filmov
tv
Cell wall structure and function | complete concept | Peak Lectures
Показать описание
Cell Wall
(To understand better and easily, I break my topic into 5 headings. These are Discovery, Definition, Composition, Structure, and Function).
√ Discovery of Cell Wall:
The cell wall was first seen by Robert Hook in 1665.
√ Definition of Cell Wall:
The cell wall is the outermost boundary of a cell except for animal cells. Protoplasm secreted the cell wall of the cell.
√ Composition of Cell Wall:
1. Animal cell has no cell wall.
2. The plant cell wall is made up of cellulose (Polysaccharide, water-insoluble and most abundant biological molecule, made up of C, H, and O) .
3. The fungus cell wall is made up of Chitin (Peptidoglycan, the only Polysaccharide having Nitrogen, made up of C, H, O, and N).
4. The bacterium's cell wall is made up of Murein (Peptidoglycan consisting of sugars and amino acids that form a mesh-like layer).
5. The protest cell wall is made up of various groups
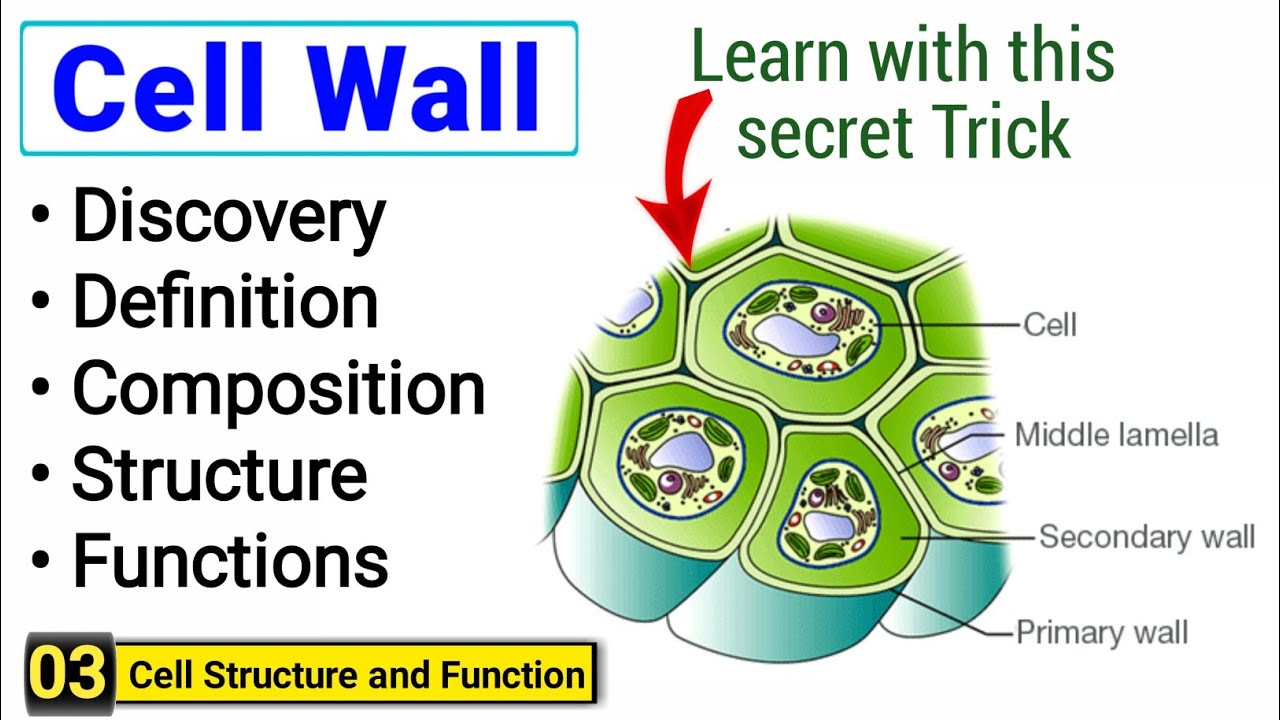
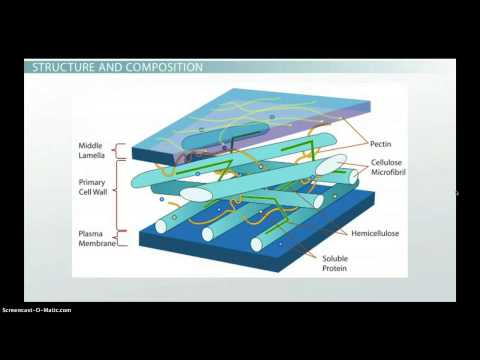
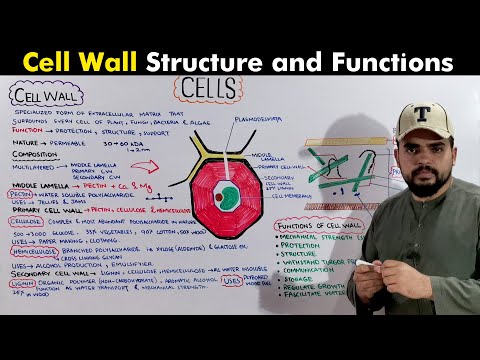
√ Structure/ Layers of Cell Wall
The cell wall has three layers
i) Middle lamella:
It works like cement, so it keeps two cells together and helps in the formation of tissues. Its thickness is about 1mm. Lignin molecules are mainly present in the middle lamella of woody tissue.
