filmov
tv
How to Copy Files and Directories in the Linux Terminal

Показать описание
**How to Copy Files and Directories in the Linux Terminal**
Welcome back to our channel! In this tutorial, we will walk you through the essential commands for copying files and directories in the Linux terminal. Whether you're managing a personal project or working on a professional server, these commands will help you efficiently handle file operations. Let's dive in!
### Copying Files
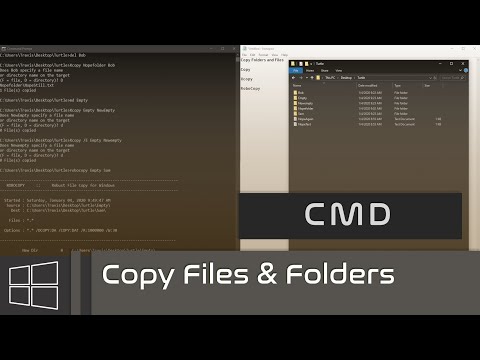
To copy files in Linux, you use the `cp` (copy) command. The basic syntax is:
```bash
cp [options] source destination
```
#### Example 1: Copy a Single File
```bash
```
#### Example 2: Copy Multiple Files
```bash
```
#### Example 3: Preserve File Attributes
To preserve the file attributes (like permissions, timestamps) while copying, use the `-p` option:
```bash
```
### Copying Directories
To copy directories and their contents, you need to use the `-r` (recursive) option with the `cp` command.
#### Example 1: Copy a Directory
To copy a directory named `projects` to a directory named `backup`, use:
```bash
cp -r projects/ backup/
```
#### Example 2: Copy a Directory with Verbose Output
To get detailed output while copying, use the `-v` (verbose) option:
```bash
cp -rv projects/ backup/
```
### Advanced Options
#### Example 1: Overwrite Without Prompting
To copy files and overwrite the destination files without prompting, use the `-f` (force) option:
```bash
```
#### Example 2: Interactive Copy
To prompt before overwriting files, use the `-i` (interactive) option:
```bash
```
#### Example 3: Copying Only When Source is Newer
To copy files only if the source file is newer than the destination file, use the `-u` (update) option:
```bash
```
### Copying with Wildcards
You can use wildcards to copy multiple files that match a certain pattern.
#### Example 1: Copy All Text Files
To copy all `.txt` files from the current directory to a directory named `backup`, use:
```bash
cp *.txt backup/
```
### Conclusion
That's it! You've learned how to copy files and directories in the Linux terminal using the `cp` command with various options to suit your needs. Mastering these commands will greatly enhance your efficiency in managing files on a Linux system. If you found this tutorial helpful, please give it a thumbs up and subscribe to our channel for more Linux tips and tutorials. Feel free to leave any questions or comments below, and we’ll get back to you as soon as possible. Thanks for watching!
#Linux #FileManagement #LinuxCommands #Terminal #CPCmd #LinuxTutorial #FileOperations #TechTutorial #OpenSource #ITSupport #TechGuide #LinuxTips
Welcome back to our channel! In this tutorial, we will walk you through the essential commands for copying files and directories in the Linux terminal. Whether you're managing a personal project or working on a professional server, these commands will help you efficiently handle file operations. Let's dive in!
### Copying Files
To copy files in Linux, you use the `cp` (copy) command. The basic syntax is:
```bash
cp [options] source destination
```
#### Example 1: Copy a Single File
```bash
```
#### Example 2: Copy Multiple Files
```bash
```
#### Example 3: Preserve File Attributes
To preserve the file attributes (like permissions, timestamps) while copying, use the `-p` option:
```bash
```
### Copying Directories
To copy directories and their contents, you need to use the `-r` (recursive) option with the `cp` command.
#### Example 1: Copy a Directory
To copy a directory named `projects` to a directory named `backup`, use:
```bash
cp -r projects/ backup/
```
#### Example 2: Copy a Directory with Verbose Output
To get detailed output while copying, use the `-v` (verbose) option:
```bash
cp -rv projects/ backup/
```
### Advanced Options
#### Example 1: Overwrite Without Prompting
To copy files and overwrite the destination files without prompting, use the `-f` (force) option:
```bash
```
#### Example 2: Interactive Copy
To prompt before overwriting files, use the `-i` (interactive) option:
```bash
```
#### Example 3: Copying Only When Source is Newer
To copy files only if the source file is newer than the destination file, use the `-u` (update) option:
```bash
```
### Copying with Wildcards
You can use wildcards to copy multiple files that match a certain pattern.
#### Example 1: Copy All Text Files
To copy all `.txt` files from the current directory to a directory named `backup`, use:
```bash
cp *.txt backup/
```
### Conclusion
That's it! You've learned how to copy files and directories in the Linux terminal using the `cp` command with various options to suit your needs. Mastering these commands will greatly enhance your efficiency in managing files on a Linux system. If you found this tutorial helpful, please give it a thumbs up and subscribe to our channel for more Linux tips and tutorials. Feel free to leave any questions or comments below, and we’ll get back to you as soon as possible. Thanks for watching!
#Linux #FileManagement #LinuxCommands #Terminal #CPCmd #LinuxTutorial #FileOperations #TechTutorial #OpenSource #ITSupport #TechGuide #LinuxTips
Комментарии
 0:00:17
0:00:17
 0:06:07
0:06:07
 0:03:03
0:03:03
 0:01:37
0:01:37
 0:14:36
0:14:36
 0:04:07
0:04:07
 0:02:53
0:02:53
 0:04:07
0:04:07
 0:03:46
0:03:46
 0:00:59
0:00:59
 0:00:40
0:00:40
 0:05:30
0:05:30
 0:02:21
0:02:21
 0:00:26
0:00:26
 0:06:46
0:06:46
 0:01:08
0:01:08
 0:00:30
0:00:30
 0:02:29
0:02:29
 0:02:02
0:02:02
 0:02:47
0:02:47
 0:09:17
0:09:17
 0:05:38
0:05:38
 0:00:22
0:00:22
 0:00:26
0:00:26