filmov
tv
⚗️ Finding Equilibrium Constants using ICE Table (Question 3)

Показать описание
Follow us:
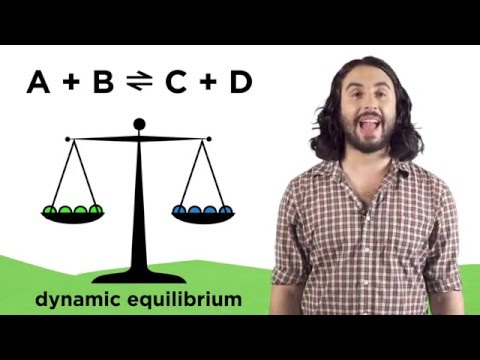
Consider the following reaction:
A reaction mixture at 1700 °C initially contains [CH4] = 0.115 M. At equilibrium, the mixture contains [C2H2] = 0.035 M. What is the value of the equilibrium constant?
The reaction of CH4 in the example above is carried out at a different temperature with an initial concentration of [CH4] = 0.087 M. At equilibrium, the concentration of H2 is 0.012 M. Find the equilibrium constant at this temperature.
Procedure For…
Finding Equilibrium Constants from Experimental Concentration Measurements
To solve these types of problems, follow the procedure outlined in this column.
Step 1 Using the balanced equation as a guide, prepare an ICE table showing the known initial concentrations and equilibrium concentrations of the reactants and products. Leave space in the middle of the table for determining the changes in concentration that occur during the reaction.
Step 2 Calculate the change in concentration that must have occurred for the reactant or product whose concentration is known both initially and at equilibrium.
Step 3 Use the change you calculated in step 2 and the stoichiometric relationships from the balanced chemical equation to determine the changes in concentration of all other reactants and products. Since reactants are consumed during the reaction, the changes in their concentrations are negative. Since products are formed, the changes in their concentrations are positive.
Step 4 Sum each column for each reactant and product to determine the equilibrium concentrations.
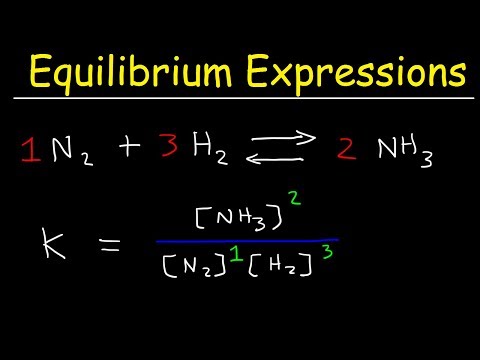
Step 5 Use the balanced equation to write an expression for the equilibrium constant and substitute the equilibrium concentrations to calculate K.
 0:08:12
0:08:12
 0:53:22
0:53:22
 0:06:15
0:06:15
 0:06:48
0:06:48
 0:06:48
0:06:48
 0:06:46
0:06:46
 0:07:51
0:07:51
 0:04:26
0:04:26
 0:17:53
0:17:53
 0:09:06
0:09:06
 0:09:29
0:09:29
 0:05:24
0:05:24
 0:03:31
0:03:31
 0:10:07
0:10:07
 0:05:11
0:05:11
 0:10:13
0:10:13
 0:05:29
0:05:29
 0:23:29
0:23:29
 0:28:41
0:28:41
 0:05:02
0:05:02
 0:10:30
0:10:30
 0:10:51
0:10:51
 0:09:48
0:09:48
 0:12:43
0:12:43