filmov
tv
Linear Programming, Lecture 16. More examples on dual problems. Duality Theorem.

Показать описание
Oct 18, 2016. Penn State University.
Linear Programming, Lecture 16. More examples on dual problems. Duality Theorem.
Linear Programming - Lecture 16 - The Network Simplex Method: Graph Theoretic Interpretations
Linear Programming, Lecture 13. More on convexity. Review for Exam 1
15. Linear Programming: LP, reductions, Simplex
STAV101 Lecture 16B Introduction to linear programming and the structure of a LP model
Linear Programming
Linear Programming, Lecture 12. Convexity.
Linear Programming 16: Basic feasible solutions - Geometry
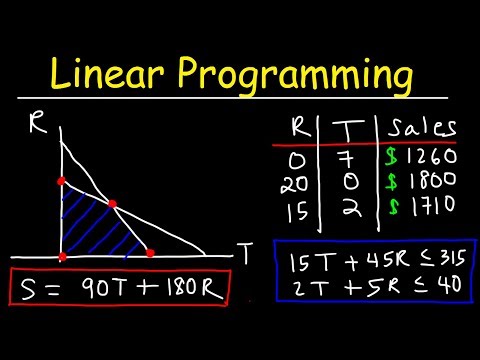
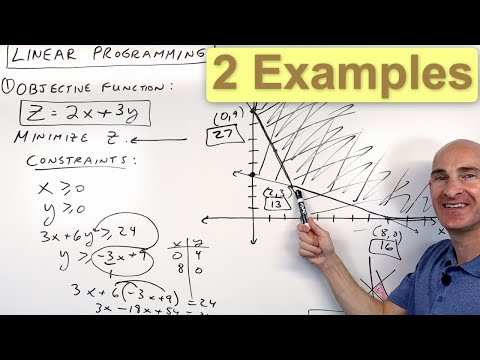
Linear Programming (Optimization) 2 Examples Minimize & Maximize
24. Linear Programming and Two-Person Games
Chapter #1: Mathematical Programming [slide 16-35]
Lesson 16 Linear Programming
Linear Programming, Lecture 1. Introduction, simple models, graphic solution
pov: you worked harder for gcses than alevels. #shorts #student
11 years later ❤️ @shrads
Lab 2021 03 16 Linear Programming Sensitivity Analysis and MATLAB
Linear Programming, Lecture 2. Graphic method, more on Modeling
IIT Bombay Lecture Hall | IIT Bombay Motivation | #shorts #ytshorts #iit
[OR1-Modeling] Lecture 2: Linear Programming #7 Simple LP formulation: Product mix
Simplex Method Problem 1- Linear Programming Problems (LPP) - Engineering Mathematics - 4
Cosplay by b.tech final year at IIT Kharagpur
13. Linear programming. Additional Maths OCR FSMQ
Best Programming Languages #programming #coding #javascript
Duality Problem 1,2 - Linear Programming Problems (LPP) - Engineering Mathematics - 4
Комментарии
 1:12:53
1:12:53
 1:27:29
1:27:29
 1:10:58
1:10:58
 1:22:27
1:22:27
 0:16:38
0:16:38
 0:33:20
0:33:20
 1:12:29
1:12:29
 0:16:52
0:16:52
 0:15:08
0:15:08
 0:53:34
0:53:34
 0:13:05
0:13:05
 0:24:11
0:24:11
 1:14:55
1:14:55
 0:00:10
0:00:10
 0:00:11
0:00:11
 1:09:56
1:09:56
 1:13:00
1:13:00
 0:00:12
0:00:12
![[OR1-Modeling] Lecture 2:](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/S6iYDxa6Fxg/hqdefault.jpg) 0:12:53
0:12:53
 0:25:22
0:25:22
 0:00:15
0:00:15
 0:22:59
0:22:59
 0:00:16
0:00:16
 0:07:32
0:07:32