filmov
tv
Classification Of Carbohydrates And Its Structure

Показать описание
This video covers the concepts of classification of carbohydrates and its structure. This video will also provide examples of each type of carbohydrates and their respective structures.
What are Carbohydrates?
Carbohydrates can be defined as a group of organic compounds which occur in starch, sugar, and cellulose.
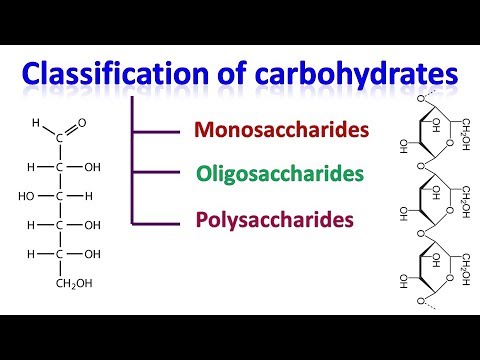
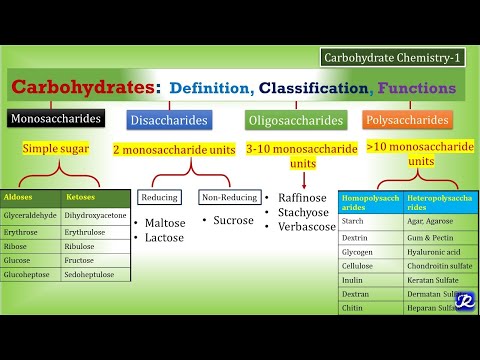
Classification of Carbohydrates:
There are 2 main classifications of carbohydrates which are sugars and non-sugars. But, based on their ability to undergo hydrolysis, carbohydrates can be further classified into three main types as:
1. Monosaccharides: They cannot be hydrolyzed further to give units of polyhydroxy aldehyde or ketone. Examples of Monosaccharide carbohydrates are glucose, fructose, etc.
2. Disaccharides: Disaccharides yield two molecules of either same or different monosaccharide upon hydrolysis. Examples of Disaccharides are Maltose and Lactose.
3. Polysaccharides: The Polysaccharides are those carbohydrates which contain long units of monosaccharides which are joined together by glycosidic linkage. Examples of polysaccharides are fibers, glycogen, etc.
It should be noted that monosaccharides and disaccharides are sugars while polysaccharides are non-sugars. Also, note that there is a fourth classification of carbohydrates called “oligosaccharides” which yields two to ten monosaccharides units on hydrolysis.
Refer to this article to learn more about the carbohydrates, classification of carbohydrates, and the structure of carbohydrates in a detailed way-
What are Carbohydrates?
Carbohydrates can be defined as a group of organic compounds which occur in starch, sugar, and cellulose.
Classification of Carbohydrates:
There are 2 main classifications of carbohydrates which are sugars and non-sugars. But, based on their ability to undergo hydrolysis, carbohydrates can be further classified into three main types as:
1. Monosaccharides: They cannot be hydrolyzed further to give units of polyhydroxy aldehyde or ketone. Examples of Monosaccharide carbohydrates are glucose, fructose, etc.
2. Disaccharides: Disaccharides yield two molecules of either same or different monosaccharide upon hydrolysis. Examples of Disaccharides are Maltose and Lactose.
3. Polysaccharides: The Polysaccharides are those carbohydrates which contain long units of monosaccharides which are joined together by glycosidic linkage. Examples of polysaccharides are fibers, glycogen, etc.
It should be noted that monosaccharides and disaccharides are sugars while polysaccharides are non-sugars. Also, note that there is a fourth classification of carbohydrates called “oligosaccharides” which yields two to ten monosaccharides units on hydrolysis.
Refer to this article to learn more about the carbohydrates, classification of carbohydrates, and the structure of carbohydrates in a detailed way-
 0:02:52
0:02:52
 0:12:30
0:12:30
 0:03:36
0:03:36
 0:11:57
0:11:57
 0:03:29
0:03:29
 0:11:38
0:11:38
 0:21:54
0:21:54
 0:16:15
0:16:15
 0:06:59
0:06:59
 0:08:59
0:08:59
 0:11:34
0:11:34
 0:07:14
0:07:14
 0:08:59
0:08:59
 0:45:53
0:45:53
 0:04:23
0:04:23
 0:12:31
0:12:31
 0:11:12
0:11:12
 0:00:39
0:00:39
 0:12:35
0:12:35
 1:03:43
1:03:43
 0:00:59
0:00:59
 0:06:50
0:06:50
 0:11:23
0:11:23
 0:30:09
0:30:09