filmov
tv
Mitosis Cell Division

Показать описание
Mitosis Cell Division. Stages of Mitosis.
For Live Classes, Concept Videos, Quizzes, Mock Tests & Revision Notes please see our Website/App:
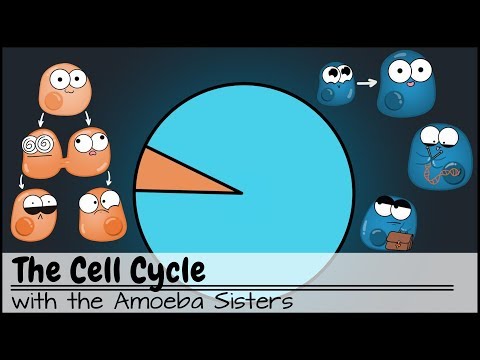
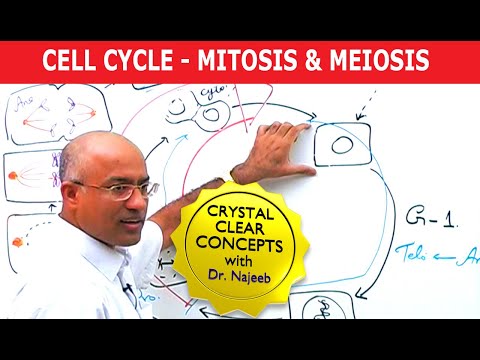
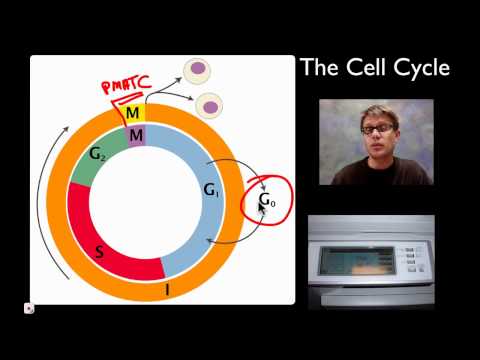
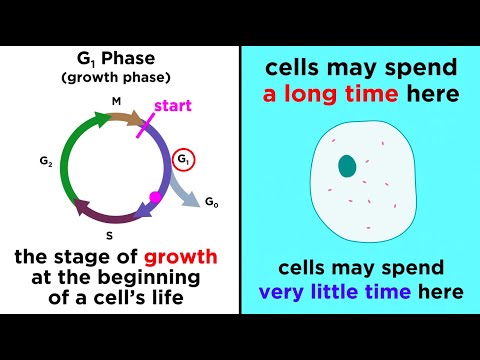
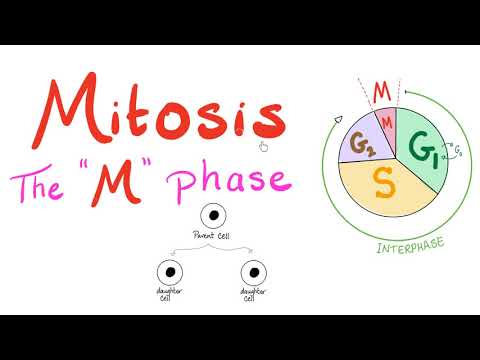
Mitosis is a type of cell division that occurs in eukaryotic cells, where a single cell divides to produce two genetically identical daughter cells. This process is crucial for growth, tissue repair, and asexual reproduction in multicellular organisms.
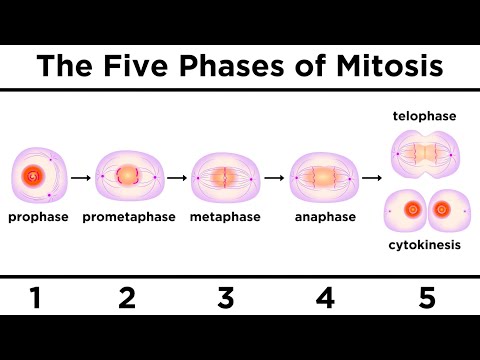
Mitosis is divided into several stages:
1. Prophase: The chromatin (DNA) condenses into visible chromosomes, and the nuclear membrane begins to disintegrate. The spindle fibers start to form.
2. Metaphase: The chromosomes align at the cell's equatorial plate, known as the metaphase plate. The spindle fibers attach to the centromeres of the chromosomes.
3. Anaphase: The sister chromatids (identical halves of a chromosome) are pulled apart by the spindle fibers toward opposite poles of the cell.
4. Telophase: The separated chromatids reach the poles, and a new nuclear membrane forms around each set of chromosomes, which begin to de-condense back into chromatin.
5. Cytokinesis: Although not technically part of mitosis, cytokinesis usually occurs immediately after telophase, where the cytoplasm divides, forming two separate daughter cells.
Each daughter cell contains the same number of chromosomes as the original cell, ensuring genetic consistency across cells in an organism.
At Manocha Academy, learning Science and Math is Easy! The school coursework is explained with simple examples that you experience every day! Yes, Science & Math is all around you! Let's learn every day from everyday life!
For Live Classes, Concept Videos, Quizzes, Mock Tests & Revision Notes please see our Website/App:
Mitosis is a type of cell division that occurs in eukaryotic cells, where a single cell divides to produce two genetically identical daughter cells. This process is crucial for growth, tissue repair, and asexual reproduction in multicellular organisms.
Mitosis is divided into several stages:
1. Prophase: The chromatin (DNA) condenses into visible chromosomes, and the nuclear membrane begins to disintegrate. The spindle fibers start to form.
2. Metaphase: The chromosomes align at the cell's equatorial plate, known as the metaphase plate. The spindle fibers attach to the centromeres of the chromosomes.
3. Anaphase: The sister chromatids (identical halves of a chromosome) are pulled apart by the spindle fibers toward opposite poles of the cell.
4. Telophase: The separated chromatids reach the poles, and a new nuclear membrane forms around each set of chromosomes, which begin to de-condense back into chromatin.
5. Cytokinesis: Although not technically part of mitosis, cytokinesis usually occurs immediately after telophase, where the cytoplasm divides, forming two separate daughter cells.
Each daughter cell contains the same number of chromosomes as the original cell, ensuring genetic consistency across cells in an organism.
At Manocha Academy, learning Science and Math is Easy! The school coursework is explained with simple examples that you experience every day! Yes, Science & Math is all around you! Let's learn every day from everyday life!
Комментарии
 0:09:53
0:09:53
 0:06:29
0:06:29
 0:47:16
0:47:16
 0:08:27
0:08:27
 0:05:01
0:05:01
 0:00:24
0:00:24
 0:09:20
0:09:20
 0:55:31
0:55:31
 0:00:59
0:00:59
 0:13:35
0:13:35
 0:03:04
0:03:04
 0:06:21
0:06:21
 0:12:40
0:12:40
 0:14:59
0:14:59
 0:00:31
0:00:31
 0:00:55
0:00:55
 0:13:34
0:13:34
 0:00:22
0:00:22
 0:12:12
0:12:12
 0:00:16
0:00:16
 0:00:45
0:00:45
 0:08:02
0:08:02
 0:11:11
0:11:11
 0:12:36
0:12:36