filmov
tv
Circuit and Packet Switching (ITS323, L19, Y15)
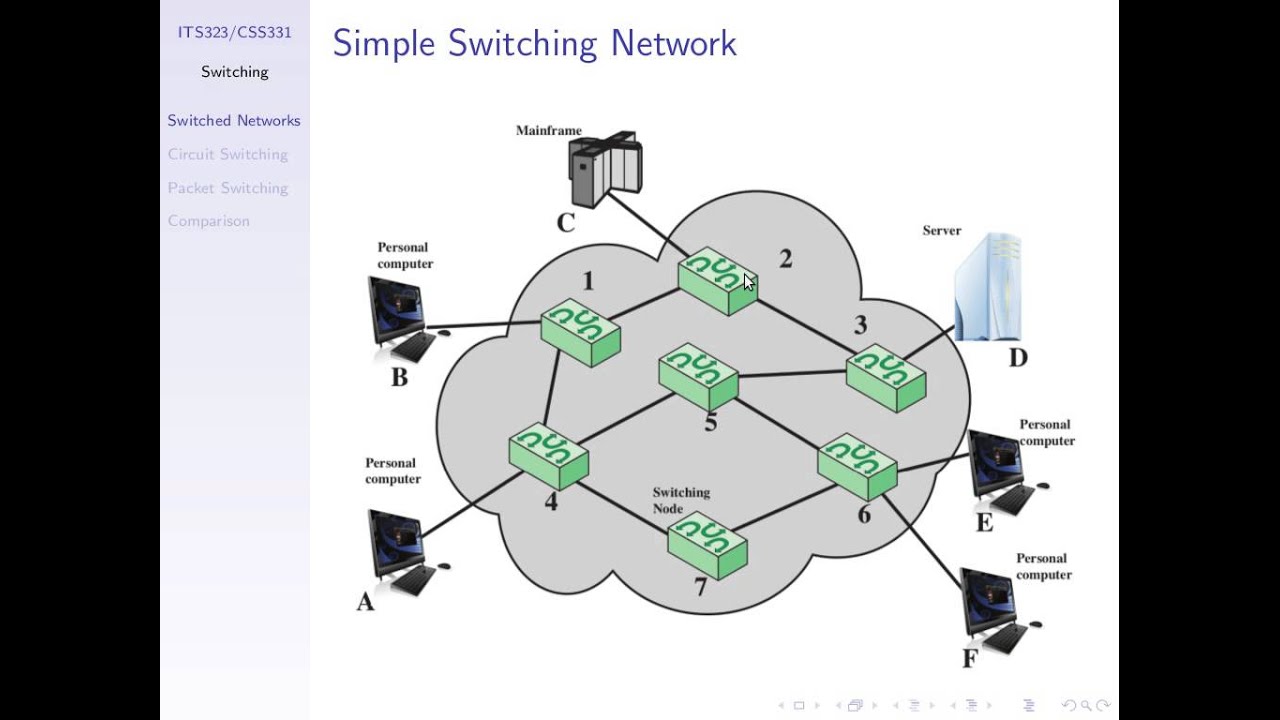
Показать описание
Circuit and Packet Switching (ITS323, L19, Y15)
Circuit and Packet Switching (ITS323, Lecture 22, 2014)
Circuit vs Packet Switching (ITS323, L20, Y15)
ITS323, Lecture 21, CS, 02 Sep 2013 - Circuit and Packet Switching
Performance of Circuit and Packet Switching (ITS323, Lecture 23, 2014)
ITS323, Lecture 22, IT, 04 Sep 2013 - Switching and Routing
Circuit switching v. packet switching.
Circuit switching v. packet switching.
ITS323, Lecture 22, CS, 04 Sep 2013 - Switching and Routing
Packet Switching vs Circuit Switching Solution - Georgia Tech - Network Implementation
Packet switching basics
Packet vs Circuit Switching
Circuit Switching And Packet Switching| AL Computer Science
Circuit Switching and Packet Switching - CompTIA Network+ N10-006 - 1.4
Circuit Switching and Packet Switching
Revision - Networks - Circuit and Packet Switching
IP Subnets and Addressing (ITS323, L25, Y15)
Packet Switching vs Circuit Switching Quiz - Georgia Tech - Network Implementation
Circuit switching & Packet switching
Introduction to Routing (ITS323, L20, Y15)
Packet switching | CN | Computer Networks | Lec-48 | Bhanu Priya
difference between circuit switching and packet switching
Packet and difference between packet switching with circuit switching
Packet Switching & Circuit Switching
Комментарии
 1:18:03
1:18:03
 1:15:21
1:15:21
 0:42:18
0:42:18
 1:23:12
1:23:12
 0:56:11
0:56:11
 1:17:09
1:17:09
 0:04:06
0:04:06
 0:05:53
0:05:53
 1:18:22
1:18:22
 0:00:16
0:00:16
 0:08:17
0:08:17
 0:09:54
0:09:54
 0:08:00
0:08:00
 0:03:21
0:03:21
 0:07:19
0:07:19
 0:01:41
0:01:41
 1:16:26
1:16:26
 0:00:23
0:00:23
 0:02:21
0:02:21
 0:33:49
0:33:49
 0:15:56
0:15:56
 0:01:28
0:01:28
 0:05:39
0:05:39
 0:04:24
0:04:24