filmov
tv
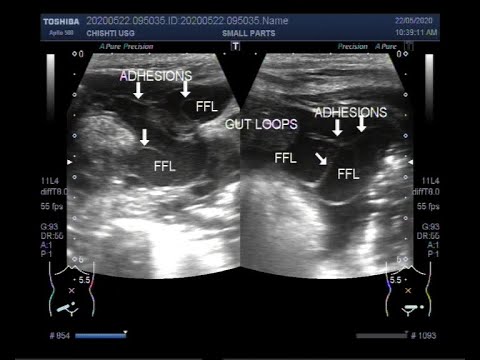
Ultrasound Video showing a leaked or ruptured Appendix.

Показать описание
This video shows a leaked or Ruptured Appendix.
If appendicitis is not treated, it can rupture. As a result, bacteria are released into the abdomen and cause a serious infection. It can make the patient very sick and be hard to treat.
An appendix is a small, thin, wormlike sac. It’s located where small and large intestines connect in the lower abdomen on the right side. It is generally thought that it doesn’t have any important function so it can be removed without causing harmful effects.
Appendicitis can happen at any age, but it is seen mostly in children and teenagers between the ages of 10 and 20 years. It’s more common in males.
A study in the Journal of the American College of Surgeons found the risk of rupture was less than 2 percent when appendicitis was treated within 36 hours of the start of symptoms. It increased to 5 percent when it was treated 36 hours or more after the start of symptoms.
The exact cause of appendicitis isn’t known for sure, it’s probably due to an infection that triggers inflammation inside the appendix.
When the opening of the appendix gets blocked, bacteria get trapped inside and reproduce quickly, causing an infection. If the infection goes untreated, pressure builds and the appendix swells. Eventually, it swells so much that the blood supply to part of the appendix gets blocked. That part of the wall then dies.
A hole or tear develops in the dead wall. The high pressure pushes the bacteria and pus into the abdominal cavity. So, a ruptured appendix usually oozes or leaks into the abdomen, rather than bursting like a balloon.
The patient will often develop the symptoms like abdominal pain mostly around the belly button toward the lower right side that doesn't go away or gets worse, a fever, and nausea or vomiting. But symptoms definitely get worse if the appendix actually bursts.
If appendicitis goes untreated it can rupture. If it happens, bacteria are released into the abdomen and cause a serious infection. This can make the patient very sick and may be hard to treat.
An appendix is a small, thin, wormlike sac located where small and large intestines connect in the lower abdomen on the right side. It is often thought that it doesn’t have any important function and can be removed without causing adverse effects.
Appendicitis can happen at any age, but it occurs most often in children and teenagers between the ages of 10 and 20 years. It’s more common in males.
A study in the Journal of the American College of Surgeons found the risk of rupture was less than 2 percent when appendicitis was treated within 36 hours of the start of symptoms. It increased to 5 percent when it was treated 36 hours or more after the start of symptoms.
What causes a rupture? The exact cause is unknown for sure, but it is thought it’s probably due to an infection that triggers inflammation inside Appendix.
Classical symptoms of appendicitis include:-
-Fever
-Nausea and vomiting
-Abdominal pain that may start in the upper or middle abdomen but usually settles in the lower abdomen on the right side
-Abdominal pain that increases with walking, standing, jumping, coughing, or sneezing
-Decreased appetite
-Constipation or diarrhea
-Inability to pass gas
-Bloated or swollen abdomen
-Abdominal tenderness when you push on it that may worsen when you quickly stop pressing on it.
If appendicitis is not treated, it can rupture. As a result, bacteria are released into the abdomen and cause a serious infection. It can make the patient very sick and be hard to treat.
An appendix is a small, thin, wormlike sac. It’s located where small and large intestines connect in the lower abdomen on the right side. It is generally thought that it doesn’t have any important function so it can be removed without causing harmful effects.
Appendicitis can happen at any age, but it is seen mostly in children and teenagers between the ages of 10 and 20 years. It’s more common in males.
A study in the Journal of the American College of Surgeons found the risk of rupture was less than 2 percent when appendicitis was treated within 36 hours of the start of symptoms. It increased to 5 percent when it was treated 36 hours or more after the start of symptoms.
The exact cause of appendicitis isn’t known for sure, it’s probably due to an infection that triggers inflammation inside the appendix.
When the opening of the appendix gets blocked, bacteria get trapped inside and reproduce quickly, causing an infection. If the infection goes untreated, pressure builds and the appendix swells. Eventually, it swells so much that the blood supply to part of the appendix gets blocked. That part of the wall then dies.
A hole or tear develops in the dead wall. The high pressure pushes the bacteria and pus into the abdominal cavity. So, a ruptured appendix usually oozes or leaks into the abdomen, rather than bursting like a balloon.
The patient will often develop the symptoms like abdominal pain mostly around the belly button toward the lower right side that doesn't go away or gets worse, a fever, and nausea or vomiting. But symptoms definitely get worse if the appendix actually bursts.
If appendicitis goes untreated it can rupture. If it happens, bacteria are released into the abdomen and cause a serious infection. This can make the patient very sick and may be hard to treat.
An appendix is a small, thin, wormlike sac located where small and large intestines connect in the lower abdomen on the right side. It is often thought that it doesn’t have any important function and can be removed without causing adverse effects.
Appendicitis can happen at any age, but it occurs most often in children and teenagers between the ages of 10 and 20 years. It’s more common in males.
A study in the Journal of the American College of Surgeons found the risk of rupture was less than 2 percent when appendicitis was treated within 36 hours of the start of symptoms. It increased to 5 percent when it was treated 36 hours or more after the start of symptoms.
What causes a rupture? The exact cause is unknown for sure, but it is thought it’s probably due to an infection that triggers inflammation inside Appendix.
Classical symptoms of appendicitis include:-
-Fever
-Nausea and vomiting
-Abdominal pain that may start in the upper or middle abdomen but usually settles in the lower abdomen on the right side
-Abdominal pain that increases with walking, standing, jumping, coughing, or sneezing
-Decreased appetite
-Constipation or diarrhea
-Inability to pass gas
-Bloated or swollen abdomen
-Abdominal tenderness when you push on it that may worsen when you quickly stop pressing on it.
Комментарии
 0:02:59
0:02:59
 0:00:20
0:00:20
 0:00:36
0:00:36
 0:05:07
0:05:07
 0:03:40
0:03:40
 0:04:57
0:04:57
 0:04:23
0:04:23
 0:00:05
0:00:05
 0:04:51
0:04:51
 0:04:13
0:04:13
 0:00:23
0:00:23
 0:05:47
0:05:47
 0:04:13
0:04:13
 0:01:04
0:01:04
 0:00:15
0:00:15
 0:04:26
0:04:26
 0:00:29
0:00:29
 0:01:21
0:01:21
 0:04:56
0:04:56
 0:01:50
0:01:50
 0:02:49
0:02:49
 0:04:37
0:04:37
 0:07:31
0:07:31
 0:09:41
0:09:41