filmov
tv
3.6 - Solved Example Problem - Hydrostatic Force and Center of Pressure - SemiCircular and Circular

Показать описание
In this segment, we go over the detailed steps to calculate the circular and semi-circular observation window on the side of a water tank.
Table of Contents:
1:25 - Pressure Force on a Circular Surface
3:40 - Center of Pressure for a Circular Surface
5:25 - Pressure Force on a Semi-Circular Surface
9:40 - Center of Pressure for a Semi-Circular Surface
Module 3: Fluid Statics -- Forces on Submerged Plane and Curved Surfaces
In modules 2 and 3, we cover essential real-life applications of fluids in which the fluid is either stationary or moving with a constant velocity. For both these cases, the shear stresses become zero, and all primary stresses become minus pressure, which simplifies the mathematics significantly when compared to fluid dynamics applications.
Specifically, in module 3, we apply fundamentals to find hydrostatic forces and center of pressure on submerged planes and curved surfaces. We also discuss buoyancy and stability.
Student Learning Outcomes:
After completing this module, you should be able to:
1) Calculate the hydrostatic pressure force on a plane or curved submerged surface
2) Calculate the buoyant force and determine the stability of floating or submerged objects This material is based upon work supported by the National Science Foundation under Grant No. 2019664. Any opinions, findings, and conclusions, or recommendations expressed in this material are those of the author and do not necessarily reflect the views of the National Science Foundation.
Table of Contents:
1:25 - Pressure Force on a Circular Surface
3:40 - Center of Pressure for a Circular Surface
5:25 - Pressure Force on a Semi-Circular Surface
9:40 - Center of Pressure for a Semi-Circular Surface
Module 3: Fluid Statics -- Forces on Submerged Plane and Curved Surfaces
In modules 2 and 3, we cover essential real-life applications of fluids in which the fluid is either stationary or moving with a constant velocity. For both these cases, the shear stresses become zero, and all primary stresses become minus pressure, which simplifies the mathematics significantly when compared to fluid dynamics applications.
Specifically, in module 3, we apply fundamentals to find hydrostatic forces and center of pressure on submerged planes and curved surfaces. We also discuss buoyancy and stability.
Student Learning Outcomes:
After completing this module, you should be able to:
1) Calculate the hydrostatic pressure force on a plane or curved submerged surface
2) Calculate the buoyant force and determine the stability of floating or submerged objects This material is based upon work supported by the National Science Foundation under Grant No. 2019664. Any opinions, findings, and conclusions, or recommendations expressed in this material are those of the author and do not necessarily reflect the views of the National Science Foundation.
 0:08:08
0:08:08
 0:12:44
0:12:44
 0:13:48
0:13:48
 0:03:50
0:03:50
 0:35:30
0:35:30
 0:07:15
0:07:15
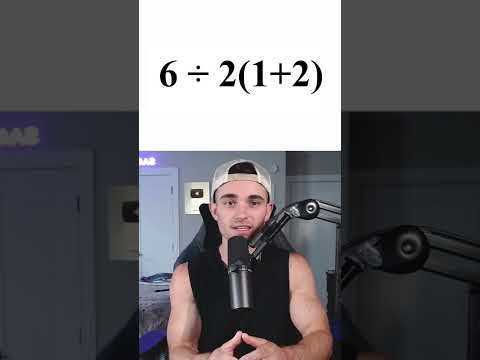 0:00:28
0:00:28
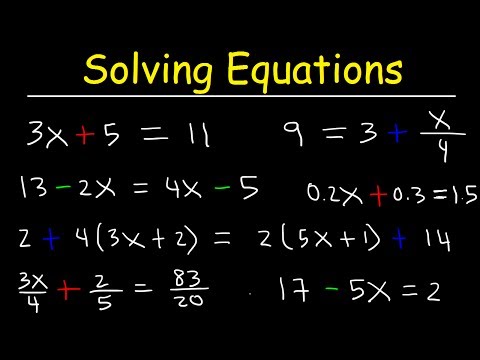 0:25:05
0:25:05
 0:06:45
0:06:45
 0:01:09
0:01:09
 0:17:00
0:17:00
 0:11:03
0:11:03
 0:06:13
0:06:13
 0:01:00
0:01:00
 0:14:06
0:14:06
 0:15:41
0:15:41
 0:15:55
0:15:55
 0:04:22
0:04:22
 0:22:09
0:22:09
 0:03:51
0:03:51
 0:23:42
0:23:42
 0:00:51
0:00:51
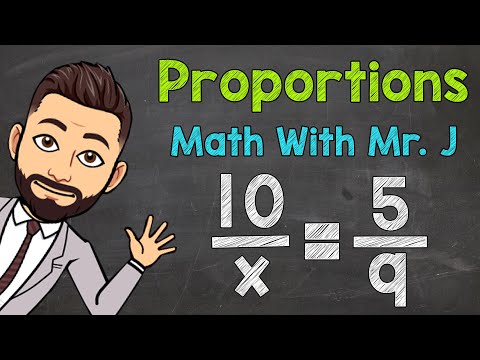 0:03:46
0:03:46
 0:00:47
0:00:47