filmov
tv
Nervous Tissue | Structural Organization in Animals | Anatomy | Inter 2nd year Class 11 Biology

Показать описание
Welcome to Elearnin, In this 3d animated video we will teach you about Nervous System and the Nervous Tissue from the chapter Structural Organisation in Animals from the Class 11 Biology - CBSE – NCERT. This video can also help Intermediate 2nd year zoology students.
In this video, you will learn about Muscle Tissue.
00:37 Cyton/ Cell Body
0:53 Axon/ Nerve Fibre
01:09 Nerve Impulse
01:58 Nerve Cells/Neurons
• Types of neurons based on divisions
• Types of neurons based on Myelin sheath
• Types of neurons based on Function
#NervousSystem #HumanAnatomy #NervousTissue #Anatomy #3dAnimation #Biology #intermediate #Inter #Neurons#NCERT #StudiousTelugu #Class11 #science #cbsc
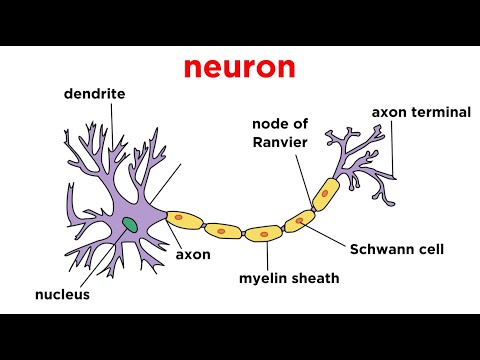
The nervous system plays a vital role in establishing fast communication between body parts. The entire nervous system is made up of neurons and nervous tissues. The neuron is made of two parts. The cyton is broad and is also known as the cell body. The axon is long and is also known as nervous fibre.
Cyton/ Cell Body:
The nucleus can be seen in the cyton. The nucleus is surrounded by Nissl’s granules. The edges of the cyton project as dendrites.
Axon/ Nerve Fibre:
It is the long fibber of the neuron. It is engulfed by a fatty Myelin layer. There is a thin layer called Neurilemma surrounding the myelin. Between the neurilemma and myelin, there are Schwann cells.
Nerve Impulse:
Nerve impulse is the quick transmission that occurs in the nervous system. This occurs in the form of an electrochemical flow. The area between two neuron ends is known as an axon terminal. The relation between the neural junction and transmission is that the synaptic junction between two neurons helps the transmission of impulse between them. The chemical which help in this transmission are known as neurotransmitters. Neurotransmitters carry the transmission up to the synapse. There are two types of cells in the nervous system
1. Nerve Cell
2. Neuroglia
The cells which transmit the impulse are called nerve cells. Those which don’t transmit are known as neuroglia.
Nerve Cells/Neurons:
These are the functional units of the nervous system. These cells get excited by the impulse and transmit or pass it on. When a neuron is suitably stimulated, an electrical disturbance is generated which swiftly travels along its plasma membrane. A neuron contains the cell body, one or more dendrites and an axon. The neuron is said to have two parts. These are
1. Cyton/Cell body
2. Axon
The part of the axon not surrounded by the Schwann cell and myelin is known as Node of Ranvier. Myelin acts as an electric insulator. Schwann cells help in the production of myelin.
Cell Body:
It is known as cyton or body. It has a lot or granules and a large nucleus in the cytoplasm. The cytoplasm contains Nissl’s structures or Nissl’s granules. There are subtle nerve fibres called lipofuscin granules. The cell bodies in the CNS are called nucleus while those in the PNS are called ganglions.
Dendrites :
The small branched structures surrounding the cell body are known as dendrites. They contain Nissl structures and nerve fibres.
Axon:
The axon is a single long cylindrical structure. It emerges from a part of the cell body known as axon hill. The plasmalemma of the axon is known as axolemma and its cytoplasm is known as axoplasm. These contain nerve fibres but not Nissl structures. The axon forms collateral branches. The axon forms small filamentous structures called telodendrites which end as synaptic knobs. The axon transmits the impulse to other neurons and muscle fibres. The axon bundles in CNS are known as tracts while those in the PNS are known as nerves.
Synapse:
The subtle gap between the axon terminal of the previous neuron and the dendrite of the next is known as the synapse.
Types of neurons based on divisions
1. Unipolar Nerve Cells
These are sensory cells. There is only projection from the cell body here. This divides into two branches. One of these forms dendrites while the other is the axon. These are known as pseudo unipolar nerve cells.
2. Bipolar Neurons
Here, dendrite and axon from directly from the cell body. They are present in the retina of the eye, inner ear and in the olfactory sensory epithelium.
3. Multipolar Neurons
These have an axon and one or more dendrites. Most neurons in our body are multipolar.
Nerve
The axons in the PNS form nerves. Every nerve is covered by a thin layer of connective tissue known as endoneurium. A collection of axons is called fascicle. It is covered by perineurium. All the fascicles in the nerve form a bundle and are covered by the connective tissue covering called epineurium. This forms a nerve.
