filmov
tv
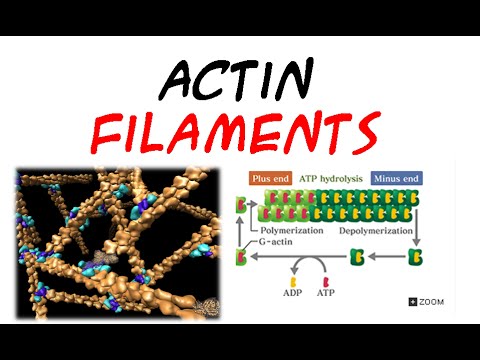
Actin filament assembly
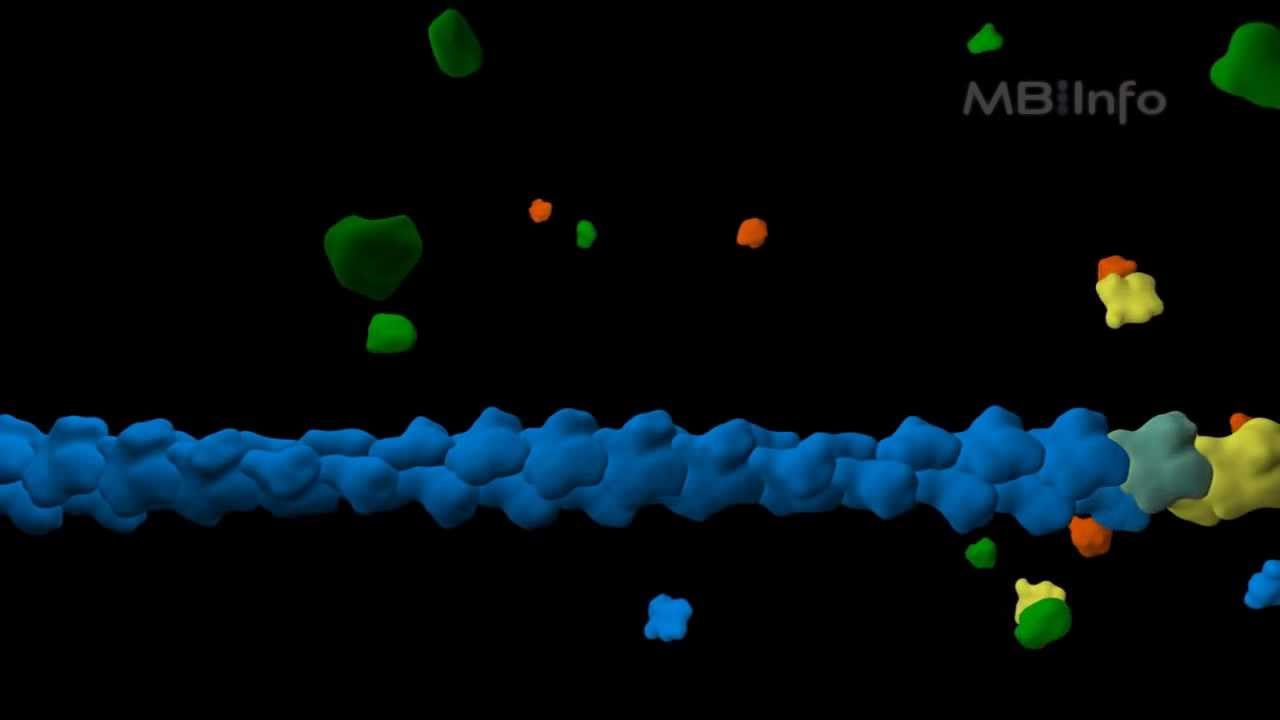
Показать описание
Related links:
Actin filament assembly
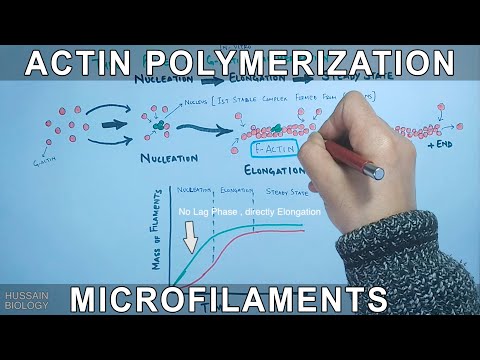
Actin polymerization (Micro filament assembly )
Microfilaments (Structure, Assembly, and Function)
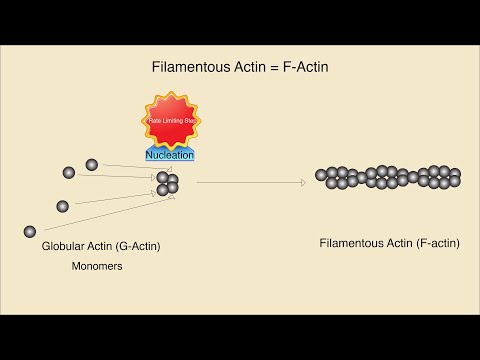
Actin Polymerization | G-Actins
Actin nucleation by Formin
THE CYTOSKELETON - MICROTUBULES, INTERMEDIATE FILAMENTS, MICROFILAMENTS
Actin Polymerisation | Actin Filament Assembly | Actin Treadmilling |
Cytoskel Actin Treadmilling
Cytoskeleton Structure & Function
Formin mediated actin nucleation and filament assembly
Actin Treadmilling | Cell Bio | Video Textbooks - Preview
Actin Filaments and Treadmilling (BIOS 041)
Actin filaments structure and function | Microfilaments | actin filaments assembly and disassembly
Microfilaments
Actin filaments | structure and assembly
Generation of contractile actomyosin bundles depends on mechanosensitive actin filament assembly
Actin Polymerisation
Actin Nucleation by Arp-2/3 Complex
Actin Treadmilling I Actin Assembly
Actin Polymerization and Cell Motility | Cell Bio | Video Textbooks - Preview
Formation of Higher-order Actin Filaments | Cell Bio | Video Textbooks - Preview
Actin filament branching at the leading edge
Collaborative Actin filament nucleation by Spire + Formin
F actin filament structure
Комментарии
 0:02:49
0:02:49
 0:09:02
0:09:02
 0:05:30
0:05:30
 0:03:40
0:03:40
 0:00:17
0:00:17
 0:09:10
0:09:10
 0:06:55
0:06:55
 0:06:10
0:06:10
 0:43:29
0:43:29
 0:02:40
0:02:40
 0:00:23
0:00:23
 0:03:23
0:03:23
 0:22:12
0:22:12
 0:03:43
0:03:43
 0:15:13
0:15:13
 0:01:31
0:01:31
 0:00:18
0:00:18
 0:02:39
0:02:39
 0:03:30
0:03:30
 0:00:23
0:00:23
 0:00:23
0:00:23
 0:03:09
0:03:09
 0:00:25
0:00:25
 0:01:07
0:01:07