filmov
tv
Azure monitoring and alerting Create view and manage Alerts Using Azure Monitor Metrics LOG Alerts

Показать описание
Azure monitoring and alerting
Create, view, and manage Alerts Using Azure Monitor - Metrics Alerts and LOG Alerts
Azure monitoring and alerting Create view and manage Alerts Using Azure Monitor Metrics LOG Alerts
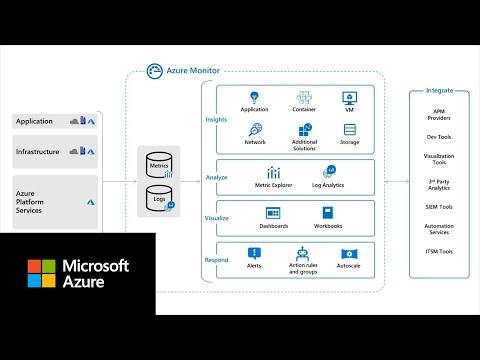
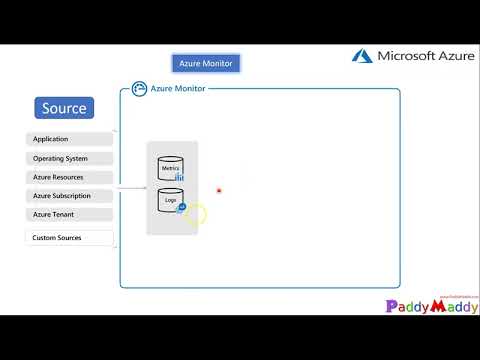
Metric alerts in Azure Monitor provide a way to get notified when one of your metrics crosses a threshold. Metric alerts work on a range of multi-dimensional platform metrics, custom metrics, Application Insights standard and custom metrics. In this article, we will describe how to create, view, and manage metric alert rules through Azure portal and Azure CLI.
What are alerts in Microsoft Azure?
Alerts proactively notify you when issues are found with your infrastructure or application using your monitoring data in Azure Monitor. They allow you to identify and address issues before the users of your system notice them.
How do metric alerts work?
You can define a metric alert rule by specifying a target resource to be monitored, metric name, condition type (static or dynamic), and the condition (an operator and a threshold/sensitivity) and an action group to be triggered when the alert rule fires. Condition types affect the way thresholds are determined
Metric alerts in Azure Monitor work on top of multi-dimensional metrics. These metrics could be platform metrics, custom metrics, popular logs from Azure Monitor converted to metrics and Application Insights metrics. Metric alerts evaluate at regular intervals to check if conditions on one or more metric time-series are true and notify you when the evaluations are met. Metric alerts are stateful, that is, they only send out notifications when the state changes.
The following are key attributes of an alert rule:
Target Resource - Defines the scope and signals available for alerting. A target can be any Azure resource. Example targets:
Virtual machines.
Storage accounts.
Log Analytics workspace.
Application Insights.
For certain resources (like virtual machines), you can specify multiple resources as the target of the alert rule.
Signal - Emitted by the target resource. Signals can be of the following types: metric, activity log, Application Insights, and log.
Criteria - A combination of signal and logic applied on a target resource. Examples:
Percentage CPU 70%
Server Response Time 4 ms
Result count of a log query 100
Alert Name - A specific name for the alert rule configured by the user.
Alert Description - A description for the alert rule configured by the user.
Severity - The severity of the alert after the criteria specified in the alert rule is met. Severity can range from 0 to 4.
Sev 0 = Critical
Sev 1 = Error
Sev 2 = Warning
Sev 3 = Informational
Sev 4 = Verbose
Action - A specific action taken when the alert is fired
You can alert on metrics and logs, as described in monitoring data sources. Signals include but aren't limited to:
Metric values
Log search queries
Activity log events
Health of the underlying Azure platform
Tests for website availability
Manage alerts
You can set the state of an alert to specify where it is in the resolution process. When the criteria specified in the alert rule is met, an alert is created or fired, and it has a status of New. You can change the status when you acknowledge an alert and when you close it. All state changes are stored in the history of the alert.
▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬
Other Full Courses by PaddyMaddy
AZ-900 Full course 10+ Hours - Exam AZ-900: Microsoft Azure Fundamentals
AZ-500 Full Course - 17 Hours Exam AZ-500: Microsoft Azure Security Technologies
AZ-303 Full Course -30 Hours Exam AZ-303: Microsoft Azure Architect Technologies
Each video 10 hrs of content on Deep drive to AZ-303 Exam
Windows Powershell Scripting Full training Course for Windows Admins 6 hours training
#PaddyMaddy #cloudComputing #azuretutorial #microsoftazuretutorialforbeginners #azureforbeginners #azurebasics #microsoftazuretraining #Az900 #AZ500, #microsoftazurecertification, #AZ303 #az300 #az104 #paddyMaddy #azuretraining
Create, view, and manage Alerts Using Azure Monitor - Metrics Alerts and LOG Alerts
Azure monitoring and alerting Create view and manage Alerts Using Azure Monitor Metrics LOG Alerts
Metric alerts in Azure Monitor provide a way to get notified when one of your metrics crosses a threshold. Metric alerts work on a range of multi-dimensional platform metrics, custom metrics, Application Insights standard and custom metrics. In this article, we will describe how to create, view, and manage metric alert rules through Azure portal and Azure CLI.
What are alerts in Microsoft Azure?
Alerts proactively notify you when issues are found with your infrastructure or application using your monitoring data in Azure Monitor. They allow you to identify and address issues before the users of your system notice them.
How do metric alerts work?
You can define a metric alert rule by specifying a target resource to be monitored, metric name, condition type (static or dynamic), and the condition (an operator and a threshold/sensitivity) and an action group to be triggered when the alert rule fires. Condition types affect the way thresholds are determined
Metric alerts in Azure Monitor work on top of multi-dimensional metrics. These metrics could be platform metrics, custom metrics, popular logs from Azure Monitor converted to metrics and Application Insights metrics. Metric alerts evaluate at regular intervals to check if conditions on one or more metric time-series are true and notify you when the evaluations are met. Metric alerts are stateful, that is, they only send out notifications when the state changes.
The following are key attributes of an alert rule:
Target Resource - Defines the scope and signals available for alerting. A target can be any Azure resource. Example targets:
Virtual machines.
Storage accounts.
Log Analytics workspace.
Application Insights.
For certain resources (like virtual machines), you can specify multiple resources as the target of the alert rule.
Signal - Emitted by the target resource. Signals can be of the following types: metric, activity log, Application Insights, and log.
Criteria - A combination of signal and logic applied on a target resource. Examples:
Percentage CPU 70%
Server Response Time 4 ms
Result count of a log query 100
Alert Name - A specific name for the alert rule configured by the user.
Alert Description - A description for the alert rule configured by the user.
Severity - The severity of the alert after the criteria specified in the alert rule is met. Severity can range from 0 to 4.
Sev 0 = Critical
Sev 1 = Error
Sev 2 = Warning
Sev 3 = Informational
Sev 4 = Verbose
Action - A specific action taken when the alert is fired
You can alert on metrics and logs, as described in monitoring data sources. Signals include but aren't limited to:
Metric values
Log search queries
Activity log events
Health of the underlying Azure platform
Tests for website availability
Manage alerts
You can set the state of an alert to specify where it is in the resolution process. When the criteria specified in the alert rule is met, an alert is created or fired, and it has a status of New. You can change the status when you acknowledge an alert and when you close it. All state changes are stored in the history of the alert.
▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬
Other Full Courses by PaddyMaddy
AZ-900 Full course 10+ Hours - Exam AZ-900: Microsoft Azure Fundamentals
AZ-500 Full Course - 17 Hours Exam AZ-500: Microsoft Azure Security Technologies
AZ-303 Full Course -30 Hours Exam AZ-303: Microsoft Azure Architect Technologies
Each video 10 hrs of content on Deep drive to AZ-303 Exam
Windows Powershell Scripting Full training Course for Windows Admins 6 hours training
#PaddyMaddy #cloudComputing #azuretutorial #microsoftazuretutorialforbeginners #azureforbeginners #azurebasics #microsoftazuretraining #Az900 #AZ500, #microsoftazurecertification, #AZ303 #az300 #az104 #paddyMaddy #azuretraining
Комментарии
 0:16:44
0:16:44
 0:06:37
0:06:37
 0:05:01
0:05:01
 0:22:34
0:22:34
 0:10:20
0:10:20
 0:19:43
0:19:43
 0:51:56
0:51:56
 0:11:32
0:11:32
 0:35:52
0:35:52
 0:16:15
0:16:15
 0:12:37
0:12:37
 0:18:09
0:18:09
 0:19:34
0:19:34
 0:20:25
0:20:25
 0:18:42
0:18:42
 2:07:58
2:07:58
 0:45:52
0:45:52
 0:13:13
0:13:13
 0:11:15
0:11:15
 0:23:19
0:23:19
 0:13:30
0:13:30
 0:02:45
0:02:45
 0:02:30
0:02:30
 0:29:30
0:29:30