filmov
tv
Gravitational Potential Energy simplified

Показать описание
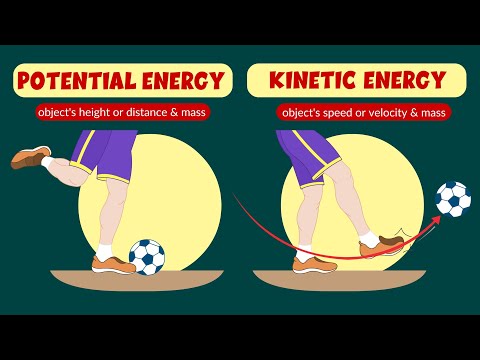
1. Definition: Gravitational potential energy is the energy stored in an object as a result of its height or elevation relative to a reference point in a gravitational field. It represents the ability of the object to do work when it is released or allowed to move under the influence of gravity.
2. Calculation: The gravitational potential energy of an object near the Earth's surface can be calculated using the equation: PE = mgh, where PE is the gravitational potential energy, m is the mass of the object, g is the acceleration due to gravity (approximately 9.8 m/s² on Earth), and h is the height or vertical distance above the reference point.
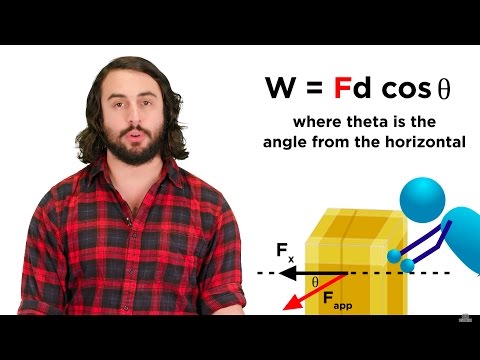
3. Relationship to Work: Gravitational potential energy is closely related to the concept of work. When an object falls or moves downward under the influence of gravity, its potential energy decreases, and an equal amount of energy is converted into kinetic energy, which is the energy of motion. This conversion is described by the work-energy theorem.
4. Conservation of Energy: The total mechanical energy of an object, which includes both kinetic energy and gravitational potential energy, is conserved in the absence of external forces such as air resistance. This means that as an object falls, its potential energy decreases, but its kinetic energy increases by an equal amount, keeping the total mechanical energy constant.
5. Applications: Gravitational potential energy has practical applications in various fields. It is utilized in activities such as rock climbing, bungee jumping, and roller coasters. Understanding gravitational potential energy is crucial in engineering and architecture when designing structures that involve elevations and potential energy considerations.
#sciencefacts #gravity #gravitationalforce #potentialenergy #work #scienceshorts #homeschool #scienceclass #physicsfacts #physics
2. Calculation: The gravitational potential energy of an object near the Earth's surface can be calculated using the equation: PE = mgh, where PE is the gravitational potential energy, m is the mass of the object, g is the acceleration due to gravity (approximately 9.8 m/s² on Earth), and h is the height or vertical distance above the reference point.
3. Relationship to Work: Gravitational potential energy is closely related to the concept of work. When an object falls or moves downward under the influence of gravity, its potential energy decreases, and an equal amount of energy is converted into kinetic energy, which is the energy of motion. This conversion is described by the work-energy theorem.
4. Conservation of Energy: The total mechanical energy of an object, which includes both kinetic energy and gravitational potential energy, is conserved in the absence of external forces such as air resistance. This means that as an object falls, its potential energy decreases, but its kinetic energy increases by an equal amount, keeping the total mechanical energy constant.
5. Applications: Gravitational potential energy has practical applications in various fields. It is utilized in activities such as rock climbing, bungee jumping, and roller coasters. Understanding gravitational potential energy is crucial in engineering and architecture when designing structures that involve elevations and potential energy considerations.
#sciencefacts #gravity #gravitationalforce #potentialenergy #work #scienceshorts #homeschool #scienceclass #physicsfacts #physics
 0:01:34
0:01:34
 0:03:19
0:03:19
 0:00:14
0:00:14
 0:04:49
0:04:49
 0:09:06
0:09:06
 0:17:59
0:17:59
 0:06:44
0:06:44
 0:05:38
0:05:38
 0:00:29
0:00:29
 0:02:18
0:02:18
 0:03:56
0:03:56
 0:06:57
0:06:57
 0:10:09
0:10:09
 0:08:35
0:08:35
 0:01:16
0:01:16
 0:10:29
0:10:29
 0:04:57
0:04:57
 0:00:54
0:00:54
 0:00:30
0:00:30
 0:00:21
0:00:21
 0:01:51
0:01:51
 0:04:28
0:04:28
 0:08:07
0:08:07
 0:11:16
0:11:16