filmov
tv
#5 Linked List Implementation in Java Part 1 | Data Structures

Показать описание
Check out our courses:
Coupon: TELUSKO10 (10% Discount)
Coupon: TELUSKO20 (20% Discount)
Udemy Courses:
For More Queries WhatsApp or Call on : +919008963671
Code for LinkedList in Java
Linked List implementaion in Java without using Collection
We will use Eclipse IDE here
In this video we will see :
- What is Node
- Step by step explanation on how linked list works
- Operations of Linked list
- insert
- insertAfter
- insertAtIndex
- delete
- showList
- An example explaining LinkedList creation, insertion and show
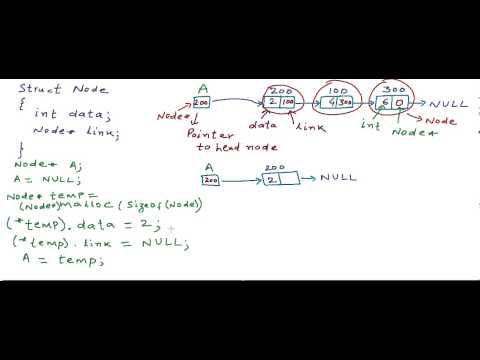
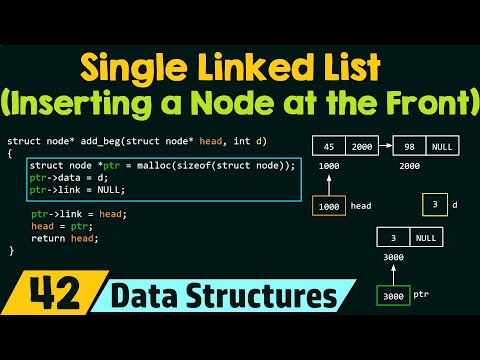
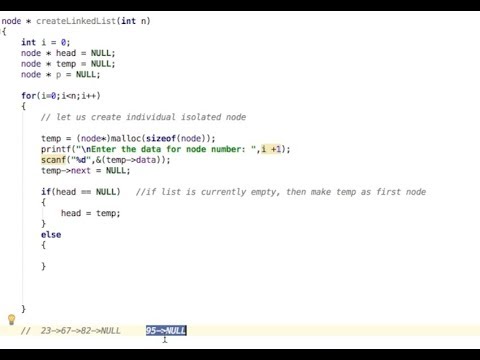
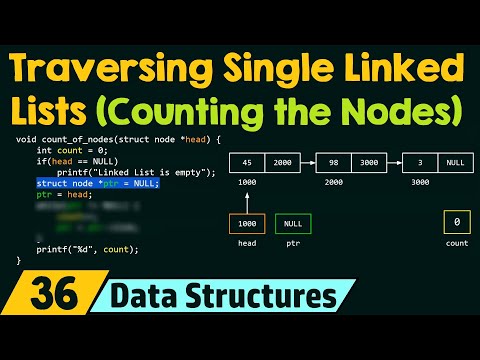
Linked list is a linear collection of data elements, in which linear order is not given by their physical placement in memory.
Instead, each element points to the next.
It is a data structure consisting of a group of nodes which together represent a sequence.
Under the simplest form, each node is composed of data and a reference (in other words, a link) to the next node in the sequence.
This structure allows for efficient insertion or removal of elements from any position in the sequence during iteration.
Editing Monitors :
Editing Laptop :
Mics
Subscribe to our other channel:
Telusko Hindi :
Coupon: TELUSKO10 (10% Discount)
Coupon: TELUSKO20 (20% Discount)
Udemy Courses:
For More Queries WhatsApp or Call on : +919008963671
Code for LinkedList in Java
Linked List implementaion in Java without using Collection
We will use Eclipse IDE here
In this video we will see :
- What is Node
- Step by step explanation on how linked list works
- Operations of Linked list
- insert
- insertAfter
- insertAtIndex
- delete
- showList
- An example explaining LinkedList creation, insertion and show
Linked list is a linear collection of data elements, in which linear order is not given by their physical placement in memory.
Instead, each element points to the next.
It is a data structure consisting of a group of nodes which together represent a sequence.
Under the simplest form, each node is composed of data and a reference (in other words, a link) to the next node in the sequence.
This structure allows for efficient insertion or removal of elements from any position in the sequence during iteration.
Editing Monitors :
Editing Laptop :
Mics
Subscribe to our other channel:
Telusko Hindi :
Комментарии
 0:23:05
0:23:05
 0:18:47
0:18:47
 0:06:21
0:06:21
 0:06:00
0:06:00
 0:13:24
0:13:24
 0:13:58
0:13:58
 0:05:37
0:05:37
 0:29:01
0:29:01
 0:15:09
0:15:09
 0:04:22
0:04:22
 0:06:14
0:06:14
 0:12:48
0:12:48
 1:07:23
1:07:23
 0:06:52
0:06:52
 0:14:39
0:14:39
 0:18:57
0:18:57
 0:27:07
0:27:07
 0:28:16
0:28:16
 0:11:02
0:11:02
 0:03:34
0:03:34
 0:07:43
0:07:43
 1:55:57
1:55:57
 0:08:59
0:08:59
 0:06:07
0:06:07