In this video, you will learn about Muscle Tissue.
00:37 Cyton/ Cell Body
0:53 Axon/ Nerve Fibre
01:09 Nerve Impulse
01:58 Nerve Cells/Neurons
• Types of neurons based on divisions
• Types of neurons based on Myelin sheath
• Types of neurons based on Function
#NervousSystem #HumanAnatomy #NervousTissue #Anatomy #3dAnimation #Biology #intermediate #Inter #Neurons#NCERT #StudiousTelugu #Class11 #science #cbsc
The nervous system plays a vital role in establishing fast communication between body parts. The entire nervous system is made up of neurons and nervous tissues. The neuron is made of two parts. The cyton is broad and is also known as the cell body. The axon is long and is also known as nervous fibre.
Cyton/ Cell Body:
The nucleus can be seen in the cyton. The nucleus is surrounded by Nissl’s granules. The edges of the cyton project as dendrites.
Axon/ Nerve Fibre:
It is the long fibber of the neuron. It is engulfed by a fatty Myelin layer. There is a thin layer called Neurilemma surrounding the myelin. Between the neurilemma and myelin, there are Schwann cells.
Nerve Impulse:
Nerve impulse is the quick transmission that occurs in the nervous system. This occurs in the form of an electrochemical flow. The area between two neuron ends is known as an axon terminal. The relation between the neural junction and transmission is that the synaptic junction between two neurons helps the transmission of impulse between them. The chemical which help in this transmission are known as neurotransmitters. Neurotransmitters carry the transmission up to the synapse. There are two types of cells in the nervous system
1. Nerve Cell
2. Neuroglia
The cells which transmit the impulse are called nerve cells. Those which don’t transmit are known as neuroglia.
Nerve Cells/Neurons:
These are the functional units of the nervous system. These cells get excited by the impulse and transmit or pass it on. When a neuron is suitably stimulated, an electrical disturbance is generated which swiftly travels along its plasma membrane. A neuron contains the cell body, one or more dendrites and an axon. The neuron is said to have two parts. These are
1. Cyton/Cell body
2. Axon
The part of the axon not surrounded by the Schwann cell and myelin is known as Node of Ranvier. Myelin acts as an electric insulator. Schwann cells help in the production of myelin.
Cell Body:
It is known as cyton or body. It has a lot or granules and a large nucleus in the cytoplasm. The cytoplasm contains Nissl’s structures or Nissl’s granules. There are subtle nerve fibres called lipofuscin granules. The cell bodies in the CNS are called nucleus while those in the PNS are called ganglions.
Dendrites :
The small branched structures surrounding the cell body are known as dendrites. They contain Nissl structures and nerve fibres.
Axon:
The axon is a single long cylindrical structure. It emerges from a part of the cell body known as axon hill. The plasmalemma of the axon is known as axolemma and its cytoplasm is known as axoplasm. These contain nerve fibres but not Nissl structures. The axon forms collateral branches. The axon forms small filamentous structures called telodendrites which end as synaptic knobs. The axon transmits the impulse to other neurons and muscle fibres. The axon bundles in CNS are known as tracts while those in the PNS are known as nerves.
Synapse:
The subtle gap between the axon terminal of the previous neuron and the dendrite of the next is known as the synapse.
Types of neurons based on divisions
1. Unipolar Nerve Cells
These are sensory cells. There is only projection from the cell body here. This divides into two branches. One of these forms dendrites while the other is the axon. These are known as pseudo unipolar nerve cells.
2. Bipolar Neurons
Here, dendrite and axon from directly from the cell body. They are present in the retina of the eye, inner ear and in the olfactory sensory epithelium.
3. Multipolar Neurons
These have an axon and one or more dendrites. Most neurons in our body are multipolar.
Nerve
The axons in the PNS form nerves. Every nerve is covered by a thin layer of connective tissue known as endoneurium. A collection of axons is called fascicle. It is covered by perineurium. All the fascicles in the nerve form a bundle and are covered by the connective tissue covering called epineurium. This forms a nerve.
Комментарии
 0:06:55
0:06:55
 0:13:53
0:13:53
 0:03:52
0:03:52
 0:03:31
0:03:31
 0:05:49
0:05:49
 0:11:32
0:11:32
 0:10:36
0:10:36
 0:05:10
0:05:10
 2:02:59
2:02:59
 0:09:12
0:09:12
 0:55:48
0:55:48
 0:01:58
0:01:58
 0:08:48
0:08:48
 0:03:30
0:03:30
 0:44:33
0:44:33
 0:34:22
0:34:22
 0:00:23
0:00:23
 0:42:05
0:42:05
 0:26:21
0:26:21
 1:19:53
1:19:53
 0:01:00
0:01:00
 0:00:15
0:00:15
 0:58:28
0:58:28
 0:00:16
0:00:16