filmov
tv
Undamped Mechanical Vibrations & Hooke's Law // Simple Harmonic Motion

Показать описание
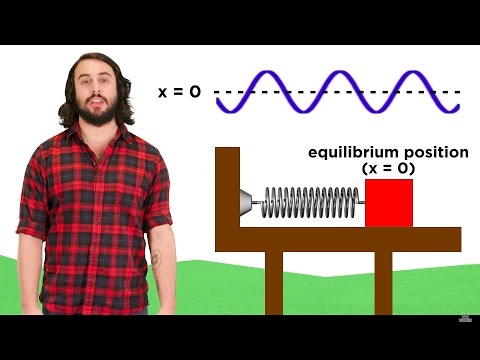
Consider a mass on a spring moving horizontally. The only force on the mass is the spring itself which we can model using Hooke's Law. Then by Newton's Second Law that F=ma, this gives the differential equation mx''+kx=0. This is a second order, constant coefficient, homogeneous differential equation which we can study! We use our techniques from ODEs to solve this system and then do a bit of trigonometry to convert the answer to the standard form. This type of oscillation is often called either undamped mechanical vibrations or more generally simple harmonic motion as this occurs in a myriad of places in physics beyond just this scenario.
0:00 Mass on a Spring
1:18 Newton's 2nd Law & Hooke's Law
2:51 Solving the ODE
4:28 Rewriting into standard Form
OTHER COURSE PLAYLISTS:
OTHER PLAYLISTS:
► Learning Math Series
►Cool Math Series:
BECOME A MEMBER:
MATH BOOKS & MERCH I LOVE:
SOCIALS:
Undamped Mechanical Vibrations & Hooke's Law // Simple Harmonic Motion
Mechanical Vibrations: Underdamped vs Overdamped vs Critically Damped
3.4a Mechanical Vibrations Free Undamped Motion
Simple Harmonic Motion: Hooke's Law
Section 3.7: Mechanical Vibrations (Part 1, Introduction and Undamped Free Vibrations)
Mechanical Vibrations: Ch-2 Free undamped 1 dof vibration systems (2/12) | Mechanical Vibrations
Hooke's Law free, undamped motion
Example 3 1 response to harmonic force undamped system
Mechanical vibration with external force
Mechanical Vibrations
Mechanical Vibrations: Ch-2 Free undamped 1 dof vibration systems (9/12)
Differential Equations - Intro Video - Mechanical Vibrations
Simple Harmonic Motion and Natural Undamped Vibrations
Session 23: Modeling of Undamped Mass Spring system with some examples (Part I).
Undamped Free Vibration of SDOF Systems
DE 5.1.1 - Linear Models: Spring - Mass Systems - Free Undamped Motion
Mechanical Vibrations - Ordinary Differential Equations | Lecture 18
Differential Equations - Mechanical and Electrical Vibrations - Example 2
Video3-21: Spring-mass system; undamped free oscillation. Elementary Differential Equations
Ch 2 - 2.2.1 Free Undamped Oscillation
Vibration free undamped motion with rotating rod and spring
Hooke's Law free, damped motion
Lecture 6: Equation of motion of spring mass system: Mechanical vibrations
Mechanical Vibrations 31 - Forced Vibrations of SDOF Systems 3 (Harmonic Excitations)
Комментарии
 0:08:10
0:08:10
 0:11:16
0:11:16
 0:18:41
0:18:41
 0:04:49
0:04:49
 0:31:41
0:31:41
 0:12:42
0:12:42
 0:41:59
0:41:59
 0:04:44
0:04:44
 0:28:46
0:28:46
 0:58:17
0:58:17
 0:27:24
0:27:24
 0:06:46
0:06:46
 0:18:13
0:18:13
 0:18:42
0:18:42
 0:14:32
0:14:32
 1:04:46
1:04:46
 0:52:16
0:52:16
 0:04:37
0:04:37
 0:21:25
0:21:25
 0:04:26
0:04:26
 0:16:33
0:16:33
 0:23:43
0:23:43
 0:50:45
0:50:45
 0:16:48
0:16:48