filmov
tv
Sterilization

Показать описание
Sterilization is a process used to eliminate or kill all forms of microbial life, including bacteria, viruses, spores, and fungi, from a surface, object, or substance. It is a critical procedure in various industries, including healthcare, food production, pharmaceuticals, and laboratory settings, to ensure the safety of products, equipment, and environments. Sterilization aims to prevent the spread of infections, maintain product quality, and ensure the effectiveness of medical procedures.
There are several methods of sterilization, each with its own advantages, disadvantages, and appropriate applications:
1. Heat Sterilization:
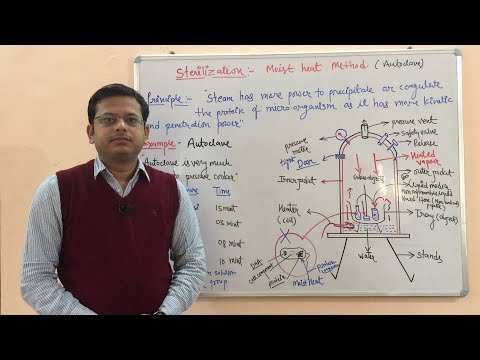
- Autoclaving: This is one of the most common methods, involving the use of high-pressure steam to achieve temperatures above 121°C (250°F). Autoclaving is highly effective in killing a wide range of microorganisms, including spores.
- Dry Heat: Heat can also be applied in a dry environment, typically at higher temperatures for longer durations compared to autoclaving. Dry heat is used for items that might be damaged by moisture, such as glassware and metal instruments.
2. Chemical Sterilization:
- Ethylene Oxide (ETO): A gas with strong sterilizing properties, ETO is used for items sensitive to high heat and moisture, such as plastics, electronic components, and medical devices.
- Hydrogen Peroxide Vapor: This method involves the use of hydrogen peroxide vapor to sterilize enclosed spaces, such as hospital rooms and isolators for laboratory animals.
- Formaldehyde: Formaldehyde gas is used for cold sterilization of items that cannot withstand heat. It's often used in laboratory settings.
3. Radiation Sterilization:
- Gamma Radiation: Ionizing gamma radiation is commonly used to sterilize medical equipment, pharmaceuticals, and certain types of food. It effectively kills microorganisms by damaging their DNA.
- Electron Beam Radiation: Similar to gamma radiation, this method is used for items that can't withstand heat or moisture, as well as for disposable medical products.
4. Filtration:
- Membrane Filtration: This method involves passing liquids or gases through a fine filter that traps microorganisms and particles, effectively sterilizing the fluid.
5. Plasma Sterilization:
- Low-temperature plasma is a mixture of ionized gases that can be used to sterilize heat-sensitive medical instruments and equipment.
It's important to note that not all items and materials can be sterilized using the same method. The choice of sterilization method depends on factors such as the nature of the item, the microorganisms to be eliminated, and the potential impact of the sterilization process on the item's integrity.
Sterilization plays a crucial role in healthcare settings to prevent healthcare-associated infections, in food production to extend shelf life, in pharmaceutical manufacturing to ensure drug safety, and in laboratory research to maintain a controlled and sterile environment.
There are several methods of sterilization, each with its own advantages, disadvantages, and appropriate applications:
1. Heat Sterilization:
- Autoclaving: This is one of the most common methods, involving the use of high-pressure steam to achieve temperatures above 121°C (250°F). Autoclaving is highly effective in killing a wide range of microorganisms, including spores.
- Dry Heat: Heat can also be applied in a dry environment, typically at higher temperatures for longer durations compared to autoclaving. Dry heat is used for items that might be damaged by moisture, such as glassware and metal instruments.
2. Chemical Sterilization:
- Ethylene Oxide (ETO): A gas with strong sterilizing properties, ETO is used for items sensitive to high heat and moisture, such as plastics, electronic components, and medical devices.
- Hydrogen Peroxide Vapor: This method involves the use of hydrogen peroxide vapor to sterilize enclosed spaces, such as hospital rooms and isolators for laboratory animals.
- Formaldehyde: Formaldehyde gas is used for cold sterilization of items that cannot withstand heat. It's often used in laboratory settings.
3. Radiation Sterilization:
- Gamma Radiation: Ionizing gamma radiation is commonly used to sterilize medical equipment, pharmaceuticals, and certain types of food. It effectively kills microorganisms by damaging their DNA.
- Electron Beam Radiation: Similar to gamma radiation, this method is used for items that can't withstand heat or moisture, as well as for disposable medical products.
4. Filtration:
- Membrane Filtration: This method involves passing liquids or gases through a fine filter that traps microorganisms and particles, effectively sterilizing the fluid.
5. Plasma Sterilization:
- Low-temperature plasma is a mixture of ionized gases that can be used to sterilize heat-sensitive medical instruments and equipment.
It's important to note that not all items and materials can be sterilized using the same method. The choice of sterilization method depends on factors such as the nature of the item, the microorganisms to be eliminated, and the potential impact of the sterilization process on the item's integrity.
Sterilization plays a crucial role in healthcare settings to prevent healthcare-associated infections, in food production to extend shelf life, in pharmaceutical manufacturing to ensure drug safety, and in laboratory research to maintain a controlled and sterile environment.
Комментарии
 0:03:41
0:03:41
 0:06:39
0:06:39
 0:00:58
0:00:58
 0:03:58
0:03:58
 0:23:19
0:23:19
 0:04:06
0:04:06
 0:02:27
0:02:27
 0:03:00
0:03:00
 0:00:47
0:00:47
 0:03:09
0:03:09
 1:05:44
1:05:44
 0:04:34
0:04:34
 0:12:44
0:12:44
 0:01:01
0:01:01
 0:03:25
0:03:25
 0:05:27
0:05:27
 0:16:35
0:16:35
 0:01:45
0:01:45
 0:01:08
0:01:08
 0:10:31
0:10:31
 0:00:37
0:00:37
 1:07:27
1:07:27
 0:02:22
0:02:22
 0:10:33
0:10:33