filmov
tv
Obstructive Lung Disease vs Restrictive Lung Disease

Показать описание
Restrictive vs. Obstructive Lung Disease.
Obstructive diseases are, when air can not getting out from the lungs.
During such disease there is resistance to airflow, because of obstruction of airways.
So, Exhalation problems – it is Obstructive disease.
While during Restrictive diseases, there is problem Getting air into the lung.
During restrictive disease, lung can not expand well.
These individuals find it difficult to take a full breath.
Frequently this occurs due to a condition that causes lung stiffness, muscle weakness, or physical restriction.
Now, lets discuss which diseases are restrictive or obstructive.
Chronic obstructive airway disease
• Asthma
• Chronic bronchitis
• Emphysema
• Bronchiectasis
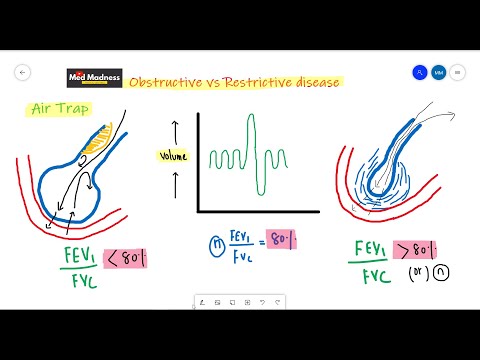
The key feature of Obstructive lung disease is:
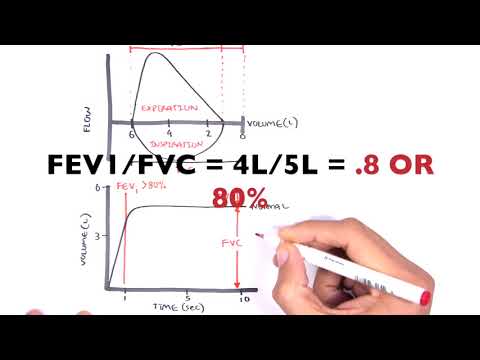
The ratio of: Forced expiratory volume in 1 second, To the Forced Vital Capacity. is decreased.
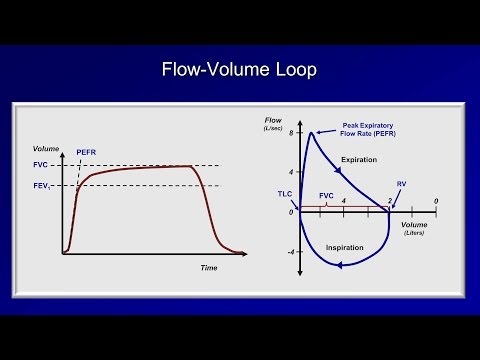
Forced expiratory volume in 1 second, is the maximum amount of air, that the subject can forcibly expel. during the first second, following maximal inhalation.
Forced Vital Capacity is, how much air a person can exhale during a forced breath.
Peak flow also decreased.
Peak flow is a quick test to measure air flowing out of the lungs.
Because the air can not get out of the lung.
Total Lung Capacity is elevated.
Total Lung Capacity is the maximal volume of gas in the lungs, after a maximal inhalation.
Residual Volume and residual capacity also elevated.
Residual Volume is the amount of air that remains in a person's lungs after fully exhaling.
Functional residual capacity is the volume in the lungs at the end of passive expiration.
The causes of restrictive lung disease are:
Chest wall disorders.
• Obesity.
• Kyphoscoliosis.
• Polio.
Interstitial and infiltrative diseases
• Acute respiratory distress syndrome.
• Pneumoconiosis
• Pulmonary fibrosis
During restrictive disease: Capacities are decreased.
Total lung capacity is Low, Pick flow is Low, Residual capacity and residual volume also low.
The ratio of: Forced expiratory volume in 1 second, To the Forced Vital Capacity. is Normal or elevated. It is important difference between obstructive and restrictive lung disease.
Obstructive diseases are, when air can not getting out from the lungs.
During such disease there is resistance to airflow, because of obstruction of airways.
So, Exhalation problems – it is Obstructive disease.
While during Restrictive diseases, there is problem Getting air into the lung.
During restrictive disease, lung can not expand well.
These individuals find it difficult to take a full breath.
Frequently this occurs due to a condition that causes lung stiffness, muscle weakness, or physical restriction.
Now, lets discuss which diseases are restrictive or obstructive.
Chronic obstructive airway disease
• Asthma
• Chronic bronchitis
• Emphysema
• Bronchiectasis
The key feature of Obstructive lung disease is:
The ratio of: Forced expiratory volume in 1 second, To the Forced Vital Capacity. is decreased.
Forced expiratory volume in 1 second, is the maximum amount of air, that the subject can forcibly expel. during the first second, following maximal inhalation.
Forced Vital Capacity is, how much air a person can exhale during a forced breath.
Peak flow also decreased.
Peak flow is a quick test to measure air flowing out of the lungs.
Because the air can not get out of the lung.
Total Lung Capacity is elevated.
Total Lung Capacity is the maximal volume of gas in the lungs, after a maximal inhalation.
Residual Volume and residual capacity also elevated.
Residual Volume is the amount of air that remains in a person's lungs after fully exhaling.
Functional residual capacity is the volume in the lungs at the end of passive expiration.
The causes of restrictive lung disease are:
Chest wall disorders.
• Obesity.
• Kyphoscoliosis.
• Polio.
Interstitial and infiltrative diseases
• Acute respiratory distress syndrome.
• Pneumoconiosis
• Pulmonary fibrosis
During restrictive disease: Capacities are decreased.
Total lung capacity is Low, Pick flow is Low, Residual capacity and residual volume also low.
The ratio of: Forced expiratory volume in 1 second, To the Forced Vital Capacity. is Normal or elevated. It is important difference between obstructive and restrictive lung disease.
Комментарии
 0:14:39
0:14:39
 0:04:18
0:04:18
 0:09:33
0:09:33
 1:25:51
1:25:51
 0:14:12
0:14:12
 0:20:28
0:20:28
 0:01:16
0:01:16
 0:04:38
0:04:38
 0:27:28
0:27:28
 0:10:08
0:10:08
 0:04:09
0:04:09
 0:15:05
0:15:05
 0:03:07
0:03:07
 0:01:09
0:01:09
 0:02:04
0:02:04
 0:03:26
0:03:26
 0:09:18
0:09:18
 0:08:47
0:08:47
 0:46:22
0:46:22
 0:18:04
0:18:04
 0:05:21
0:05:21
 0:08:09
0:08:09
 0:06:38
0:06:38