ii) Primary Wall:
• The primary wall is the first wall formed during cell development.
• It is outermost.
• The thickness of the primary wall is 1-3um.
• The primary wall is more elastic.
• The primary wall is less optically active.
• Primary wall is composed of cellulose, hemicellulose, and pectic compounds
iii) Secondary wall:
• The second wall follows the order of the primary wall.
• It lies inside the primary wall.
• The thickness of the second wall is 5-10um
• The secondary wall is less elastic.
• The secondary wall is more optically active.
• Secondary wall is composed of cellulose, hemicellulose, lignin, non-cellulosic molecules, and silica.
Functions of Cell Wall
1. Cell walls provide shape for the cell.
2. It also provides strength to the cell.
3. Help with the protection of the cell.
4. Also, avoid overexpansion of cells.
👉 Cell Structure and Function Complete Chapter:
👉 Tricks and Mnemonics:
#cellwall
J Biology - Instructor Jawad Ahmad
(To understand better and easily, I break my topic into 5 headings. These are Discovery, Definition, Composition, Structure, and Function).
√ Discovery of Cell Wall:
The cell wall was first seen by Robert Hook in 1665.
√ Definition of Cell Wall:
The cell wall is the outermost boundary of a cell except for animal cells. Protoplasm secreted the cell wall of the cell.
√ Composition of Cell Wall:
1. Animal cell has no cell wall.
2. The plant cell wall is made up of cellulose (Polysaccharide, water-insoluble and most abundant biological molecule, made up of C, H, and O) .
3. The fungus cell wall is made up of Chitin (Peptidoglycan, the only Polysaccharide having Nitrogen, made up of C, H, O, and N).
4. The bacterium's cell wall is made up of Murein (Peptidoglycan consisting of sugars and amino acids that form a mesh-like layer).
5. The protest cell wall is made up of various groups
√ Structure/ Layers of Cell Wall
The cell wall has three layers
i) Middle lamella:
It works like cement, so it keeps two cells together and helps in the formation of tissues. Its thickness is about 1mm. Lignin molecules are mainly present in the middle lamella of woody tissue.
ii) Primary Wall:
• The primary wall is the first wall formed during cell development.
• It is outermost.
• The thickness of the primary wall is 1-3um.
• The primary wall is more elastic.
• The primary wall is less optically active.
• Primary wall is composed of cellulose, hemicellulose, and pectic compounds
iii) Secondary wall:
• The second wall follows the order of the primary wall.
• It lies inside the primary wall.
• The thickness of the second wall is 5-10um
• The secondary wall is less elastic.
• The secondary wall is more optically active.
• Secondary wall is composed of cellulose, hemicellulose, lignin, non-cellulosic molecules, and silica.
Functions of Cell Wall
1. Cell walls provide shape for the cell.
2. It also provides strength to the cell.
3. Help with the protection of the cell.
4. Also, avoid overexpansion of cells.
👉 Cell Structure and Function Complete Chapter:
👉 Tricks and Mnemonics:
#cellwall
J Biology - Instructor Jawad Ahmad
Комментарии
 0:07:42
0:07:42
 0:10:59
0:10:59
 0:03:04
0:03:04
 0:07:22
0:07:22
 0:03:52
0:03:52
 0:02:36
0:02:36
 0:15:36
0:15:36
 0:05:15
0:05:15
 0:07:13
0:07:13
 0:04:29
0:04:29
 0:05:50
0:05:50
 0:13:08
0:13:08
 0:28:50
0:28:50
 0:08:38
0:08:38
 0:08:32
0:08:32
 0:20:52
0:20:52
 0:02:33
0:02:33
 0:08:15
0:08:15
 0:14:17
0:14:17
 0:39:16
0:39:16
 0:09:09
0:09:09
 0:13:43
0:13:43
 0:11:56
0:11:56
 0:04:16
0:04:16