filmov
tv
🔵21c - Method of Undetermined Coefficients 3 - G(x) = Exponential Functions - Non - Homogeneous D.E

Показать описание
In this lesson we shall learn how to solve the general solution of a 2nd order linear non-homgeneous differential equation.
Given a non-homogeneous differential equation: ay'' + by' + cy = G(x), where G(x) is not zero.
The general solution is given by: y = yc + yp.
To find the general solution, you first need to treat the given D.E as a homogeneous D.E, and solve its general solution - that becomes the general solution called the complementary function, yc.
For the yp, the particular integral, is obtained using the method of undetermined coefficients.
00:00 - Exponential Functions
01:26 - Example 5
08:09 - Example 6
20:21 - Example 7
Playlists on various Course
1. Applied Electricity
2. Linear Algebra / Math 151
3. Basic Mechanics
4. Calculus with Analysis / Calculus 1 / Math 152
5. Differential Equations / Math 251
6. Electric Circuit Theory / Circuit Design
Make sure to watch till the end.
Like, share, and subscribe.
Thank you.
Given a non-homogeneous differential equation: ay'' + by' + cy = G(x), where G(x) is not zero.
The general solution is given by: y = yc + yp.
To find the general solution, you first need to treat the given D.E as a homogeneous D.E, and solve its general solution - that becomes the general solution called the complementary function, yc.
For the yp, the particular integral, is obtained using the method of undetermined coefficients.
00:00 - Exponential Functions
01:26 - Example 5
08:09 - Example 6
20:21 - Example 7
Playlists on various Course
1. Applied Electricity
2. Linear Algebra / Math 151
3. Basic Mechanics
4. Calculus with Analysis / Calculus 1 / Math 152
5. Differential Equations / Math 251
6. Electric Circuit Theory / Circuit Design
Make sure to watch till the end.
Like, share, and subscribe.
Thank you.
🔵21c - Method of Undetermined Coefficients 3 - G(x) = Exponential Functions - Non - Homogeneous D.E...
Method of Undetermined Coefficients - Ordinary Differential Equations | Lecture 21
🔵21e - Method of Undetermined Coefficients 5 - G(x) = Sum of Functions
Method of undetermined coefficients when there is duplication
🔵21d - Method of Undetermined Coefficients 4 - G(x) = Sine and Cosine Functions
How to Solve DE's with the Method of Undetermined Coefficients y'' - y' + (1/4)y...
Method of undetermined coefficients with initial conditions
Solve using the Method of Undetermined Coefficients (1/4)y'' + y' + y = x^2 - 3x
Method of undetermined coefficients | 2nd order differential equations, g(x) = exponential
The Method of Undetermined Coefficients -- Differential Equations Examples #11
Method of Undetermined Coefficients general Solution of a NON-Homogeneous ODE
Undetermined Coefficients, second order linear differential equation, f(t) is a polynomial
2 METHODS for Undetermined Coefficients in Polynomial Equalities #shorts
Undetermined Coefficients
🔵21a - Method of Undetermined Coefficients 1 - G(x) = Constant: 2nd Order Non - Homogeneous D.E
Annihilator Method-Method of Undetermined Coefficients with Trig Example
Solving a Differential Equation with the Method of Undetermined Coefficients
Annihilator Method-Method of Undetermined Coefficients Example
Differential Equations Undetermined Coefficients: y'' + y = sin x
The method of undetermined coefficients - introduction
Method of Undetermined Coefficients - Examples
How to Use the Method of Undetermined Coefficients to Solve a DE (1/4)y'' + y' + y = ...
undetermined coefficients with first order linear DEs
Undetermined Coefficients Example with Trig Function
Комментарии
 0:30:13
0:30:13
 0:20:33
0:20:33
 0:21:29
0:21:29
 0:10:53
0:10:53
 0:09:43
0:09:43
 0:13:25
0:13:25
 0:13:15
0:13:15
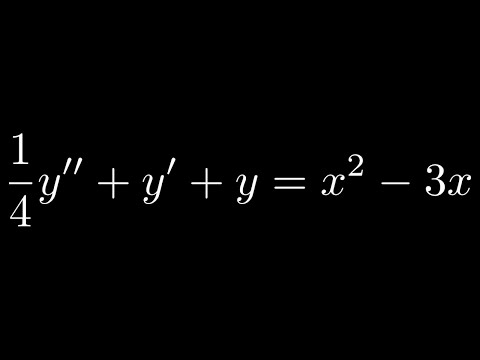 0:12:04
0:12:04
 0:05:36
0:05:36
 0:21:35
0:21:35
 0:13:10
0:13:10
 0:06:01
0:06:01
 0:01:00
0:01:00
 0:29:47
0:29:47
 0:15:25
0:15:25
 0:13:21
0:13:21
 0:26:39
0:26:39
 0:10:31
0:10:31
 0:04:21
0:04:21
 0:03:22
0:03:22
 0:21:14
0:21:14
 0:11:21
0:11:21
 0:13:50
0:13:50
 0:12:55
0:12:55