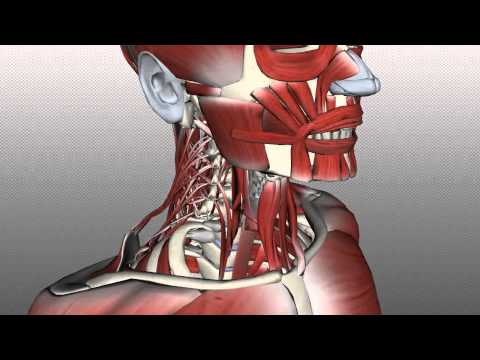
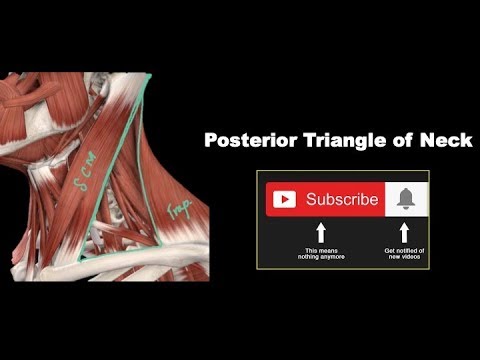
The posterior triangle is located in the lateral cervical region of the neck.
The apex is formed by meeting of the anterior and posterior borders. Union of the sternocleidomastoid and the trapezius muscles at the superior nuchal line of the occipital bone.
The borders of the posterior triangle include:
1-Base: middle one-third of the clavicle.
2-Anterior border: posterior border of the sternocleidomastoid muscle.
3-Posterior border: anterior border of the trapezius.
Roof of the triangle is covered by skin as well as superficial fascia that contains the platysma, the external jugular vein, the cutaneous branches of the cervical plexus and the deep fascia.
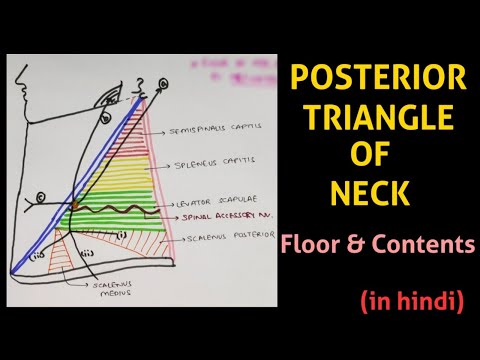
The floor of the triangle is formed by:
1-Splenius muscles
2-Levator scapula muscles
3-Scalenus medius muscle
4-Anterior scalene muscle.
The inferior belly of the omohyoid muscle crosses the triangle about 2.5 cm above the clavicle. The omohyoid muscle divides the space into two triangles: occipital triangle, subclavian or supraclavicular triangle.
Content:
•Nerves: spinal accessory nerve, branches of the cervical plexus, the phrenic nerve and roots, and trunks of the brachial plexus, which lie between the scalenus anterior and medius muscles.
•Arteries and veins: transverse cervical artery, subclavian artery (third part), suprascapular artery, and occipital artery, terminal part of external jugular vein, and subclavian vein.
•Lymph nodes: deep cervical lymph nodes. The spinal accessory nerve is vulnerable to damage during lymph node biopsy. After lymph node biopsy, the patient may have shoulder pain, dysfunction and lateral winging of the scapula that can occur due to spinal accessory nerve injury. Accessory nerve injury typically occurs from blunt or penetrating trauma, surgical dissection of the posterior triangle of the neck such as lymph node biopsy.
Treatment of spinal accessory nerve injury:
•Physical therapy
•Surgical repair of the nerve may be considered up to 1 year
•Muscle transfer for chronic cases such as levator scapulae and rhomboid transfer.
Become a friend on facebook:
Follow me on twitter:
Donate to the University of Toledo Foundation Department of Orthopaedic Surgery Endowed Chair Fund:
The posterior triangle is located in the lateral cervical region of the neck.
The apex is formed by meeting of the anterior and posterior borders. Union of the sternocleidomastoid and the trapezius muscles at the superior nuchal line of the occipital bone.
The borders of the posterior triangle include:
1-Base: middle one-third of the clavicle.
2-Anterior border: posterior border of the sternocleidomastoid muscle.
3-Posterior border: anterior border of the trapezius.
Roof of the triangle is covered by skin as well as superficial fascia that contains the platysma, the external jugular vein, the cutaneous branches of the cervical plexus and the deep fascia.
The floor of the triangle is formed by:
1-Splenius muscles
2-Levator scapula muscles
3-Scalenus medius muscle
4-Anterior scalene muscle.
The inferior belly of the omohyoid muscle crosses the triangle about 2.5 cm above the clavicle. The omohyoid muscle divides the space into two triangles: occipital triangle, subclavian or supraclavicular triangle.
Content:
•Nerves: spinal accessory nerve, branches of the cervical plexus, the phrenic nerve and roots, and trunks of the brachial plexus, which lie between the scalenus anterior and medius muscles.
•Arteries and veins: transverse cervical artery, subclavian artery (third part), suprascapular artery, and occipital artery, terminal part of external jugular vein, and subclavian vein.
•Lymph nodes: deep cervical lymph nodes. The spinal accessory nerve is vulnerable to damage during lymph node biopsy. After lymph node biopsy, the patient may have shoulder pain, dysfunction and lateral winging of the scapula that can occur due to spinal accessory nerve injury. Accessory nerve injury typically occurs from blunt or penetrating trauma, surgical dissection of the posterior triangle of the neck such as lymph node biopsy.
Treatment of spinal accessory nerve injury:
•Physical therapy
•Surgical repair of the nerve may be considered up to 1 year
•Muscle transfer for chronic cases such as levator scapulae and rhomboid transfer.
Become a friend on facebook:
Follow me on twitter:
Donate to the University of Toledo Foundation Department of Orthopaedic Surgery Endowed Chair Fund:
Комментарии
 0:05:04
0:05:04
 0:04:10
0:04:10
 0:18:27
0:18:27
 0:11:09
0:11:09
 0:24:03
0:24:03
 0:15:58
0:15:58
 0:03:28
0:03:28
 0:05:04
0:05:04
 0:17:33
0:17:33
 0:11:00
0:11:00
 0:30:14
0:30:14
 0:21:52
0:21:52
 0:12:46
0:12:46
 0:17:13
0:17:13
 0:00:13
0:00:13
 0:49:49
0:49:49
 0:00:39
0:00:39
 0:00:50
0:00:50
 0:40:52
0:40:52
 0:03:34
0:03:34
 0:13:32
0:13:32
 0:11:40
0:11:40
 0:08:13
0:08:13
 0:04:36
0:04:36