filmov
tv
This is how our heart pumps blood 🤯 #cardiology

Показать описание
RELATED VIDEO..
The human heart is a muscular organ roughly the size of a fist, located slightly left of the center of the chest. It functions as a pump to circulate blood throughout the body, delivering oxygen and nutrients to tissues and removing waste products.
Anatomy of the Heart
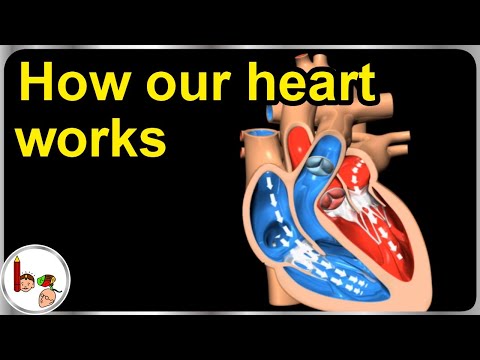
- Chambers: The heart has four chambers: two atria (upper chambers) and two ventricles (lower chambers).
- Valves: Four valves ensure unidirectional blood flow through the heart: the tricuspid, pulmonary, mitral, and aortic valves.
- Septum: A muscular wall called the septum divides the left and right sides of the heart.
Circulation Pathways
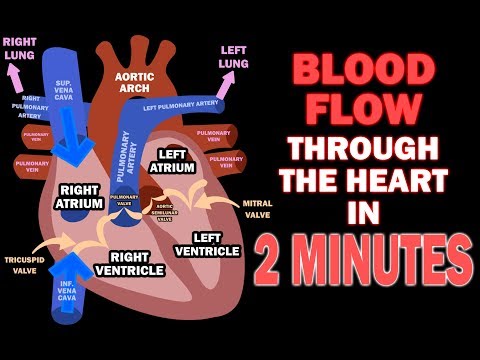
- Pulmonary Circulation: Blood is pumped from the right ventricle to the lungs via the pulmonary arteries to receive oxygen and release carbon dioxide. Oxygenated blood then returns to the left atrium through the pulmonary veins.
- Systemic Circulation: Oxygen-rich blood is pumped from the left ventricle to the rest of the body through the aorta. After delivering oxygen and nutrients, deoxygenated blood returns to the right atrium via the superior and inferior vena cavae.
Electrical System
- The heart's pumping action is regulated by an electrical conduction system, including the sinoatrial (SA) node, atrioventricular (AV) node, and conducting fibers. The SA node initiates each heartbeat, setting the pace for the heart rate.
Function
- The primary function of the heart is to maintain blood flow, which is crucial for sustaining life. The rhythmic contractions of the heart muscle (myocardium) ensure continuous circulation.
Maintaining a healthy heart is vital, and factors like diet, exercise, and avoiding smoking play a significant role in cardiovascular health.
...........
#cardiology #humanheart #heart #3danimation #medical #science #biology #heartanatomy #shorts
The human heart is a muscular organ roughly the size of a fist, located slightly left of the center of the chest. It functions as a pump to circulate blood throughout the body, delivering oxygen and nutrients to tissues and removing waste products.
Anatomy of the Heart
- Chambers: The heart has four chambers: two atria (upper chambers) and two ventricles (lower chambers).
- Valves: Four valves ensure unidirectional blood flow through the heart: the tricuspid, pulmonary, mitral, and aortic valves.
- Septum: A muscular wall called the septum divides the left and right sides of the heart.
Circulation Pathways
- Pulmonary Circulation: Blood is pumped from the right ventricle to the lungs via the pulmonary arteries to receive oxygen and release carbon dioxide. Oxygenated blood then returns to the left atrium through the pulmonary veins.
- Systemic Circulation: Oxygen-rich blood is pumped from the left ventricle to the rest of the body through the aorta. After delivering oxygen and nutrients, deoxygenated blood returns to the right atrium via the superior and inferior vena cavae.
Electrical System
- The heart's pumping action is regulated by an electrical conduction system, including the sinoatrial (SA) node, atrioventricular (AV) node, and conducting fibers. The SA node initiates each heartbeat, setting the pace for the heart rate.
Function
- The primary function of the heart is to maintain blood flow, which is crucial for sustaining life. The rhythmic contractions of the heart muscle (myocardium) ensure continuous circulation.
Maintaining a healthy heart is vital, and factors like diet, exercise, and avoiding smoking play a significant role in cardiovascular health.
...........
#cardiology #humanheart #heart #3danimation #medical #science #biology #heartanatomy #shorts
Комментарии
 0:06:10
0:06:10
 0:05:03
0:05:03
 0:08:14
0:08:14
 0:04:53
0:04:53
 0:04:36
0:04:36
 0:05:04
0:05:04
 0:02:42
0:02:42
 0:00:27
0:00:27
 0:00:58
0:00:58
 0:01:46
0:01:46
 0:10:08
0:10:08
 2:29:54
2:29:54
 0:01:57
0:01:57
 0:00:09
0:00:09
 0:04:26
0:04:26
 0:06:08
0:06:08
 0:02:12
0:02:12
 0:03:35
0:03:35
 0:00:26
0:00:26
 0:21:33
0:21:33
 0:03:50
0:03:50
 0:01:35
0:01:35
 0:02:08
0:02:08
 0:14:26
0:14:26