filmov
tv
JVM Architecture

Показать описание
ATTENTION DATA SCIENCE ASPIRANTS:
Click Below Link to Download Proven 90-Day Roadmap to become a Data Scientist in 90 days
This video explains about the internals of the JVM architecture. In this video, I am going to explain about the 3 major components of JVM architecture,
Class Loader, runtime data area, and execution engine.
class loader is the first main component in JVM architecture, which has 3 phases loading, linking, and initialization. First let’s look at the loading phase of class loader component. In the loading phase, we have 3 types of class loaders.
Second main component in JVM architecture is the run time data area. Just like how a car needs a road, or how a train needs a railway track to run, similarly JVM needs memory area to store the class files and execute them.
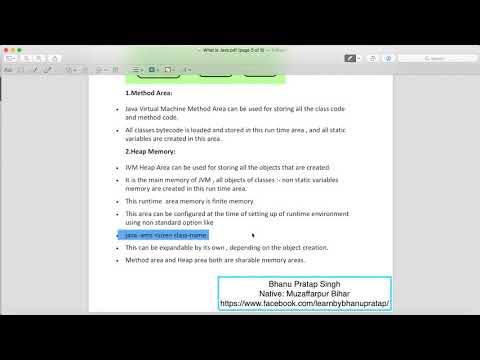
There are 5 types of memory data area. They are method area, Heap memory, Stack memory, PC Registers, and Native method stacks
Method area- all the class level data are stored in this memory area. For example, class level static variables are stored in this memory area.
Heap memory – all the objects and instance variables are stored in this memory area.
Stack memory – this contains three sections of memory areas.
Local variable – memory area that stores all the local variables that is used within a method
Operand stack – contains all the operands that are used within a method.
Frame data – this contains any catch block information, in case any exception occurs within method.
PC registers – this memory area holds the current executing instructions
Native method stacks – memory area which holds the native method information
The 3rd main component in JVM architecture is the execution engine. This is the actual engine that converts the bytecode to machine code and executes the instructions. This contains Interpreter, JIT compiler, Garbage collector, and Java Native method interface.
Interpreter – Interpreter is the one that reads the class files or bytecode and executes it one by one. The problem with the interpreter is that, when a method is called multiple times, it interprets those lines of bytecode again and again.
JIT compiler – JIT compiler helps in overcoming the problem of the interpreter. When repeated method calls occur, JIT compiler compiles the bytecode to native code. This native code will be used directly for repeated method calls. JIT compiler contains few components to achieve this feature
Intermediate code generator – generates intermediate code
Code optimizer – optimizes the intermediate code for better performance
Target code generator – converts intermediate code to native machine code
Profiler – it is responsible for finding the hotspots, methods which are called repeatedly.
Garbage collector – Garbage collector is responsible for destroying the objects that are no longer used.
Java native method interface – It is responsible for interacting with native libraries and makes it available for the JVM execution engine.
In this video, we saw that the JVM architecture has 3 main components namely class loader, run time data area, and execution engine.
Class loader in turn has 3 subsystems, which are loading phase, linking phase, and initialization phase.
Second main component is the Runtime data area, which has 5 memory areas namely method area, heap memory, stack memory, PC registers and JNI.
The 3rd main component is the execution engine. This contains some components like interpreter, JIT compiler, JNI, and Garbage collector.
In the next video, we will look at the “Class structure and components”
Click Below Link to Download Proven 90-Day Roadmap to become a Data Scientist in 90 days
This video explains about the internals of the JVM architecture. In this video, I am going to explain about the 3 major components of JVM architecture,
Class Loader, runtime data area, and execution engine.
class loader is the first main component in JVM architecture, which has 3 phases loading, linking, and initialization. First let’s look at the loading phase of class loader component. In the loading phase, we have 3 types of class loaders.
Second main component in JVM architecture is the run time data area. Just like how a car needs a road, or how a train needs a railway track to run, similarly JVM needs memory area to store the class files and execute them.
There are 5 types of memory data area. They are method area, Heap memory, Stack memory, PC Registers, and Native method stacks
Method area- all the class level data are stored in this memory area. For example, class level static variables are stored in this memory area.
Heap memory – all the objects and instance variables are stored in this memory area.
Stack memory – this contains three sections of memory areas.
Local variable – memory area that stores all the local variables that is used within a method
Operand stack – contains all the operands that are used within a method.
Frame data – this contains any catch block information, in case any exception occurs within method.
PC registers – this memory area holds the current executing instructions
Native method stacks – memory area which holds the native method information
The 3rd main component in JVM architecture is the execution engine. This is the actual engine that converts the bytecode to machine code and executes the instructions. This contains Interpreter, JIT compiler, Garbage collector, and Java Native method interface.
Interpreter – Interpreter is the one that reads the class files or bytecode and executes it one by one. The problem with the interpreter is that, when a method is called multiple times, it interprets those lines of bytecode again and again.
JIT compiler – JIT compiler helps in overcoming the problem of the interpreter. When repeated method calls occur, JIT compiler compiles the bytecode to native code. This native code will be used directly for repeated method calls. JIT compiler contains few components to achieve this feature
Intermediate code generator – generates intermediate code
Code optimizer – optimizes the intermediate code for better performance
Target code generator – converts intermediate code to native machine code
Profiler – it is responsible for finding the hotspots, methods which are called repeatedly.
Garbage collector – Garbage collector is responsible for destroying the objects that are no longer used.
Java native method interface – It is responsible for interacting with native libraries and makes it available for the JVM execution engine.
In this video, we saw that the JVM architecture has 3 main components namely class loader, run time data area, and execution engine.
Class loader in turn has 3 subsystems, which are loading phase, linking phase, and initialization phase.
Second main component is the Runtime data area, which has 5 memory areas namely method area, heap memory, stack memory, PC registers and JNI.
The 3rd main component is the execution engine. This contains some components like interpreter, JIT compiler, JNI, and Garbage collector.
In the next video, we will look at the “Class structure and components”
Комментарии
 0:08:18
0:08:18
 0:29:16
0:29:16
 0:27:35
0:27:35
 0:21:25
0:21:25
 0:05:22
0:05:22
 0:02:48
0:02:48
 0:02:25
0:02:25
 0:12:22
0:12:22
 0:12:03
0:12:03
 0:34:48
0:34:48
 0:48:10
0:48:10
 0:05:28
0:05:28
 0:04:26
0:04:26
 0:18:02
0:18:02
 0:10:04
0:10:04
 0:48:01
0:48:01
 0:01:05
0:01:05
 0:12:09
0:12:09
 0:36:02
0:36:02
 0:08:23
0:08:23
 0:06:26
0:06:26
 0:07:48
0:07:48
 0:10:09
0:10:09
 0:12:38
0:12:38