filmov
tv
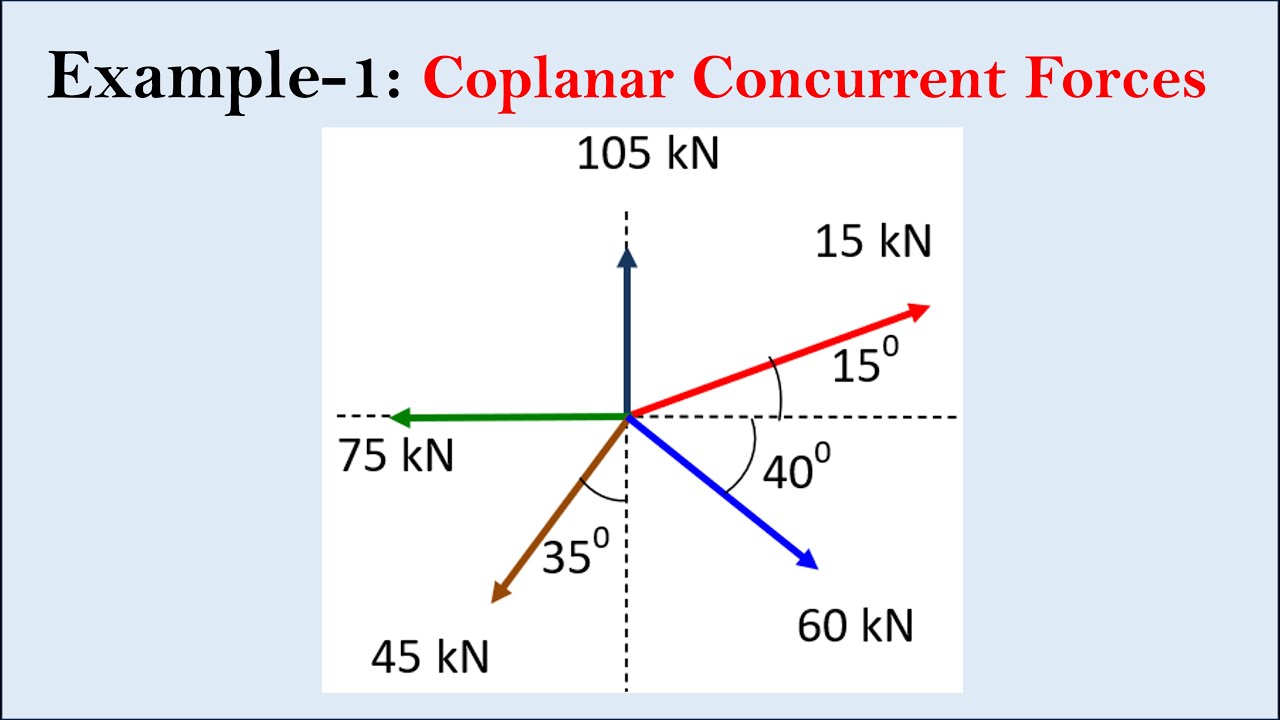
Example -1 : Resultant of Coplanar concurrent forces | Engineering mechanics
Показать описание
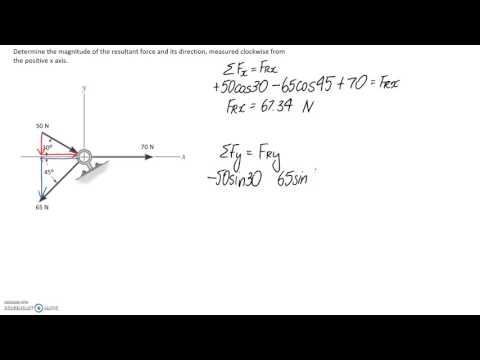
Coplanar concurrent forces refer to a specific type of force system in physics and engineering. In this context:
Coplanar: All the forces act within the same single plane. This means that if you were to draw a flat surface, all the forces would lie on that surface without any forces acting perpendicular to it.
Concurrent: All the forces have a common point of intersection or origin. In other words, all the forces meet at a single point, known as the point of concurrency.
In a coplanar concurrent force system, the forces can either be in equilibrium or not. Here are a few key points to consider:
Equilibrium: If the forces in the system are in equilibrium, it means that the vector sum of all the forces at the point of concurrency equals zero. This implies that the forces are balanced, and there is no net force acting at the point.
Non-Equilibrium: If the forces in the system are not in equilibrium, there is a net force acting at the point of concurrency. This can cause either translational motion (if the net force is not counteracted by other forces) or rotational motion (if there is also a net torque or moment).
Engineers and physicists often analyze coplanar concurrent force systems when designing structures or analyzing the stability of objects to ensure they can withstand various forces without failure. This analysis typically involves using vector mathematics and principles of statics to determine the resultant force, the point of action, and whether equilibrium is maintained.
Coplanar: All the forces act within the same single plane. This means that if you were to draw a flat surface, all the forces would lie on that surface without any forces acting perpendicular to it.
Concurrent: All the forces have a common point of intersection or origin. In other words, all the forces meet at a single point, known as the point of concurrency.
In a coplanar concurrent force system, the forces can either be in equilibrium or not. Here are a few key points to consider:
Equilibrium: If the forces in the system are in equilibrium, it means that the vector sum of all the forces at the point of concurrency equals zero. This implies that the forces are balanced, and there is no net force acting at the point.
Non-Equilibrium: If the forces in the system are not in equilibrium, there is a net force acting at the point of concurrency. This can cause either translational motion (if the net force is not counteracted by other forces) or rotational motion (if there is also a net torque or moment).
Engineers and physicists often analyze coplanar concurrent force systems when designing structures or analyzing the stability of objects to ensure they can withstand various forces without failure. This analysis typically involves using vector mathematics and principles of statics to determine the resultant force, the point of action, and whether equilibrium is maintained.
Комментарии
 0:10:38
0:10:38
 0:06:48
0:06:48
 0:06:38
0:06:38
 0:07:12
0:07:12
 0:00:16
0:00:16
 0:07:50
0:07:50
 0:05:50
0:05:50
 0:11:10
0:11:10
 0:41:05
0:41:05
 0:13:43
0:13:43
 0:13:42
0:13:42
 0:06:07
0:06:07
 0:13:45
0:13:45
 0:04:20
0:04:20
 0:12:01
0:12:01
 0:07:39
0:07:39
 0:07:11
0:07:11
 0:09:52
0:09:52
 0:03:51
0:03:51
 0:04:14
0:04:14
 0:04:20
0:04:20
 0:08:15
0:08:15
 0:04:38
0:04:38
 0:06:30
0:06:30